Urinary Catheterization: Types, Procedures, and Considerations
advertisement

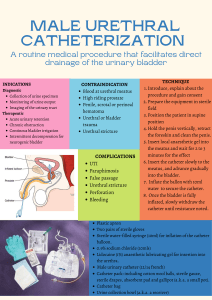
Urinary Catheterization Urinary Catheterization • Is the insertion of urethral catheter into the urinary bladder to drain urine or instill solution. Types of Catheter 1 3 •Intermittent •Indwelling Catheter 2 •Suprapubic Catheter 4 LOGO Straight Catheter Also called a red-rubber catheter or straight catheter. It is a single lumen and do not have a balloon near the tip. Straight catheter is inserted only for as much time as it takes to drain the bladder or obtain urine specimen. Indwelling Catheter • Also called foley or retention catheter. • It has 2 lumen, one for the urine drainage and the other for inflation of the balloon near the tip. There are three-way foley catheters with a third lumen for irrigation. Intermittent • The catheter is inserted and removed immediately after emptying the bladder. • To relieve acute urinary retention or when medically indicated to obtain a urine specimen, or to check post void residual bladder volume Straight Catheter Coude Catheter 2 Way Foley Catheter 3 Way Foley Catheter Condom Catheter Catheter length • Catheters are available in 3 lengths: Pediatric, Regular length and Female length. • Female length is a shorter length catheter (20-25cm). A shorter length catheter may be more convenient for ambulant women with a long term catheter. • A shorter length catheter is not appropriate for all women particularly those who are bedridden or obese. • In obese women, the inflation valve of the shorter catheter may cause soreness by rubbing against the inside of the thighs, and the catheter is more likely to pull on the bladder neck BALLOON SIZE • Balloon sizes: 5 – 30 mls. The most commonly indicated balloon size is 10ml. • Always inflate the balloon to the manufacturers recommended volume indicated on the inflation valve of the catheter as well as written on the packaging. The balloon should be fully inflated to the recommended size. • Under-inflated balloons may occlude the drainage holes of the catheter, or cause distortion of the catheter tip, leading to irritation and trauma to the bladder wall Purposes To relieve acute or chronic urinary retention / bladder distention. To promote urinary drainage prior to diagnostic procedure or surgery. To empty the urine from the bladder, prostate or vaginal surgery. To determine amount of residual urine output in critically ill patient. To collect urine specimen from a client with bladder incontinence or from a female with menstruation. To instill a medications into the bladder. To keep perineal area dry to assist healing Determine accurate fluid balance To collect a sterile specimen of urine. Special Considerations Check the doctor’s order. Provide privacy. Invasive procedure elicit anxiety and feeling of embarrassment. Use a calm, straight forward, professional manner to relieve the patient’s anxiety. Practice aseptic technique. Urinary bladder is a sterile cavity. Provide perineal care before catheterization. Facilitate insertion of the catheter, prevent pain Equipment Tray with towel lining containing the following: Catheterization Set: Sterile drape or towel Sterile kidney basin Sterile medicine glass Sterile specimen bottle Urinary catheter: Single lumen straight catheter Double lumen indwelling catheter Triple lumen indwelling catheter Sizes • Fr. 8 - infants and children • Fr. 14 – 16 - females • Fr. 16 – 20 - males Urinary Catheterization Sterile gloves Droplight Sterile cotton swabs Povidone iodine solution Sterile pick-up forceps Water soluble lubricant Sterile 4x4 gauze Clean emesis basin • Additional equipment for indwelling catheters • Drainage tubing and collecting bag • Sterile syringe and needle with 5 ml or 30 ml • Adhesive tape • Bed pan Urinary Drainage Bag CATHETER DRAINAGE BAG SELECTION 1. Disposable 2 litre plastic bags (night bag) • For general use. • Catheter bags should have 120cm length tubing with an outlet port to allow emptying. • It is recommended that catheter bags also have one-way valves to prevent urine backflow, and an access port for the collection of urine specimens. • Bags should be changed when they become damaged, contaminated, malodorous and at catheter changes CATHETER DRAINAGE BAG SELECTION 2. Disposable Leg Bags (500-750mls) • Designed for day wear and can be secured to the leg in a variety of ways eg straps, legi fix catheter bag holders strapped from the waist. (Leg bags can also be used to reduce trauma for the confused or forgetful patient while in hospital) • Tubing on leg bags is available in different lengths and can be tailored to individuals requirements. Some people may choose to wear the leg bag on their thigh, others prefer to wear the leg bag on their calf. Again others may prefer “the bellybag” • The general recommendation for changing disposable drainage bags is weekly or when they become damaged, odorous or have sediment in the bottom. CATHETER DRAINAGE BAG SELECTION 3. Disposable 4 liter plastic bags • • Bags with non returnable valve. Used post operatively in urology and for bladder • irrigation. • • Usually short term and only changed if damaged, contaminated or malodorous. Male Catheterization 1. Assess the patient’s need for catheterization and refer patient to the doctor. 2. Verify the doctor’s order for catheterization. 3. Prepare for the necessary materials. 4. Perform handwashing. 5. Identify the right patient. • Explain the procedure. • Position the patient properly, supine position. Ensure privacy. • Practice aseptic technique in the entire procedure. • Open the catheterization kit. • Add and prepare the materials to be used. Male Catheterization 11.Don first glove and fill the syringe with sterile water. 12.Don second glove and applies sterile drapes for the patient. 13.Grab the penis firmly behind the glans with the nondominant hand and retracts the foreskin of the uncircumcised male. • With the dominant hand, use sterile forcep to pick up swabs. Clean first from the meatus and then wipe the tissue surrounding the meatus in circular motion using a new swab for each stroke. • Pick up the catheter and place the drainage end of the catheter in the urine receptacle using the uncontaminated hand. • Lubricate the insertion end or tip of the catheter. Male Catheterization 17.Lift the penis to a position of 90 degree angle and insert the catheter until urine flows. 18.Connect the catheter to the urine bag and ensure that the emptying base of the bag is closed. 19.Inflate the balloon by injecting 5 – 10 cc of PNSS and check for anchorage. 20.Tape the catheter into the thigh using non-allergenic tape. 21.Dispose soiled materials properly. 22.Accurately record the procedures done. Female Catheterization 1. Assess the patient’s need for catheterization and refer patient to the doctor. 2. Verify the doctor’s order for catheterization. 3. Prepare for the necessary materials. 4. Perform handwashing. 5. Identify the right patient. • Explain the procedure. • Position the patient properly, supine position. Ensure privacy. • Practice aseptic technique in the entire procedure. • Open the catheterization kit. • Add and prepare the materials to be used. Female Catheterization 11.Don first glove and fill the syringe with sterile water. 12.Don second glove and applies sterile drapes for the patient. 13.With the non-dominant hand, separate the labia minora with thumb and index finger. Never remove fingers until catheter is inserted. 14.With the dominant hand, use sterile forcep to pick up swabs. Clean first from the meatus and then wipe the tissue surrounding the meatus in circular motion using a new swab for each stroke. 15.Pick up the catheter and place the drainage end of the catheter in the urine receptacle using the uncontaminated hand. 16.Lubricate the insertion end or tip of the catheter. Female Catheterization 17.Lift the penis to a position of 90 degree angle and insert the catheter until urine flows. 18.Connect the catheter to the urine bag and ensure that the emptying base of the bag is closed. 19.Inflate the balloon by injecting 5 – 10 cc of PNSS and check for anchorage. 20.Tape the catheter into the thigh using non-allergenic tape. 21.Dispose soiled materials properly. 22.Accurately record the procedures done. Female Catheterization Female Catheterization