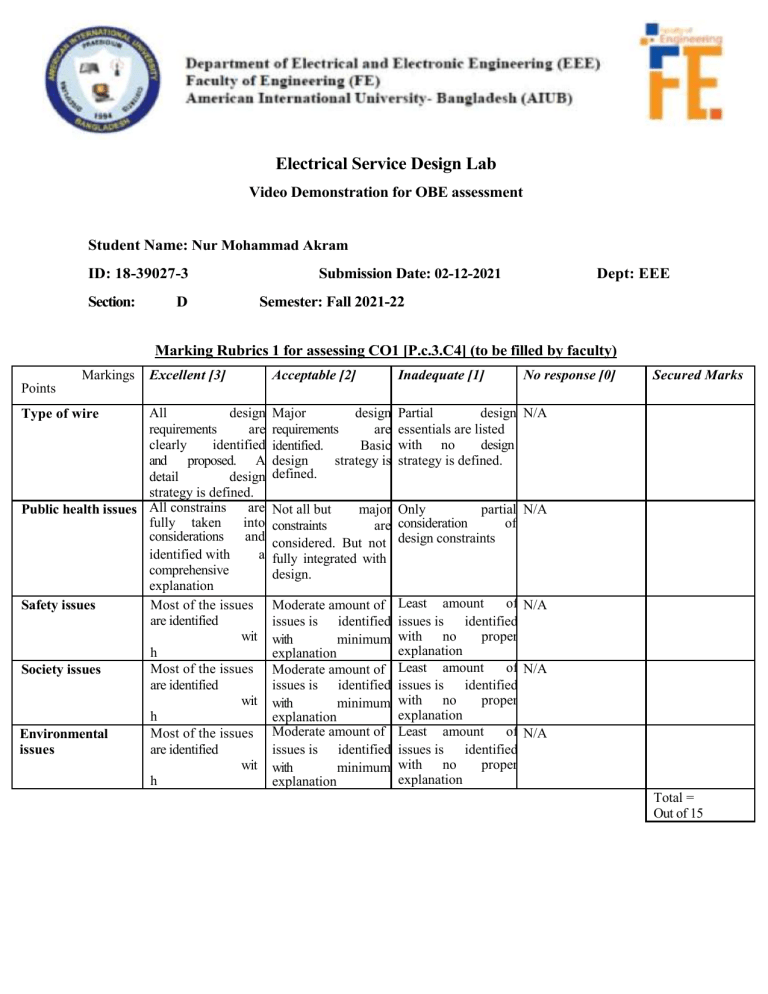
Electrical Service Design Lab Video Demonstration for OBE assessment Student Name: Nur Mohammad Akram ID: 18-39027-3 Section: D Submission Date: 02-12-2021 Dept: EEE Semester: Fall 2021-22 Marking Rubrics 1 for assessing CO1 [P.c.3.C4] (to be filled by faculty) Markings Excellent [3] Acceptable [2] Inadequate [1] No response [0] Major design requirements are identified. Basic design strategy is defined. Partial design N/A essentials are listed with no design strategy is defined. Secured Marks Points All design requirements are clearly identified and proposed. A detail design strategy is defined. are Public health issues All constrains fully taken into considerations and identified with a comprehensive explanation Most of the issues Safety issues are identified wit h properofexplanation Most the issues Society issues are identified wit h proper Most ofexplanation the issues Environmental are identified issues wit h proper explanation Type of wire Not all but major Only partial N/A of constraints are consideration design constraints considered. But not fully integrated with design. Moderate amount of issues is identified with minimum explanation Moderate amount of issues is identified with minimum explanation Moderate amount of issues is identified with minimum explanation Least amount of N/A issues is identified with no proper explanation Least amount of N/A issues is identified with no proper explanation Least amount of N/A issues is identified with no proper explanation Total = Out of 15 Marking Rubrics 2 for assessing CO2 [P.f.1.A3] (to be filled by faculty) Markings Excellent [3] Acceptable [2] Inadequate [1] No response [0] Exact calculation of current has done before selecting wire AWG. Proper method of calculation is followed Nearly correct calculation is used to identify the wire AWG Wrong calculation with incorrect method is used to identify wire AWG N/A Wire classification Different type of wire classification is shown. Clear explanation is used to identify wires for branch circuit Several type of wire classifications points out but explanation is not proper during selection Least amount of wire classification with no explanation N/A Average Market research Market research does not reflect anything meaningful N/A Safety percussions Most of the issues are identified with proper explanation Moderate amount of issues is identified with minimum explanation Least amount of issues is identified with no proper explanation N/A Most of the issues are identified with proper explanation Moderate amount of issues is identified with minimum explanation Least amount of issues is identified with no proper explanation N/A Points Wire selection Market research Health issues during setup Immense market research has been done for wires availability Secured Marks Total = Out of 15 Question: Analyze a plan for feeder and branch circuit wiring incase of AIUB. For feeder circuit wiring please address these issues like type of wire, public health issues, safety issues, societal and environmental issues as well. For branch circuit wiring, selection procedure is little bit different than the feeder circuit. You need to focus in these topics like wire selection, classification, market research, safety percussion and health issue as well. Please make a power point presentation along with a clear video demonstration and send the link of your demonstration in my mail. Single line diagram for 400v AC power Distribution General Notes: ➢ The conductor system by means of which electric power is conveyed from a generating station to the consumer’s premises may, in general, be divided into two distinct parts i.e. transmission system and distribution system. ➢ Each part can again be sub-divided into two: primary transmission and secondary transmission and similarly, primary distribution and secondary distribution and then finally the system of supply to individual consumers. A typical layout of a generating, transmission and distribution network of a large system would be made up of elements as shown by a single-line although it has to be realized that one or more of these elements may be missing in any particular system. ➢ For example, in a certain system, there may be no secondary transmission and in another case, when the generating station is nearby, there may be no transmission and the distribution system proper may begin at the generator bus-bars. ➢ Now-a-days, generation and transmission is almost exclusively three-phase. The secondary transmission is also 3-phase whereas the distribution to the ultimate customer may be 3-phase or single- phase depending upon the requirements of the customers. ➢ Taking the generated voltage as 11 kV, the 3-phase transformers step it up to 132 kV as shown. Primary or high-voltage transmission is carried out at 132 kV*. ➢ The transmission voltage is, to a very large extent, determined by economic considerations. High voltage transmission requires conductors of smaller cross-section which results in economy of copper or aluminium. But at the same time cost of insulating the line and other expenses are increased. ➢ The secondary distribution is done at 400/230 V for which purpose voltage is reduced from 3.3 kV to 400 V at the distribution substations. Feeders radiating from distribution substation supply power to distribution networks in their respective areas. ➢ If the distribution network happens to be at a great distance from substation, then they are supplied from the secondaries of distribution transformers which are either pole-mounted or else housed in kiosks at suitable points of the distribution networks. ➢ The most common system for secondary distribution is 400/230-V, 3-phase 4-wire system. The single-phase residential lighting load is connected between any one line and the neutral whereas 3-phase, 400-V motor load is connected across 3-phase lines directly. It should be noted that low-voltage distribution system is sub-divided into feeders, distributors and service mains. ➢ ➢ No consumer is given direct connection from the feeders, instead consumers are connected to distribution network through their service mains. The A.C. distributors are, in many ways, similar to the D.C. distributors as regards their constructional details and restrictions on drops in voltage. Public health issues: The first step toward protecting yourself is recognizing the many hazards you face on the job. To do this, we must know which situations can place you in danger. Knowing where to look helps you to recognize hazards. + Inadequate wiring is dangerous. + Exposed electrical parts are dangerous. + Overhead powerlines are dangerous. + Wires with bad insulation can give you a shock. + Electrical systems and tools that are not grounded or double-insulated are dangerous. + Overloaded circuits are dangerous. + Damaged power tools and equipment are electrical hazards. + Using the wrong PPE is dangerous. + Using the wrong tool is dangerous. + Some on-site chemicals are harmful. + Defective ladders and scaffolding are dangerous. + Ladders that conduct electricity are dangerous. + Electrical hazards can be made worse if the worker, location, or equipment is wet. Safety issues : A safe work environment is not enough to control all electrical hazards. You must also work safely. Safe work practices help you control your risk of injury or death from workplace hazards. If you are working on electrical circuits or with electrical tools and equipment, you need to use safe work practices. Circuit Diagram: Symbol Blocks: Schematic Library Symbols Below is an illustrated listing of the schematic symbols (along with the appropriate block name) supplied with AutoCAD Electrical. The schematic symbols are illustrated here along with the appropriate block name. Push Buttons Illuminated Push Buttons Selector Switches Selector Switches (continued) Illuminated Selector Switches Limit Switches Pressure Switches Temperature Switches Flow Switches Level Switches Proximity Switches Photo Eyes Power Distribution Blocks Timers Relays