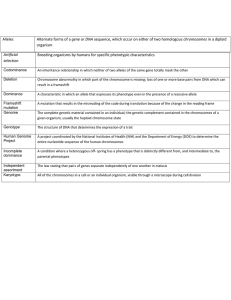
Genetics: - Multiple Choice Questions Answer all questions. Indicate your choice by circling the response you consider to be most correct. 1. The diagram below shows a cell in meiosis. What can be deduced from this diagram? Stage of meiosis shown 2. 3. Haploid number of chromosomes in this cell A. Metaphase I 6 B. Prophase I 3 C. Prophase I 6 D. Metaphase I 3 Which characteristics are used to identify chromosomes when constructing a karyotype? I. The length of the chromosome. II. The position of the centromere on the chromosome. III. The pattern of bands on the chromosome. IV. The position of the chromosome on the spindle. A. I only B. I and II only C. I, II and III only D. I, II, III and IV What is always a difference between the alleles of a gene? A. Their position on the chromosome B. Their amino acid sequence C. The number of codons that each contains D. Their base sequence 1 4. 5. 6. A gene has three alleles. How many different genotypes can be found for this gene? A. 3 B. 6 C. 9 D. 12 Why is amniotic fluid collected during prenatal testing for abnormal chromosomes? A. To obtain uterine cells B. To obtain fetal cells C. To obtain dissolved chemical by-products of fetal development D. To replace it with fluid containing special growth hormones What can be concluded on the basis of the following karyotype? A. Female with a normal set of chromosomes B. Male with Down syndrome C. Female with Down syndrome D. Male with a normal set of chromosomes 2 7. 8. 9. 10. A cell replicates its DNA and then starts to divide by meiosis. What is the expected arrangement of chromosomes if crossing over has taken place between the two genes shown? A. B. C. D. If a person inherited an allele with the same base substitution mutation from both parents, what sequences could be altered from normal in the person’s cells? A. One mRNA base sequence only B. Two mRNA base sequences only C. One mRNA base sequence and one polypeptide amino acid sequence only D. Two mRNA base sequences and two polypeptide amino acid sequences only Which processes result in the greatest amount of genetic variation in a population? A. Natural selection and meiosis B. Meiosis and mutation C. Mutation and mitosis D. Mitosis and natural selection In what way are eukaryotic chromosomes different from prokaryotic chromosomes? Eukaryotic chromosomes Prokaryotic chromosomes A. Protein is present Protein is absent B. DNA is present DNA is absent C. RNA is present RNA is absent D. RNA is absent RNA is present 3 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Which response describes the behaviour of chromosomes in metaphase I and anaphase II of meiosis? Metaphase I Anaphase II A. Chromosomes line up at the equator Separation of homologous chromosomes B. Tetrads (bivalents) line up at the equator Separation of homologous chromosomes C. Chromosomes line up at the equator Separation of sister chromatids D. Tetrads (bivalents) line up at the equator Separation of sister chromatids What is the usual cause of Down’s syndrome? A. 21 pairs of chromosomes B. Trisomy 21 C. Non-disjunction of sex chromosomes D. Fertilization of the egg by two sperm If the haploid number of an organism is 8, how many different varieties of gametes are possible, not considering the effects of crossing over? A. 16 B. 64 C. 128 D. 256 Which event occurs first in meiosis? A. Centromere appearance B. Chiasmata formation C. Crossing over D. Synapsis What are homologous chromosomes? A. Two chromosomes with differing sets of genes, in the same sequence, with the same alleles B. Two chromosomes with the same set of genes, in a different sequence, with the same alleles C. Two chromosomes with a different set of genes, in the same sequence, with different alleles D. Two chromosomes with the same set of genes, in the same sequence, sometimes with different alleles 4 16. 17. What is a sex-linked gene? A. A gene whose locus is on the X chromosome only. B. A gene whose locus is on the X or Y chromosomes. C. A gene whose locus is on the both X and Y chromosomes. D. A gene whose locus is on the Y chromosome only. The pedigree chart below shows the inheritance of a genetic disease in a family. What is the nature of the allele that causes this disease? A. Dominant and sex linked B. Dominant and non-sex linked C. Recessive and sex linked D. Recessive and non-sex linked 5 18. Hypophosphataemia is a disorder involving poor re-absorption of phosphate from glomerular filtrate in humans. It shows a sex-linked dominant pattern of inheritance as illustrated in the following pedigree. Which row in the table correctly identifies the genotypes of individuals 1 and 2? 19. 20. Individual 1 Individual 2 A. XHXh XHY B. Xh Y XHXH C. Xh Y XHXh D. unaffected affected What is the genetic cross called between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual who is homozygous recessive for a particular trait? A. Test-cross B. Hybrid cross C. Dihybrid cross D. F1 cross Which of the following represents a test cross to determine if phenotype T is homozygous or heterozygous? (Note: allele T is dominant to allele t.) A. Phenotype T crossed with another phenotype T B. Phenotype T crossed with a phenotype T which is homozygous C. Phenotype T crossed with a phenotype T which is heterozygous D. Phenotype T crossed with phenotype t 6 21. 22. 23. 24. Which of the following blood group phenotypes always has a homozygous genotype? A. A B. B C. AB D. O What does the genotype XH Xh indicate? A. A co-dominant female B. A heterozygous male C. A heterozygous female D. A co-dominant male If a purple flowered (Pp) and a white flowered pea plant (pp) are crossed, what will the offspring be? A. 1 : 1 ratio of purple and white flowers B. 3 : 1 ratio of purple to white flowers C. 1 : 3 ratio of purple to white flowers D. All purple flowers Hemophilia is sex-linked and is caused by a recessive allele. A woman’s father has hemophilia, but her husband does not. What is the probability of the women and her husband having a child with hemophilia? 25. Probability of a son having hemophilia Probability of a daughter having hemophilia A. 50% 0% B. 0% 0% C. 100% 0% D. 0% 50% A gene in cattle controls whether horns develop or not. When cattle without horns are mated together, none of the offspring ever has horns. A male with horns is mated with females without horns. If half of the offspring have horns and half do not, what is the conclusion? A. The male is homozygous dominant. B. The male is homozygous recessive. C. The male is heterozygous. D. Only males have horns. 7 26. In garden peas, the pairs of alleles coding for seed shape and seed colour are unlinked. The allele for smooth seeds (S) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds (s). The allele for yellow seeds (Y) is dominant over the allele for green seeds (y). If a plant of genotype Ssyy is crossed with a plant of genotype ssYy, which offspring are recombinants? 27. A. SsYy and Ssyy B. SsYy and ssYy C. SsYy and ssyy D. Ssyy and ssYy A cross is performed between two organisms with the genotypes AaBb and aabb. What genotypes in the offspring are the results of recombination? 28. 29. A. Aabb, AaBb B. AaBb, aabb C. aabb, Aabb D. Aabb, aaBb If red (RR) is crossed with white (rr) and produces a pink flower (Rr), and tall (D) is dominant to dwarf (d), what is the phenotypic ratio from a cross of Rr dd and rr Dd? A. 9:3:3:1 B. 50% pink, 50% white and all tall C. 1:1:1:1, in which 50% are tall, 50% dwarf, 50% pink and 50% white D. 3:1 A cross is carried out between two heterozygous individuals (AaBb) where the genes A and B are not linked genes. What would be the proportions of genotypic recombinants amongst the offspring of this cross? A. 0 B. 2 C. 7 D. 100 8 30. 31. In Drosophila the allele for normal wings (W) is dominant over the allele for vestigal wings (w) and the allele for normal body (G) is dominant over the allele for ebony body (g). If two Drosophila with the genotypes Wwgg and wwGg are crossed together, what ratio of phenotypes is expected in the offspring? A. 9 × normal wings, normal body : 3 × normal wings, ebony body : 3 × vestigal wings, normal body : 1 × vestigal wings, ebony body B. 3 × normal wings, normal body : 3 × normal wings, ebony body : 3 × vestigal wings, normal body : 1 × vestigal wings, ebony body C. 3 × normal wings, normal body : 1 × normal wings, ebony body : 3 × vestigal wings, normal body : 1 × vestigal wings, ebony body D. 1 × normal wings, normal body : 1 × normal wings, ebony body : 1 × vestigal wings, normal body : 1 × vestigal wings, ebony body Humans are in blood group M, N or MN. The alleles for blood group M (M) and blood group N (N) are co-dominant. Humans are also in blood group A, B, AB or O. The alleles controlling these blood groups are IA, IB and i. If two parents have the genotypes ii MM and IA i MN what is the ratio of possible phenotypes of their offspring? 32. 33. A. 9 group A, group M 3 group A, group N 3 group O, group M 1 group O, group N B. 9 group O, group M 3 group O, group N 3 group A, group M 1 group A, group N C. 3 group O, group M 3 group O, group MN 1 group A, group M 1 group A, group MN D. 1 group A, group M 1 group A, group MN 1 group O, group M 1 group O, group MN A polygenic character is controlled by two genes each with two alleles. How many different possible genotypes are there for this character? A. 2 B. 4 C. 9 D. 16 Which human trait shows a pattern of polygenic inheritance? A. ABO blood type B. Sickle cell anemia C. Skin colour D. Co-dominant alleles 9 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. Which enzymes are needed to produce recombinant plasmids that are used in gene transfer? A. DNA polymerase and ligase B. DNA polymerase and restriction enzymes C. Restriction enzymes and ligase D. Helicase and restriction enzymes Why is it possible for a gene from one organism to be introduced and function in a different organism? A. All organisms are made of cells. B. All organisms have nuclei. C. The genetic code is universal. D. All organisms have ribosomes. Which enzyme is used to produce complementary DNA (cDNA) from mRNA? A. Restriction endonuclease B. Reverse transcriptase C. DNA ligase D. RNA primase What happens to the unfertilized egg used in the cloning process of a differentiated cell? A. It becomes fertilized. B. Its nucleus is replaced by the nucleus of the differentiated cell. C. Its nucleus is fused with the nucleus of the differentiated cell. D. Its nucleus is exchanged with the nucleus of the sperm. What was the original goal of the Human Genome Project? A. To determine the function of genes B. To determine the nucleotide sequence of all human chromosomes C. To determine how genes control biological processes D. To understand the evolution of species 10 39. 40. Which features of DNA fragments are used to separate them in the process of gel electrophoresis? A. Their charge and their size B. Their charge and base composition C. The sequence of their bases and their charge D. Their base composition and their size There are many different views on the ethics of reproductive cloning in humans. Which is a valid argument against cloning in humans? A. It involves the use of donor sperm which is unethical. B. It happens naturally when identical twins are conceived. C. Only females can be cloned. D. The life expectancy of children produced by cloning might be lower than normal. 11 Genetics (MCQs) Marking Scheme 1. B 21. D 2. C 22. C 3. D 23. A 4. B 24. A 5. B 25. C 6. C 26. C 7. C 27. D 8. C 28. C 9. B 29. C 10. A 30. D 11. C/D 31. D 12. B 32. C 13. D 33. C 14. A/D 34. C 15. D 35. C 16. B 36. B 17. B 37. B 18. C 38. B 19. A 39. A 20. D 40. D 12