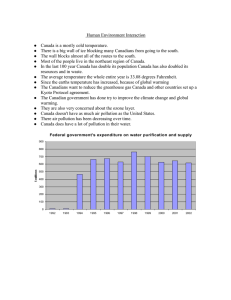
Air pollution effects on global economy Air pollution is composed of chemicals or particles in the air that can harm the health of humans, animals and plants. It also damages the building. Air pollutants come in many forms. They can be gases, solid particles, or droplets. Air pollution puts a strain on the economy in several ways: it sacrifices lives, reduces people's ability to work, affects essential products such as food, and damages cultural and historical monuments. Money, which reduces the ability of ecosystems to carry out social needs, and it costs money during refurbishment or restoration. Pollution reaches the atmosphere through a variety of routes. People are responsible for the majority of air pollution, which comes from factories, cars, planes, and aerosol cans. Smoke from other people's cigarettes is also considered pollution. Anthropogenic sources are pollution sources that are created by humans. Certain types of air pollution, such as smoke and volcanic ash from forest fires, occur naturally. These are called natural resources. Air pollution is most common in large cities where emissions from many different sources are concentrated. Mountains and skyscrapers can prevent the spread of air pollution. This air pollution often manifests itself as clouds that cloud the air. It's called smog. The word "smog" comes from the combination of the words "smoke" and "fog". Large cities in impoverished and developing countries have significantly higher levels of air pollution than cities in industrialized countries. The World Health Organization (WHO) lists Karachi, Pakistan, New Delhi, India, Beijing, China, Lima, Peru, and Cairo, Egypt as some of the world's most polluted cities. However, air pollution is a concern in many developed countries. Smog City is a nickname for Los Angeles, California. Indoor Air Pollution Air pollution is usually thought of as smoke from large factories or exhaust fumes from vehicles. However, there are many types of indoor air pollution. Burning materials such as asquerosen, wood, and coal to warm the house can pollute the air inside the house. Ash and smoke make breathing difficult and can adhere to walls, food and clothing. Naturally occurring radon gas, a carcinogen, can also accumulate in the home. Radon is released from the surface of the earth. Inexpensive systems installed by specialists can reduce radon exposure. Some building materials, including insulation, are harmful to your health. In addition, ventilation and air movements in homes and rooms can lead to the spread of toxic molds. A single colony of mold can be found in a damp, cool place in the house, such as between walls. The mold's spores enter the air and spread throughout the house. People can become sick from breathing in the spores. Effects On Humans When exposed to air pollution, people experience a variety of health effects. Effects can be divided into short-term effects and long-term effects. Temporary short-term effects include illnesses such as pneumonia and bronchitis. This includes symptoms such as inflammation of the nose, throat, eyes and skin. Air pollution can also cause headaches, dizziness and nausea. Bad odors from factories, garbage and sewers are also considered air pollution. These odors are not so serious, but they are still unpleasant. Air pollution's long-term impacts can continue for years or even a lifetime. They have the potential to kill a person. Heart disease, lung cancer, and respiratory disorders like emphysema are all long-term health repercussions of air pollution. Air pollution can harm people's nerves, brains, kidneys, livers, and other organs over time. Some scientists believe that contaminants in the air cause birth abnormalities. Every year, almost 2.5 million people die as a result of the consequences of outdoor or indoor air pollution around the world. Varied types of air pollution have different effects on people. Pollution is frequently more sensitive in young children and older adults, whose immune systems are weaker. Exposure to air pollution can aggravate conditions like asthma, heart disease, and lung illness. The time of exposure, as well as the amount and kind of pollutants, are all important considerations. Effects On The Environment Like humans, animals and plants, the entire ecosystem can suffer from air pollution. Like smog, haze is a visible form of air pollution that obscures shapes and colors. Hazy air pollution can muffle even noise. Air pollutant particles will eventually fall to Earth. Air pollution can directly pollute the surface of water and soil. This can kill crops and reduce yields. It can kill young trees and other plants. Sulfur dioxide and nitric oxide particles in the air can cause acid rain when mixed with atmospheric water and oxygen. These air pollutants are mainly generated from coal-fired power plants and automobiles. When acid rain falls on the earth, it changes the composition of the soil and damages plants. It deteriorates the water quality of rivers, lakes and streams. Harm to crops. It can lead to deterioration of buildings and monuments. Like humans, animals can be affected by air pollution. Birth defects, illnesses, and reduced fertility are all due to air pollution. Global Warming Global warming is an environmental phenomenon caused by natural and anthropogenic air pollution. This refers to rising temperatures and sea temperatures around the world. This temperature rise is, at least in part, caused by an increase in the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat energy in the Earth's atmosphere. (Usually more heat from the earth escapes into space.) Carbon dioxide is one of the greenhouse gases that has had the greatest impact on global warming. Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels (coal, gasoline, natural gas). People rely on fossil fuels to power cars and planes, warm homes, and run factories. It pollutes the air with carbon dioxide. Other greenhouse gases emitted from natural and man-made sources also include methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases. Methane is an important emission from coal-fired power plants and agricultural processes. Nitrous oxide is a common emission from the combustion of fossil fuels in industrial plants, agriculture, and automobiles. Fluorocarbons and other fluorinated gases are emitted by industry. Fluorocarbons are often used instead of gases such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs are banned in many places because they destroy the ozone layer. Many countries around the world are taking steps to reduce or limit greenhouse gas emissions to combat global warming. The Kyoto Protocol, first adopted in Kyoto, Japan in 1997, is an agreement between 183 countries working to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. The United States did not sign this treaty. Regulation In addition to the International Kyoto Protocol, most developed countries have passed legislation to regulate emissions and reduce air pollution. In the United States, a system called cap-and-trade to limit emissions is being discussed. This system limits or limits the amount of pollution a company allows. Companies that exceed the limit will have to pay. Companies with less than the limit of pollution can sell or sell the remaining pollution tolerance to other companies. Cap and trade will essentially pay companies to limit pollution. In 2006, the World Health Organization published new guidelines on air quality. WHO guidelines are stricter than most national guidelines. The WHO guidelines aim to reduce the number of deaths from air pollution by 15 percent annually. Reduction Anyone can take steps to reduce air pollution. Millions of people make simple daily changes to their lives to do so. To reduce air pollution, you can use public transportation instead of a car, or you can ride a bicycle instead of a car that emits carbon dioxide. Other options include avoiding aerosol cans, recycling farm ingredients instead of burning them, and not smoking.