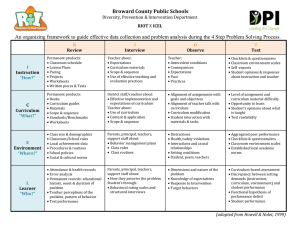
Functional Behavior Assessment Functional Analysis What is it? Assessment Methods Where/when is it conducted? Descriptive Behavioral Assessment Indirect Behavior Assessment Systematically manipulating environmental events thought to maintain problem behavior within an experimental design Observation of the problem behavior in relation to events that are not arranged in a systematic manner. Use structured interviews, checklists, rating scales, or questionnaires to obtain information from person who are familiar with the individual exhibiting the problem behavior Analog conditions ABC Recording - Continuous - Narrative A test condition includes an MO and a potential reinforcer - Control conditions (play) - Test conditions (escape, attention, alone) Simulated settings ***Analog conditions refer to the arrangements of variables rather than the setting in which assessment occurs*** Scatterplots Continuous: record every occurrence of the targeted PBs AND selected environmental events in the natural routine during a period of time Narrative: data are collected only when behaviors of interest are observed; recording is open-ended What do you do with the results? Structured interviews, checklists, rating scales, and/or questionnaires The function that problem behavior serves for a person can be determined from the graphs Scatterplot: divide the day into blocks; use symbols to indicate if target behavior occurred a lot, some, or not at all ABC Continuous: likely to provide useful information for designing a subsequent FA Function = test condition during which the most problem behavior occurred Scatterplots: identify time periods during which behavior occurs Teachers, parents, caregivers, and/or the individual him- or herself Identify possible conditions or events in the natural environmental that correlate with the problem behavior Intervention (teach alternative behaviors; alter consequence variables) and Prevention (alter antecedent variables) Advantages Limitations Ability to yield a clear demonstration of the variable(s) that relate to the occurrence of a problem behavior Easier to do than functional analyses Represent contingencies that occur within the individual’s natural routine Easy to conduct Requires expertise to implement and interpret Biased and unreliable Provide correlations NOT functional relations Limited accuracy Not the best choice for hypothesis formulation