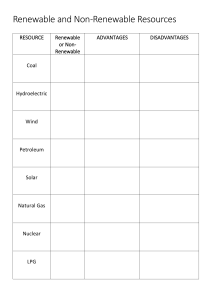
Do Now - Retrieval Instructions: Explain how the images are connected to the ..... Explain in your own words and from your memory. Wednesday, 12 January 2022 Physics Revision To know: To understand & apply: To evaluate: • Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams • Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions • Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Energy Resources The main energy resources available for use on Earth include: • • • • • • • • • Fossil Fuels – Coal, Oil and Gas Nuclear Fuel Biofuel Wind Hydroelectric Geothermal Tides Sun Water waves Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Renewable Energy Resource A renewable resource is one that is being (or can be) replenished as it is used e.g. solar, wind, tidal, wave Non-Renewable Energy Resource A non-renewable resource is one that is will run out because it is a finite resource e.g. coal, oil, gas Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Energy Resource Uses Include • Transport – Petrol, diesel, kerosene • Electricity generation – Fossil fuels, nuclear, solar, wind, • Heating – Gas, electricity Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Energy resource Fossil fuels (oil, coal and natural gases) Energy store Renewable or non-renewable Uses Transport, heating, electricity High generation Chemical Non-renewable Nuclear fuels Nuclear Non-renewable Electricity generation Biofuel Chemical Renewable Transport, heating, electricity Medium generation Wind Kinetic Renewable Electricity generation Power output Very high Very low Hydroelectricity Gravitational potential Renewable Electricity generation Medium Geothermal Internal (thermal) Renewable Electricity generation, heating Medium Tides Kinetic Renewable Sun Nuclear Renewable Water waves Kinetic Renewable Impact on environment Releases CO2 (causes global warming) Radioactive waste (needs to be disposed of safely) 'Carbon neutral' - little or no effect on the environment. Although growing biofuels can take up land that could be used for farming. Takes up large areas that could be used for farming. Windmills change the landscape Local habitats are affected by the large areas that need to be flooded to build dams Very low Tidal barrages can block Potentially very high, but hard sewage which needs to go out Electricity generation to harness to sea. Local habitats also affected Dependent on the weather Electricity generation, heating and only available during Very little daylight Electricity generation Low Very low Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Plugs • Need a live wire (4) (its Potential difference changes every second) • Need a neutral wire (2) (connected to an Earth at the local sub station). • Some items also have an additional Earth (3) (metallic items in particular). • The case is made of an insulator. Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Potential Difference Between the live wire and the Earth is 230V. The neutral wire is at, or close to, 0V. The Earth wire is at 0V. Our bodies are at Earth potential, OV. Touching the live wire produces a large potential difference across out body. This causes current to flow through our body, resulting in an electric shock. Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Direct Current (D.C.) Cells and batteries supply current that always passes in the same direction. Alternating Current (A.C.) Alternating current is one that changes direction. Main electricity in the UK is about 230V and has a frequency of 50Hz – What does that mean? Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Radioactive Atoms Many elements have different isotopes. An isotope is an atom with same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. e.g. Carbon-14 and Carbon-12 Other isotopes tend to be radioactive as their nucleus is unstable, so decays (breaks down) and emits radiation. Carbon-14 is an unstable isotope. Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Radioactive Decay Decay is a random process. You can not say when decay is going to happen. You can not do anything to make decay happen. It is not affected by temperature or chemical bonding. Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave There are three types of radiation (at GCSE): - Alpha - Beta - Gamma Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Alpha What is it? Properties Penetration Effect in Electric Field Ionising Power Beta Gamma Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Ernest Rutherford Alpha – stopped by paper. Beta – not stopped by paper, stopped by aluminium foil Later, gamma was discovered even more penetrating than beta radiation. Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Penetration Power - Alpha – Weak (stopped by paper) - Beta – Moderate (stopped by Aluminium) - Gamma – Highly (stopped by thick block of lead) Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Alpha Beta Gamma Helium Nuclei Electron E/M Wave Properties Heavy Formed when a neutron converts to a proton and electron. No mass Penetration Weak – stopped by paper. Range in air is just a few cm. Moderate – stopped by metal (5mm Al) or a few metres of air. Strong – stopped by lead. Can travel log distances in air. Effect in Electric Field Positive – so affected by electric field Negative – so affected by electric field No charge Ionising Power Strongly Ionising Moderate Weakly Ionising What is it? Review and retrieve knowledge needed for your Physics mock exams Apply key knowledge to level 2 exam questions Evaluate your current knowledge and adjust your revision accordingly Keywords: Renewable, non-renewable, energy, energy resource, fossil fuel, DC, AC, mains electricity, frequency, voltage, live, neutral, earth, three-core cable, alpha, beta, gamma, neutron, proton, electromagnetic wave Radio Wave Radio was invented before the microwave Micro Wave Infra Red Next to Red Visible Light Ultra Violet ROYGBI V Next to Violet Look for the patterns and characteristics! X-Rays Gamma Rays Short wavelength – short names Radio Waves Features: • Wavelengths longer than 1m. • Can be diffracted. • Produced by oscillations in electrical circuits. • Can be reflected off of the Earth’s ionosphere. • When absorbed they may create alternating current with the same frequency as the radio wave itself. Uses: • Communication • Broadcasting • MRI – Magnetic resonance imaging Microwaves Features: • Wavelengths of around 1mm to 1m. Uses: • Heating food • Mobile phones • Satellite communication • Wifi Infra-Red Waves Features: • Cause a temperature rise • Emitted by hot objects Uses: • Infra-red cameras • Cooking food – grills • Remote controls • Optical fibres • Military radios • Heaters Visible Waves Features: • White light is made up of seven colours. • Detected by the human eye. • Can be reflected. • Can be refracted. Uses: • Photography • Illumination • CDs • DVDs • Blu-Ray • Surveying Ultra-Violet Waves Features: • Higher frequency than violet light. • UV sensitive materials absorb UV and re-emit it as visible light. • Can have hazardous effects on human body tissue – cause skin to age prematurely, increase risk of skin cancer. Uses: • Fluorescent lightbulbs • Suntan • Banknotes • Kill germs in dirty water • Energy efficient lamps X-Rays Features: • High energy • Short wavelength • Pass through soft tissue • Absorbed by bones and teeth • Can have hazardous effects on human body tissue. • Ionising radiation that can cause mutations of genes and cancer. Uses: • Medical imaging in hospitals. • Airport security scanners • Archaeology Gamma Waves Features: • Short wavelength • Very high frequency • Can be produced by cosmic events • Highest energy waves • Ionising radiation that can cause mutations of genes and cancer. • Originate from changes in the nucleus of the atom. • Can have hazardous effects on human body tissue. Uses: • Radiotherapy - Kill cancer cells • Sterilise medical equipment • Detect leaks in pipes • Medical tracers