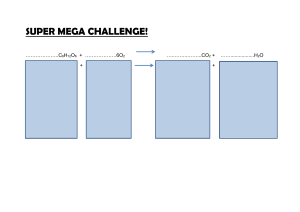
SBI4U Biochemistry- Biochemical Reactions We are learning about: Biochemical Reactions I know I am successful when I can: Identify and describe these biochemical reactions: ___________________, _________________________. Chemical reactions involve ____________ and ____________ of chemical _____________ leading to changes in the composition of _____________. Example: 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 H2O (l) Chemical Equilibrium Some chemical reactions go to completion (all ________________ are converted to _____________) Most reactions are _________________meaning that products of the forward reaction become the ______________ of the reverse reaction Example: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O (respiration) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 (photosynthesis) OR 3H2 + N2 2NH3 Equilibrium is reached when ammonia __________________ as quickly as it is formed Metabolism refers to all the __________________________ that occur within cells to keep cells alive. Reactions are either _______________ or ___________________. SBI4U Catabolism refers to chemical reactions in which complex chemical structures are ________________ into simpler molecules by the process of ___________________. Organic molecules broken down within the cell provide the cell with ____________. Hydrolysis separating a larger molecule into two ones by adding ___________ molecule to a bond the H+ and OH- _________________ the original functional groups e.g. triglycerides –OH in glycerol + -C-OH in fatty acids Anabolism refers to chemical reactions in which simple chemical substances are ______________ to form complex chemical structures by _____________________ or ______________________. Organic molecules are linked up within cells to form large ______________________ essential for life. Condensation the opposite of __________________. Water gets __________________. The joining of _______________between ____________ functional groups e.g. –OH in glycerol + -C-OH in fatty acids triglycerides