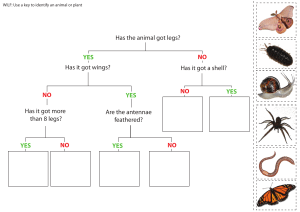
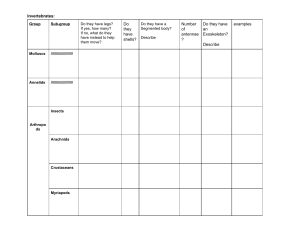
Classification and variation Chapter 7 Biology (1st week) Common features Compare a cow and a dolphin, you might think they do not have many things in common but you will be surprised. How many features common to both cows and dolphins can you think of? Common features What is classification? Cows and dolphins have several features in common. Many other organisms also share common features. Scientists use common features to put organisms into groups. Grouping organisms based on their common features is called classification. The modern classification method consists of 7 levels: Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species • • Which is the biggest group? Which is the smallest group? Helpful way to remember the 7 levels •King Philip Came Over For Green Skittles. •Kids Playing Catch On Freeway Get Squashed. The classification system The classification system begins with very big groups that include a lot of organisms and then moves down to smaller groups made up of fewer organisms. The biggest groups are called the kingdoms. All living things are classified into five different kingdoms. living things plants animals fungi Monera Protoctista Classifying animals How can different types of animals be classified? Animal classification The animal kingdom is divided into two groups: Animals Vertebrates Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone. They have a firm body because of the muscles that connect to their Skeleton (made of bone or cartilage). Invertebrates Invertebrates are animals that do not have a backbone. They have soft inner bodies which are held in shape by a flexible covering of outer cells or by a hard covering called an exoskeleton. Animal kingdom Vertebrates Echinoderms Molluscs Invertebrates Arthropods Nematode worms Annelid worms Flatworms Jellyfish Invertebrates 1) Arthropods Myriapods - Have one pair of antennae. Have long cylindrical or flat bodies. Many legs Ex. Centipedes and millipedes. Crustaceans - Have two pair of antennae. Ex. Lobster and woodlouse Arachnids Insects - - Have one pair of antennae. Have three pairs of legs. They have up to two pair of wings. - - Includes spiders and scorpions, mites and ticks. Do not have antennae or wings. Have four pairs of legs. 2) Annelids - They have long, thin, soft bodies divided into segments or rings. - Example: Earthworms 3) Nematodes - They have thin, cylindrical bodies not divided into segments or rings. 4) Jellyfish 5) Flatworm 6) Echinoderm 7) Molluscs - The group gets the name from the Latin word mollis which means soft. - Most molluscs have a shell to protect their soft bodies. - Examples: Snail, slug and octopus. Animal kingdom Vertebrates Fish Amphibians Reptiles Invertebrates Birds Mammals Vertebrates 1) Mammals - They have hair or fur. They give birth to young. They feed on their mothers’ milk. Lungs to breathe in oxygen. 2) Fish - They have scales. They have fins. Lay eggs in water, some give birth. Have gills. 3) Birds - Feathers Lay eggs Have lungs Two legs Have wings 4) Amphibians - Smooth moist skin. - Lay eggs in water. - Live part of their life in water (young) and part on land (adults). 5) Reptiles - Dry skin. Covered in scales. Lungs Some lay eggs, some give birth.