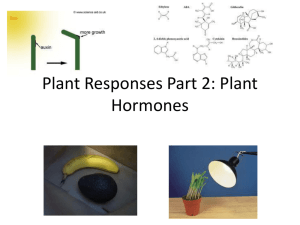
14.5 Tropic responses Core • • Define gravitropism as a response in which parts of a plant grow towards or away from gravity Define phototropism as a response in which parts of a plant grow towards or away from the direction from which light is coming • Investigate gravitropism and phototropism in shoots and roots Supplement • Explain phototropism and gravitropism of a shoot as examples of the chemical control of plant growth • Explain the role of auxin in controlling shoot growth, limited to: o auxin made in shoot tip (only) o auxin spreads through the plant from the shoot tip o auxin is unequally distributed in response to light and gravity o auxin stimulates cell elongation • Describe the use in weedkillers of the synthetic plant hormone 2,4-D Gravitropism = response in which parts of a plant grow towards or away from gravity Phototropism = response in which parts of a plant grow towards or away from the direction from which light is coming Positive tropism = towards stimulus Negative tropisms = away from stimulus The growth of plants in shoots and in roots are controlled by the plant hormone called auxin. So plant growth is controlled by chemical substances, in this case hormones. They control the response towards light and gravity In the shoot = auxin make cells elongate in response to LIGHT = POSITIVE PHOTOTROPISM 1. auxin is made in the shoot tip only (the very top layer). 2. spread downwards. 3. move to the side where it is shaded. 4. And cause cell elongation (absorb more water) 5. When one side grow longer than the other, cause shoot to bend towards light. In the roots = auxin make stops cell elongation in response to LIGHT = NEGATIVE PHOTOTROPISM 1. Auxin is made in the root tip. 2. Auxin will again gather at the shaded side. 3. However, in the root, auxin make roots cells absorb less water 4. And inhibits cell elongation 5. Causing root to bend away from light To test for auxin response to gravity, plants are placed horizontally in the absence of light In the shoot = auxin make cells grow more quickly in response to GRAVITY = NEGATIVE GEOTROPISM Auxin gathers at the bottom due to gravity, cause shoot to bend upwards In the roots = auxin make cells grow more slowly in response to GRAVITY = POSITIVE GEOTROPISM Auxin gathers at the bottom due to gravity, cause roots to bend downwards Experiment Shoots that have their tip cut off, cannot respond to light = proving that chemicals produced at the tip controls phototropism in the shoot. Shoots covered with opaque cap will grow upwards, as they are covered = showing that light influence the distribution of auxin in the tip Selective Weedkillers (herbicide) = synthetic plant hormone 2,4-D Synthetic plant hormone 2,4-D acts like an auxin plant hormone It is used to spray on weeds And cause rapid, uncontrolled cell growth, elongation and cell respiration Resulting in the death of the weeds However, different plant species have different sensitivity to auxins, so synthetic plant hormone 2,4-D are only able to kill dicot weeds with broad leaves, such as dandelions and not monocots (narrow leaves weeds such as grasses and cereal crops), making them useful in such cases. Other synthetic plant hormones use: Rooting powder Rooting powder makes stem cuttings quickly develop roots. Rooting powder contains growth hormones that causes stem cuttings to grow roots so that valuable plants can be cloned. Controlling fruit ripening Some hormones slow the ripening of fruits and others speed it up. These hormones and their inhibitors are useful for delaying ripening during transport or when fruit is displayed in shops. It is also useful to allow fruit development at the same time for efficient picking. Dormancy Dormancy stops seeds germinating until conditions are ideal for growth. Hormones can be used to remove the dormancy of a seed so it can germinate at all times of year. Buds and flowers can also be naturally dormant. Hormones can also be used to make plants grow bushier, make them flower or control the growth of hedge plants. Seedless fruits A hormone spray can make fruits such as apples and grapes develop without fertilisation. Since no fertilisation has taken place, no seeds are formed. This also reduces the grower’s dependence on pollinating insects.