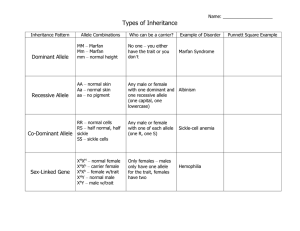
Names: _____________________________________________________________________________ Inheritance of Sex-Linked Traits Pre-Lab Questions Sex-linked genes are genes on the X and Y chromosomes. Traits controlled by these genes are called sex-linked traits. Two sex-linked traits include hemophilia and colorblindness. Hemophilia is a genetic disorder in which a person’s blood clots slowly or not at all. If a person has the dominant allele XH, he or she will have normal blood. If a person has only the recessive allele Xh, he or she will have hemophilia. Red-green colorblindness is also a genetic disorder. In this disorder, the person does not see red and green properly. This person will see green as gray and red as yellow. If a person has at least one dominant allele XC, he or she will not have colorblindness. If a person has only the recessive allele Xc, he or she will have colorblindness. A carrier is a person who has one dominant allele and one recessive allele for a trait. The person will have the dominant trait, but could pass the recessive allele to her offspring. For sex-linked traits, ONLY females can be carriers. In this investigation, you will see how hemophilia and colorblindness are inherited. 1. How are the alleles for sex-linked genes passed from parents to child? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Write the sex chromosomes for each gender: Male – ______________ Female – _______________ 3. Write what each allele represents: XH – ______________________________ Xh – ______________________________ XC – ______________________________ Xc – ______________________________ 4. What is a carrier? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Problem: How are hemophilia and red-green colorblindness inherited? Directions: 1. Decide who will be the mom and who will be the dad. Give one penny to each person. 2. Take turns flipping your coins and recording the alleles. Record your allele combinations on a separate sheet of paper. 3. Complete 20 trials of flipping your coins, and recording the alleles. 4. After you have completed the 20 trials, use tally marks to record how many of each allele combination you created. 5. Complete the Punnett square for each family. 6. Answer the Post-Lab questions. Part A: Hemophilia Family 1. Parents do not have hemophilia; mother is a carrier of hemophilia (XHXh). Mom: heads – XH tails – Xh Allele Combination Dad: heads – XH tails – Y Children of Family 1 XHXh Mother and XHY Father Children Observed Total Percent (Total / 20) XHXH XHXh XhXh XHY XhY Punnett Square Predicted Probabilities: XHXH _______________% XHXh________________% XhXh________________% XHY________________% XhY________________% ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Family 2. Father has hemophilia; mother is a carrier of hemophilia (XHXh). Mom: heads – XH tails – Xh Dad: heads – Xh tails – Y Children of Family 2 X Xh Mother and XhY Father Children Observed H Allele Combination XHXH XHXh XhXh XHY XhY Total Percent (Total / 20) Punnett Square Predicted Probabilities: XHXH _______________% XHXh________________% XhXh________________% XHY________________% XhY________________% ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Part B: Colorblindness Family 3. Father is colorblind, mother has 2 dominant alleles. Mom: heads – XC tails – XC Dad: heads – Xc tails – Y Children of Family 3 X XC Mother and XcY Father Children Observed C Allele Combination Total Percent (Total / 20) XCXC XCXc XcXc XCY XcY Punnett Square Predicted Probabilities: XCXC _______________% XCXc________________% XcXc________________% XCY________________% XcY________________% ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Family 4. Parents are not colorblind, mother is heterozygous. Mom: heads – XC tails – Xc Dad: heads – XC tails – Y Children of Family 4 X Xc Mother and XCY Father Children Observed C Allele Combination Total Percent (Total / 20) XCXC XCXc XcXc XCY XcY Punnett Square Predicted Probabilities: XCXC _______________% XCXc________________% XcXc________________% XCY________________% XcY________________% Post-Lab Questions: Analyze and Conclude 1. a. How many alleles for hemophilia do females have? ______________________ b. How many alleles for red-green colorblindness do females have? ______________________ c. How many alleles for hemophilia do males have? ______________________ d. How many alleles for red-green colorblindness do males have? ______________________ 2. Why is there a difference in the number of alleles for hemophilia and red-green colorblindness between males and females? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Why are only females carries for sex-linked traits? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Which of the parents can pass the allele for hemophilia to a son? Explain. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Which of the parents can pass the allele for hemophilia to a daughter? Explain. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 6. In Family 3, why are there no colorblind children even though one of the parents is colorblind? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Does your data from the lab support the predicted results from the Punnett squares? Give an example to support your answer. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Extension: Extra Credit Answer each question below, creating a Punnett square to help you. 1. The brother of a woman’s father has hemophilia. Her father does not have hemophilia, but she is concerned that her son might. Could she have passed the allele for hemophilia to her son? Explain. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 2. A woman’s father is colorblind. She marries a colorblind man. Could their son be colorblind? Could their daughter be colorblind? Explain. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 3. What is the possibility that a carrier and a person who has a sex-linked genetic disorder will have a son with the disorder? A daughter? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 4. What is the probability that a carrier and a person who does not have a sex-linked genetic disorder will have a son with the disorder? A daughter? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________