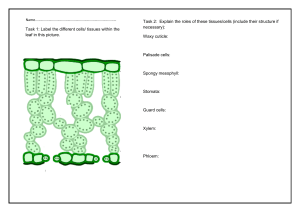
1 MEDINA COLLEGE Maningcol, Ozamiz City J U N I O Junior High School Department SCIENCE ELECTIVE 7 R H I G H S C H O O EXEQUIEL M. RAMIENTOS JR, LPT MEDINA COLLEGE SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL L 2 MODULE 4 Week 6 PLANT TISSUES AND OTHER LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION What Is This Module About? This module will provide you information on the Plant Tissues and Other levels of organization . Given the importance of plants in every aspect of our lives, humans study plants to understand processes that are critical to our own survival and to the health of the planet There is one lesson prepared for you in this module Lesson 1: The Plant Tissues What Will You Learn From This Module?1 After reading this module, you should be able to: 1. Describe the structure and function of various kinds of plant tissues How to learn from this module In order to achieve the objectives of this module successfully, you have to remember the following: 1. Read and follow the instructions carefully. 2. Answer the pretest. 3. Take down notes and record points for clarification. 4. Take the posttest and check your answers against the key at the end of the module. 5. Try to obtain at least 85% level of proficiency in the tests. EXEQUIEL M. RAMIENTOS JR, LPT MEDINA COLLEGE SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL 3 Lesson 1 Let’s Learn Plant Tissues Organs such as stem, and roots in plants, and stomach, heart and lungs in animals are made up of different kinds of tissues. A tissue is a group of cells with a common origin, structure and function. Their common origin means they are derived from the same layer of cells in the embryo. Being of a common origin, there are similar in structure and hence perform the same function. Several types of tissues organise to form an organ. Example : Blood, bone, and cartilage are some examples of animal tissues whereas parenchyma, collenchyma, xylem and phloem are different tissues present in the plants. The study of tissues is called histology. The plant tissues are mainly of two categories: 1. Meristematic (Gk. meristos : dividing) 2. Permanent (non-dividing) 1. Meristematic tissues Composed of immature or undifferentiated cells without intercellular spaces. The cells may be rounded, oval or polygonal; always living and thin-walled. Each cell has abundant cytoplasm and a prominent nucleus in it. Vacuoles may be small or absent. EXEQUIEL M. RAMIENTOS JR, LPT MEDINA COLLEGE SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL 4 2.Permanent tissues Permanent tissues are those in which growth has stopped either completely or for the time being. Cells of these tissues may be living or dead; and thin-walled or thick-walled. Thin-walled permanent tissues are generally living whereas the thick-walled tissues may be living or dead. Permanent Tissues The permanent tissues form the major portion of the plant. Simple Permanent tissues Parenchyma– These tissues are found in the soft parts of a plant such as the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. The cells of this tissue are loosely packed and contain large intercellular spaces between them. Each cell has a vacuole at the center. The functions of parenchyma tissues are storage, photosynthesis, and to help the plant float on water. Collenchyma- Are similar to parenchyma cells with thicker cell walls. They are meant to provide mechanical support to the plant structure in parts such as petiole of the leaf. Sclerenchyma- The cells of this tissue are dead. They are rigid, contain thick and lignified secondary walls. Their main function is to provide strength and support to parts of the plant. EXEQUIEL M. RAMIENTOS JR, LPT MEDINA COLLEGE SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL 5 Complex Permanent Tissue Unlike simple permanent cells which look the same and are made up of one type of cells, complex permanent tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. These different types of cells coordinate to perform a function. Xylem and Phloem are complex permanent tissues and are found in the vascular bundles in the plants. Xylem- It consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Tracheids and vessels are hollow tube-like structures that help in conducting water and minerals. The xylem conducts only in one direction i.e vertically. The xylem parenchyma is responsible for storing the prepared food and assists in the conduction of water. Xylem fibres are supportive in function. Phloem- It consists of four of elements: sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma. Unlike the xylem, phloem conducts in both directions. It is responsible for transporting food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant. Phloem contains living tissues except for fibres that are dead tissues. Functions of plant tissues Plant tissues have different functions depending upon their structure and location Help provide mechanical strength to organs. They help in providing the elasticity and flexibility to the organs. They help the tissues to bend easily in various parts of a plant like- leaf, stem, and branches without damaging the plant The xylem and phloem tissues help in transportation of material throughout the plants They divide to produce new cells and help in the growth of the plants. They help in various cellular metabolisms like photosynthesis, regeneration, respiration, etc. EXEQUIEL M. RAMIENTOS JR, LPT MEDINA COLLEGE SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL 6 Activity 1 WEEK 6 Function of Plant Tissues Directions: Complete the table below by supplying the needed information (copy the table on your answer sheet ) TYPE OF TISSUE LOCATION FUNCTION Meristematic tissues Permanent Tissues Directions : Choose the letter of the correct answer, write your answer on your answer sheet EXEQUIEL M. RAMIENTOS JR, LPT MEDINA COLLEGE SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL 7 Let’s Check What You Have Learned Directions: Write T if the statement is True ,otherwise write F if it is False. 1. Permanent tissues are those in which growth has stopped either completely or for the time being 2. Xylem and Phloem are complex permanent tissues and are found in the vascular bundles in the plants. 3. Parenchyma are found in the soft parts of a plant such as the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. 4. Collenchyma are similar to parenchyma cells with thicker cell walls. They are meant to provide mechanical support to the plant structure in parts such as petiole of the leaf. 5. Complex permanent tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. TEST II. Directions: Label the diagram below, Write your answer on your answer sheet. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. EXEQUIEL M. RAMIENTOS JR, LPT MEDINA COLLEGE SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL