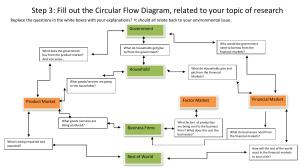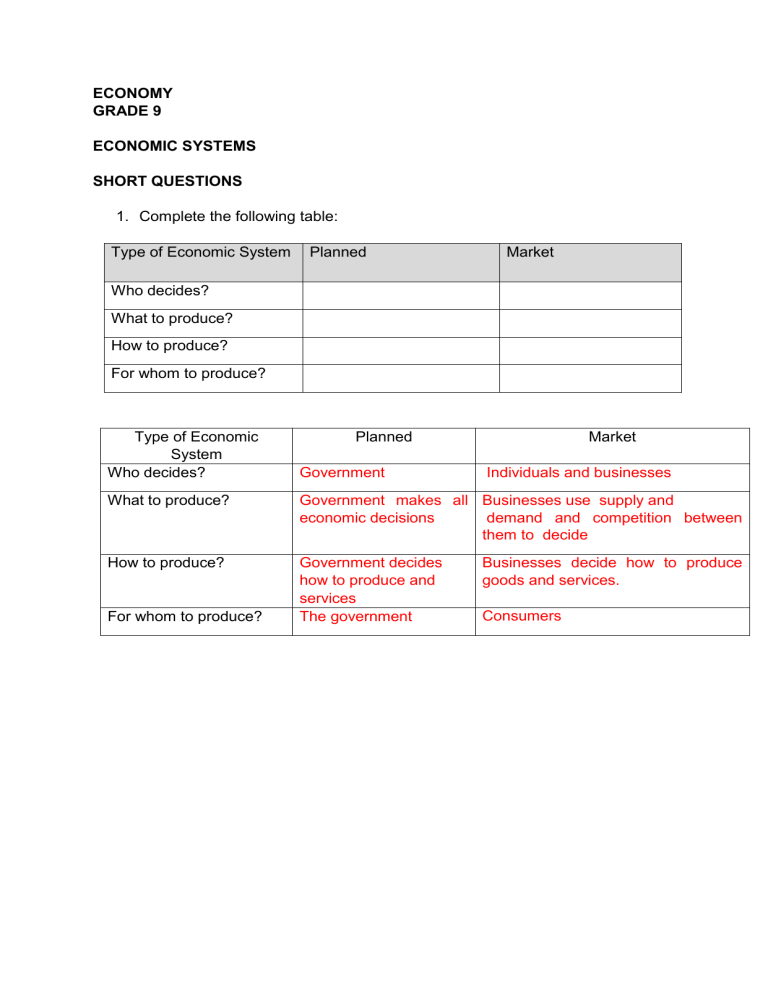
ECONOMY GRADE 9 ECONOMIC SYSTEMS SHORT QUESTIONS 1. Complete the following table: Type of Economic System Planned Market Who decides? What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce? Type of Economic System Who decides? Market Planned Government Individuals and businesses What to produce? Government makes all Businesses use supply and economic decisions demand and competition between them to decide How to produce? Government decides how to produce and services The government For whom to produce? Businesses decide how to produce goods and services. Consumers 2. Complete the following table: Characteristic Government control Profit Motive Ownership of factors of production Choice of occupation Allocation of resource Distribution of output Prices Economic growth Privatization Bureaucracy Interest Decisions Private Enterprise Planned economy Market economy Mixed economy Characteristic Planned economy Central Market economy No control Mixed economy No Yes-the driving force Private Yes – the driving force People are trained and educated according to the needs identified by government Government decides what the production targets are and allocates resources accordingly Government distributes not only capital goods but also consumer goods People can choose their field of study and level of education Consumers determine how resources are allocated People may usually choose their occupation In market place where goods are exchanged for money Fixed – set by government Determined by government Competition checks price Consumer Privatization None Privately owned Bureaucracy Very important because of central planning and centralization Interest Society Not much because government’s officials do not play a fundamental role Personal Market free to operate according to supply and demand. Government has certain license requirements Competition determine prices Consumer and government plays a role Privately and publicly owned. Increases scope of market Very little Decisions Central government Government is responsible for production Government control Profit Motive Ownership of factors of production Choice of occupation Allocation of resource Distribution of output Prices Economic growth Private Enterprise Government Individuals decentralized Can produce, buy and sell as much as they like Semi-control Private Government has key industries for whole economy. Provincial incentive schemes. Personal, society Individual Government Government provided certain services. Others by private individuals GIVE THE TERM FOR THE FOLLOWING: 1. The way in which a country runs its economy. Economic system 2. A system that a country chooses to allocate its resources and distribute its goods and resources. Economic system 3. An economic system in which government make all the decisions about the production and consumption of goods and services. Planned economy 4. An unplanned economy in which land, property and business are owned by private people not the government. Market economy 5. The government as well as people and businesses owns the land and natural resources Mixed economy 6. The increased integration of businesses and governments across the world. Globalisation 7. Highly qualified people in developing economies move to developed countries. Brain drain 8. Dump cheap surplus products in developing countries. Dumping THE CIRCULAR FLOW SHORT QUESTIONS 1. Study the passage and then answer the questions below. Dollf Winters is a tourist from the Netherlands who are on holiday in South Africa for two weeks. Dan Smith and his family sold t-shirts with the South African flag on to Dollf and other tourists along the beach under the name of "Outrages t-shirts". They have a permit obtained from the Cape Aghalhus Municipality. Complete the table below by selecting examples from the passage that represents the participants in the economic cycle. HOUSEHOLDS BUSINESSES GOVERNMENT FOREIGN SECTOR HOUSEHOLDS Dan Smith and his family BUSINESSES Outrages t-shirts GOVERNMENT Cape Aghalhus Municipality FOREIGN SECTOR Dolff Winters / Netherlands 2. Read the following statements carefully. Then identify whether these countries have an open or a closed economy. 2.1 South Africa exports iron-ore to China. Open 2.2 Zimbabwe don’t let foreigners buy shares in his companies. Closed 2.3 Japan does not allow its citizens to work in other countries. Closed 2.4 South Africa lend R200 million to Senegal. Open 2.5 Russia does not allow its citizens to work in other countries. Closed 2.6 England have invested money in oil companies in Nigeria. Open 3. Provide a different name for: 3.1 Households. Consumers 3.2 Businesses. Producers 4. What is the remuneration for the following factors of production? 4.1 Natural Resources. Rent 4.2 Labour. Wages/Salaries 4.3 Capital. Interest 4.4 Entrepreneurship. Profit 5. Study the passage and answer the questions that follow. John's family consists of himself, his father and mother and two younger sisters. His mother is a teacher who works for the WCED and his father works at Checkers. He and his two sisters are both still at school. Their parents' income is spent on food, clothing, rent, transportation and other expenses that arise. John's father also repair electrical appliances in his garage to work for extra income, under the name "Electrocare". 5.1 Identify the following from the passage. A. The household. John's family / John, his father and mother and two younger sisters. B. Businesses. Checkers/ “Electrocare”. C. Government. WCED. 5.2 Why is John's father part of households and businesses? As part of the family (households) and his business "Electrocare" (Businesses). 5.3 Give two examples of goods and services from the text that John and his family need. Food and clothes 5.4 What factor of production is owned by John's mother and father and what do they receive as compensation? Labour - salaries. 5.5 Briefly explain the main function of: A. Households. Provide the factors of production. B. Businesses. Manufacture goods and services. 6. Give two other names for the government. The state / public sector. (Any relevant answer) 7. Identify two companies owned by the state. Eskom / Telkom / SABC. (Any relevant answer) 8. Provide two examples of goods and services provide by the government. Education, Health. (Any relevant answer) 9. Explain two functions of the government. To make laws. Collecting taxes. (Any relevant answer) 10. How do the government finance services it provides? Taxation. 11. What levels of government are represented by the following? 11.1 WCED. Provincial 11.2 Theewaterskloof Municipality. Local 11.3 The Minister of Education. National 12. Explain the role of the government as a producer and consumer in the economic cycle. Producer: Provide goods and services to households and businesses. Consumer: Buying factors of production from households and buying goods and services from businesses. 13. Explain in your own words the concepts “imports” and “exports”. Imports: Goods bought from a foreign country. Exports: Goods sold to another country. 14. Who is South Africa's largest trading partner in terms of imports and exports? China 15. Study the passage and answer the questions that follow. Peter's father works at Pick and Pay. They buy their groceries at Pick and Pay at the end of each month. 15.1 Which roleplayers in the cycle are represented by Peter's father and Pick and Pay? Peter's Father- Households Pick and Pay- Businesses 15.2 Explain the flow of goods and services between the roleplayers mentioned in 15.1. Pick and Pay provides the groceries. Peter and his family receive their groceries from Pick and Pay 15.3 Which market forms part of the flow mentioned in (5.1.2) Market for goods and services 15.4 Which factor of production is mentioned in the passage? Labour 15.5 Explain the flow of the factor of production mentioned in (5.1.3) between the roleplayers in the cycle. Peter's father provide his labour to Pick and Pay 15.6 Which market forms part of the flow in (5.1.5)? Market for factors of production 16. Complete the table. Read the statements below through carefully and then make a cross By the right participant. Flows in the cycle Receive tax. B. Pay company tax. C. Receive wages. D. Receive payments for goods and services E. Pay personal income tax. F. Receive profit from sales of goods and services. G. Pay rent. H. Receive VAT from the sales of goods and services. I. Pay teachers' salaries. J. Rent received on savings. Households Businesses Government Flows in the cycle Households Businesses Government A. Receive tax. X B. Pay company tax. C. Receive wages. X X D. Receive payments for goods and services X E. Pay personal income tax. F. Receive profit from sales of goods and services. X G. Pay rent. H. Receive VAT from the sales of goods and services. X X X I. Pay teachers' salaries. J. Rent received on savings. X X GIVE THE TERM 1. A model that describes the movement of money, goods and services and factors of production in the economy and between participants. Circular flow 2. An economy that don’t interact with other economies or trade with them. Closed economy 3. An economy that interact with other economies or trade with them. Open economy 4. A market is the interaction between a buyer and a seller. Market 5. Market for goods and services. Product market 6. Market for factors of production. Factor market 7. Primary consumer of goods and services. Households 8. Owners of the factors of production. Households 9. Uses the factors of production to produce goods and services to sell on the product market. Businesses 10. Produce goods and services, e.g. education, health and security services. The government 11. Imports from other countries and Exports to other countries. Foreign sector 12. The flow of goods and services and factors of production. Real Flow 13. The flow of money (payments and income). Money Flow ECONOMY GRADE 9 Paragraph type questions (Remember to include “Accept any relevant answer”, where applicable) TOPIC: ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Planned economy Discuss the characteristics of a planned economy. (5x2) (10) Government owns the land, natural resources, factories and the farms People are not allowed to own property Government decides what should be produced and how it should be sold for Workers don’t have a choice about what they want to do Government gives workers everything they need to live, including their food Examples of countries with planned economies are Cuba, Libya, India, China, North Korea, Iran, Saudi Arabia Market economy Discuss the characteristics of a market economy. (5x2) (10) Aim of business is to make a profit Entrepreneurs decide what goods and services to produce Businesses and people borrow money from banks Workers can choose what work to do and who they want to work for Consumers, government and businesses spend money on goods and services Workers and businesses makes money from producing goods and services Government makes money from taxes Mixed economy Discuss the characteristics of a mixed economy. (5x2) (10) Private individuals own and control the factors of production Entrepreneurs decide what to produce Entrepreneurs decide how to produce Individuals decide which goods and services will be used Capital comes from banks, shareholders and the government through spending of taxes Government spends taxes on education, housing and clean water South African economy is a mixed economy TOPIC: CIRCULAR FLOW Briefly discuss the role of the participants in the circular flow. (5x2) (10) Households All people that live together and make economic decisions Primary consumer of goods and services They are the owners of the factors of production and have an influence on what businesses produce They receive an income (rent, salaries, interest and profit) by making the factors of production available to businesses and the government Households pay taxes to the government Businesses Businesses use the factors of production to produce goods and services. They sell the goods and services on the product market. Economically active members of households provide the factors of production Businesses provide and produce usable goods and services for shops, offices, factories and mines Businesses pay taxes to the government The government Levels of government: Central, Provincial and Local government Produce public goods and services, for example education, health and security services Make use of the factors of production The government buy goods and services from businesses, for example, motor vehicles The government provides public goods and services to households and businesses Foreign sector Imports from other countries. Exports to other countries. Make payments for imports (expenditure). Receive money for exports (income). Note to teacher: o The participants can be asked separately, e.g. “Briefly discuss the role of households/businesses/the government/foreign sector in the circular flow.” o Headings = 1 mark each o Examples = 1 mark each ECONOMY: GRADE 9 SECTION A: ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: 1. Education is provided by government and private institutions in a … A B C D 2. South Africa’s economic system is an example of... A B C D 3. Mixed economy. Traditional economy. Planned economy. Market economy. The market economy originates from the theories of … A B C D 5. Globalisation Planned economy Mixed economy Market economy All economic activities are driven by profit motive in … A B C D 4. Mixed economy. Market economy. Planned economy. Traditional economy. Adam Smith. Karl Marx. Friedrich Engels. Fidel Castro. The way in which the economies of most of the countries in the world are interconnected, making the world virtually one big marketplace, is called... A B C D Capitalism Marxism Globalisation Communism 6. The economic system of the USA is an example of a … A mixed economy. B market economy. C planned economy. D globalisation. 7. A planned economy is where… A. economic decisions are made by both the government and private individuals. B. there is no government and no private ownership of resources. C. all economic decisions are made by the government. D private individuals are responsible for making all economic decisions. 8. A market economic system is where… A private individuals are responsible for making all economic decisions. B all economic decisions are made by the government. C the tribe manages the economy according to their needs. D bartering is used by the government to provide for the needs of the population. 9. Which of the following characteristics define a mixed economy? A Government controls the factors of production. B Profit earned is kept by private individals. C Government decide what to produce. D all economic decisions are made by the government 10. Which of the following questions define an economic system? A What,how much, how and for whom are goods being produced? B How much tax will be paid? C What is the price of the products? D How many people live in a country? THE CIRCULAR FLOW: 1. In the economic cycle wages, rent, interest and profit are exchanged for... A B C D 2. investments. money. factors of production. goods and services The three participants in a closed economy are: A B C D government, foreign sector, businesses government, foreign sector, households businesses, households, foreign sector government, businesses, households 3. The factor market determines the price at which the factors of production are sold. These factors are... A land, labour, capital and goods B land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship C rent, wages, salaries and profits D land, rent, natural resources and businesses 4. Circular flow is a simplified model that describes the….. A B. C D inflation rate. interdependence of participants, markets and flows in an economy. income of the state. business cycle of the economy. 5. A country has a closed economy when…. A B C D they buy goods from other countries. they sell goods to other countries. they don’t trade with other countries. there is monetary flow in and out of the country. 6 A country has an open economy when… A B C D they don’t trade with other countries. there is no monetary flow in and out of the country. they don’t buy goods from other countries. they trade with other countries. 7. Who is not a participant in the circular flow? A B C D Households. Businesses. Trade Unions. Government. 8. The real flow is the…… A B C D the flow of payments of goods and services the flow of goods and services and factors of production. the flow of payment of taxes. the flow of payment for factors of production. 9. The money flow is…. A B C D the flow of income and payment. the flow of goods. the flow of factors of production. the flow of services. 10. Activities on the factor market include….. A B C D selling goods and services. selling of factors of production. buying of goods and services. buying of equipment. ECONOMY Grade 9 Matching Economic systems Column A Column B Economic Systems Set rules to determine how the resources will be allocated China A country which have a Centrally planned economic system South Africa A country which follows a Mixed economic system Centrally planned economic system An economic system in which government make all the decisions about the production and consumption of goods and services. Free market economic system An unplanned economy in which land, property and business are owned by private people not the government Globalisation The increased integration of businesses and governments across the world. The Internet is one of the main driving forces behind this phenomenon Globalisation Mixed economic systems Combine government and private business enterprises to ensure economic growth Brain drain Highly qualified people in developing economies move to developed countries Dumping Die verkoop van goedere aan ander lande teen 'n prys laer as die produksiekoste. The circular flow Column A Column B Real flow The movement of goods and services Factor market Labour, entrepreneurship, land and capital are traded in this market Circular flow model Illustrates the flows between participants in the economy Households/Consumers Primary participants and owners of the factors of production Closed economy An economy that does not include the foreign sector Market A place or mechanism through which buyers and sellers meet to do business Business Sector Use factors of production to produce goods and services Open Economy An economy where goods and services are imported and exported. Factors of production Natural resources, Capital and labour Money flow The flow of payments between participants in the economy ECONOMY GRADE 9 ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only the word true or false in the space provided. 1.1.1 STATEMENT ANSWER An economic system is the way in which people decide to organise the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services. True 1.1.2 What, how and for whom to produce are the basic economic questions that every society must answer. True 1.1.3 All societies answer the three basic questions in the same way. False 1.1.4 In a command economy, a central authority makes the decisions regarding what, how and for whom to produce. True 1.1.5 The global economy is characterized by free trade. True 1.1.6 In a market economy, only the government decides what goods and services are produced. False 1.1.7 In a command economy, the aim of businesses is to make a profit. False 1.1.8 In a command economy, the government decides how the goods and services that are produced will be distributed. True 1.1.9 In a market economy, decisions regarding production and consumption result from the interaction of consumers and producers. True 1.1.10 The USA is an example of a command economy. False THE CIRCULAR FLOW Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only the word true or false in the space provided. STATEMENT ANSWER 1.1.1 An economy that interact with other economies or trade with them is a closed economy. False 1.1.2 Technology is a factor of production. False 1.1.3 Interest is the remuneration for Capital. True 1.1.4 A factor market is a market for goods and services. False 1.1.5 Households are the primary consumer of goods and services. True 1.1.6 The government receives VAT from the sale of goods and services. True 1.1.7 The flow of goods and services is a real flow. True 1.1.8 The government is made up of the central and local government. False 1.1.9 Businesses pay taxes to Households. False 1.1.10 The government provides general goods and services to households and businesses. False