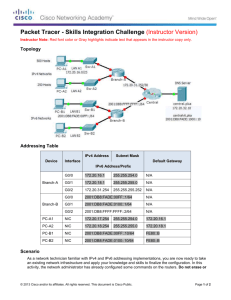
Naveed1414 Subject: internet architecture and protocols Question 1 (A) Determine the Network ID, First Valid Host, Last Valid Host, and Broadcast ID of the following network address/mask pairs? (1) 172.16.10.15/20 Ans: Since the subnet mask of this IP is 255.255.240.0. So, to find out range we subtract 240 from 256 and get 16, which implies that, Network ID = 172.16.10.0/20 First Valid Host = 172.16.10.1/20 Last Valid Host = 172.16.10.14/20 Broadcast ID = 172.16.10.15/20 (2) 192.168.10.15/26 Ans: Since the subnet mask of this IP is 255.255.255.192. So, to find out range we subtract 192 from 256 and get 64, which implies that, Network ID = 192.168.10.0/26 First Valid Host = 192.168.10.1/26 Last Valid Host = 192.168.10.62/26 Broadcast ID = 192.168.10.63/26 (B) An ISP supplies a class B network of 136.210.0.0 to an enterprise that requires ten networks each to support 110 users. What is the network mask that would be configured in each workstation and what would be the NetID, Subnet Number? Ans: To fit in 110 users in a subnet we would take 27, Therefore 27-2 = 128 – 2 = 126 (110 users can fit in) So, we have 7 bits for the hosts which we will subtract from 32 since it is an IPv4 Address to get the bits for network, 32 – 7 = 25 network bits of given Class B address The subnet mask of the given Class B address would then be 255.255.255.128 which will tell us the range for each subnet that we need for the users. Hence, the ten networks for 110 hosts each would be written as, 136.210.0.0 136.210.0.128 136.210.1.0 | | | 136.210.4.128 So, the NetID would be 136.210.0.0 And since this is a Class B address then subnet number would be 16 – 7 = 9 bits. Question 2 (A) An IPv6 packet consists of a base header and a TCP segment. The length of data is 128,000 bytes (jumbo payload). Show the packet and enter a value for each field. Ans: Since the length of payload in IP Datagram can be of maximum 65,535 bytes, but here we need a longer payload of 128,000 bytes for which we can use the jumbo payload option to define its longer length. However, the jumbo payload should also be at a multiple of 4 bytes. So, all of this can be pictured as, Page 1 of 4 Naveed1414 (B) Configure the following network using following addressing table. Write all commands and procedures for assigning the IP address on computer, servers and router. What is link local address in each interface of router? Addressing Table Device Router Sales Billing Accounting Design Engineering CAD Interface G0/0 G0/1 Link-local NIC NIC NIC NIC NIC NIC IPv6 Address/Prefix 2001:DB8:1:1::1/64 2001:DB8:1:2::1/64 FE80::1 2001:DB8:1:1::2/64 2001:DB8:1:1::3/64 2001:DB8:1:1::4/64 2001:DB8:1:2::2/64 2001:DB8:1:2::3/64 2001:DB8:1:2::4/64 Default Gateway N/A N/A N/A FE80::1 FE80::1 FE80::1 FE80::1 FE80::1 FE80::1 Ans: First, we enable unicast-routing on the router so it is enabled to forward IPv6 packets. We will use the following command for it, Router(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing Next, we will configure both the interfaces of the router with the given IPv6 Address and Link-local Address by the following commands, Router(config)#int GigabitEthernet0/0 Router(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1:1::1/64 Page 2 of 4 Naveed1414 Router(config-if)#ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local Router(config-if)#no shut Router(config-if)#exit Router(config)#int GigabitEthernet0/1 Router(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1:2::1/64 Router(config-if)#ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local Router(config-if)#no shut Now we configure the given IP Addresses on each of the nodes by opening the Desktop tab first, then going into IP configuration and set the IPv6 Address and Gateway according to given addressing table. All 6 nodes follow the same procedure. As for what is the link-local address in each of interface of router, it is Fe80::1 as evident by this screencap below, Question 3 [A] Find the interface identifier of the Ethernet physical address of your computer using the format defined for Ethernet addresses. Ans: My Physical Address is C6-46-19-6F-76-71, the interface identifier for this can be found by flipping the seventh bit of the first octet and adding FFFE in the middle and write the result in the colon hex notation at the end. So, for the first step, C6 = 11000110 This will be changed to, C4 = 11000100 Now after adding FFFE in the middle, the interface identifier in colon hex notation is C446:19FF:FE6F:7671 [B] [i] Compare and contrast IP version 4 protocol with IP version 6. IPv4 1. IPv4 has a 32-bit address length 2. Address representation of IPv4 is in decimal 3. In IPv4 checksum field is available 4. IPv4 has a header of 20-60 bytes. IPv6 1. IPv6 has a 128-bit address length 2. Address Representation of IPv6 is in hexadecimal 3. In IPv6 checksum field is not available 4. IPv6 has header of 40 bytes fixed [ii] Compare contrast OSI model with TCP/IP model. OSI 1. OSI is a generic, protocol independent standard, acting as a communication gateway between the network and end user TCP/IP 1. TCP/IP model is based on standard protocols around which the Internet has developed. It is a communication protocol, which allows connection of hosts over a network 2. In OSI model the transport layer guarantees the 2. In TCP/IP model the transport layer does not delivery of packets guarantees delivery of packets. Still the TCP/IP model is more reliable Page 3 of 4 Naveed1414 3. OSI is a reference model around which the networks 3. TCP/IP model is, in a way implementation of the are built. Generally, it is used as a guidance tool OSI model 4. It has 7 layers 4. It has 4 layers Page 4 of 4