en-15376-european-fuel-alcohol-specifications-itec compress
advertisement
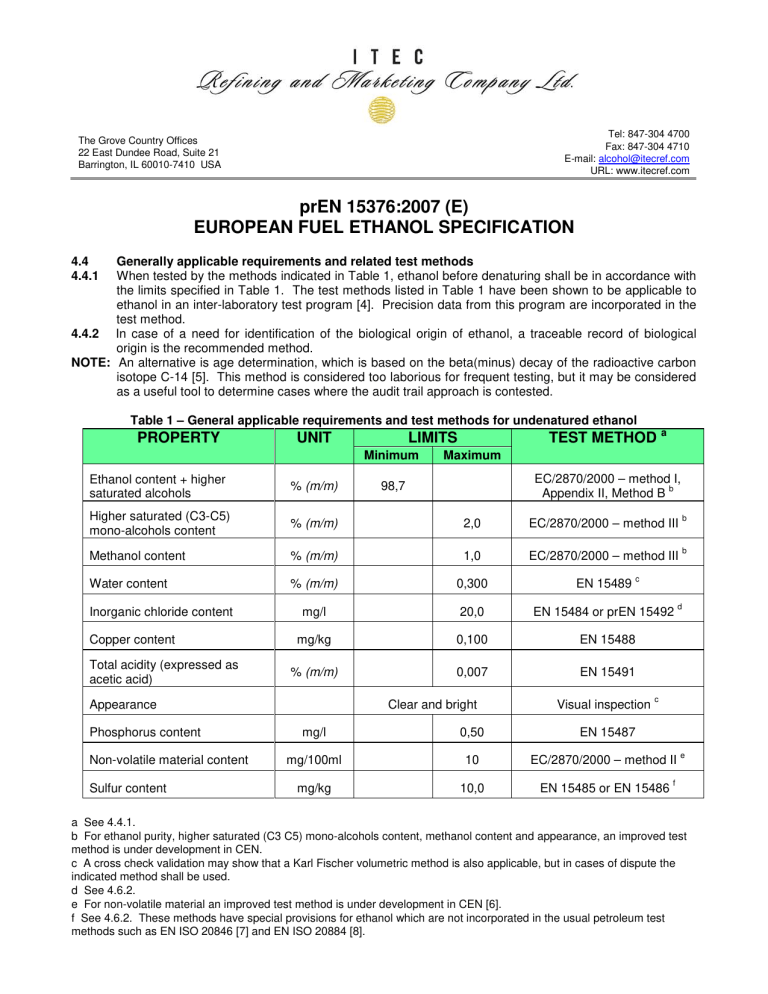
Tel: 847-304 4700 Fax: 847-304 4710 E-mail: alcohol@itecref.com URL: www.itecref.com The Grove Country Offices 22 East Dundee Road, Suite 21 Barrington, IL 60010-7410 USA prEN 15376:2007 (E) EUROPEAN FUEL ETHANOL SPECIFICATION 4.4 4.4.1 Generally applicable requirements and related test methods When tested by the methods indicated in Table 1, ethanol before denaturing shall be in accordance with the limits specified in Table 1. The test methods listed in Table 1 have been shown to be applicable to ethanol in an inter-laboratory test program [4]. Precision data from this program are incorporated in the test method. 4.4.2 In case of a need for identification of the biological origin of ethanol, a traceable record of biological origin is the recommended method. NOTE: An alternative is age determination, which is based on the beta(minus) decay of the radioactive carbon isotope C-14 [5]. This method is considered too laborious for frequent testing, but it may be considered as a useful tool to determine cases where the audit trail approach is contested. Table 1 – General applicable requirements and test methods for undenatured ethanol PROPERTY UNIT TEST METHOD a LIMITS Minimum Maximum EC/2870/2000 – method I, b Appendix II, Method B Ethanol content + higher saturated alcohols % (m/m) Higher saturated (C3-C5) mono-alcohols content % (m/m) 2,0 EC/2870/2000 – method III b Methanol content % (m/m) 1,0 EC/2870/2000 – method III b Water content % (m/m) 0,300 EN 15489 mg/l 20,0 EN 15484 or prEN 15492 mg/kg 0,100 EN 15488 % (m/m) 0,007 EN 15491 Inorganic chloride content Copper content Total acidity (expressed as acetic acid) Appearance Phosphorus content Non-volatile material content Sulfur content 98,7 Clear and bright c Visual inspection d c mg/l 0,50 EN 15487 mg/100ml 10 EC/2870/2000 – method II mg/kg 10,0 EN 15485 or EN 15486 e f a See 4.4.1. b For ethanol purity, higher saturated (C3 C5) mono-alcohols content, methanol content and appearance, an improved test method is under development in CEN. c A cross check validation may show that a Karl Fischer volumetric method is also applicable, but in cases of dispute the indicated method shall be used. d See 4.6.2. e For non-volatile material an improved test method is under development in CEN [6]. f See 4.6.2. These methods have special provisions for ethanol which are not incorporated in the usual petroleum test methods such as EN ISO 20846 [7] and EN ISO 20884 [8].