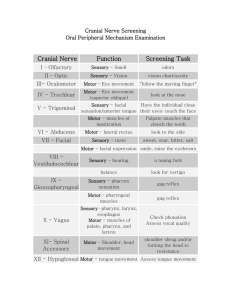
Cranial Nerve Assessment Form Function General inspection Muscle wasting Facial symmetry Loss of expression Comfort/pain CN I – Olfactory Nerve CN II – Optic Nerve CN III – Oculomotor Nerve Assessment Inspection Sensory: smell Ensure patency of each nares Use known scents to check each nostril Test one nares at a time with eyes closed Detect odor when present at 10 cm Sensory: vision Distance visual acuity: Snellen chart Near vision acuity: Jaeger, Rosenbaum hand held chart Color vision: Ishihara color plates Afferent impulse from eye to brain + CN III efferent impulse from eye to brain papillary response to light Peripheral visual fields: Confrontation test View red reflex: fundoscopy Motor: EOM Remaining eye movements: 6 cardinal fields of gaze Raises eyelid: look for ptosis (eyelid droop) Pupillary response (reflexes) to light: CN IV – Trochlear Nerve Motor: EOM CN VI – Abducens Nerve Motor: EOM Direct Consensual Pupillary response: accommodation Superior oblique muscle: moves eye down when looking towards the nose rotates eye internally Lateral rectus muscle: Comments CN V – Trigeminal Nerve Ophthalmic branch Maxillary branch Mandibular branch Sensory, Motor Sensory: forehead, nose, nasal cavity Sensory: lower eyelid, upper teeth/lip, cheek, nose Sensory: tongue, lower teeth/lip, chin, mastication muscles Motor: Muscle supply to muscles of mastication, chewing Wipe cotton ball lightly over scalp, forehead Wipe cotton ball lightly over paranasal sinuses Wipe cotton ball lightly over jaw Inspect face for muscle atrophy and tremors Have patient clench teeth and then palate the temporalis muscle and masseter muscle for muscle strength Move jaw from side to side CN VII – Facial Nerve (5 branches) Ophthalmic branch (sensory) of CN V and motor function of CN VII Sensory, Motor Sensory: Anterior 2/3 of tongue Motor: Facial muscles of scalp, ear moves eye laterally: look for nystagamus Corneal reflex X Identify sweet, salty tastes on anterior 2/3 tongue Inspect face at rest and during conversation Raise eyebrow Wrinkle forehead Squeeze eyes shut while you try to open them Smile Puff out cheeks Purse lips and blow out (whistle) Show teeth CN VIII – Acoustic (Vestibulocochlear) Nerve Vestibular division Sensory Sensory: equilibrium, balance Cochlear division CN IX Glossopharyngeal Nerve CN X Vagus Nerve CN IX and CN X are tested together Sensory Test patients who present with new onset “dizziness” Indirectly test by assessing gait and balance and looking for nystagmus Dix-Hallpike maneuver Simple test of hearing (whisper test) Rinne’s test X Weber’s test X Sensory, Motor Sensory Taste ability to identify sour and bitter tastes over posterior 1/3 of tongue Motor Test gag reflex Have patient swallow CN IX is simultaneously tested during evaluation of the vagus (CN X) for nasopharyngeal sensation (gag reflex) and motor function of swallowing Sensory, Motor, Parasympathetic Sensory Sensation behind ear and part of external ear canal Motor Vocal cords: voice quality Swallowing ability Parasympathetic Secretion of digestive enzymes; peristalsis; carotid reflex; involuntary action of heart, lungs, and digestive tract Have patient open mouth, stick out tongue, and say “Ahh” Uvula should be midline Uvula and Soft palate should rise Provoke Gag Reflex X CN XI Spinal Accessory Nerve Motor Sternocleidomastoid: ask patient to turn head against resistance applied to the side of the face Trapezius: ask patient to shrug shoulders while applying downward CN XII Hypoglossal Nerve Motor Stick out tongue: tongue should be midline Check symmetry Check atrophy Any fasiculations (tremors) Check tongue strength: push tip of tongue into inside of either cheek while you push from outside Inspect tongue movement toward nose and chin Tongue movement for lingual speech sound articulation (l, t, d, n) Notes