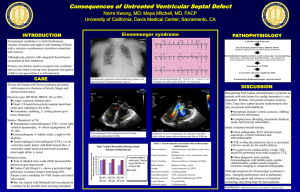
Tetralogy of Fallot By: Nence Lieu Kerron Mc Sween - Burke Abe Clements Myo Oo Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) Defect With Decreased Pulmonary Blood flow 1) Large ventricular septal defect (VSD), which is a hole between the two ventricles or pumping chambers in the heart 2) Pulmonary stenosis, which is narrowing beneath or in the blood vessel leading to the lungs 3) Overriding of the aorta, in which the aorta lies directly above the ventricular septal defect; and 4) As a result of these events, the right ventricle becomes thickened or hypertrophied. Clinical Manifestation Cyanosis (turning blue) Oxygen will not help! Clubbing of the flingers (late stage) Hypoxia (lack of oxygen) Heart Murmur (during auscultation) Tet Spells - acute extreme cyanotic event Lack of growth Inability to gain weight Visibility during an echo SOB Syncope Possible altered LOC And irritability! Nursing Interventions Calm the child (avoid any excessive activity) Family teachings - procedure to patch the hole Corrective surgery usually happens in the first year of life High caloric density foods (given via feeding tube) Clustering care Knee chest positioning Possible sedation Medications Prostaglandins (to keep the PDA open)