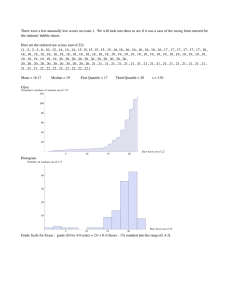
Data Analysis Prepared by: Cielito V. Maligalig, MEP CE, RCE Type of Data • Ungrouped Data • Grouped Data Measure of Central Tendency Mean • Average value of all data in the set. Median • A value that subdivide exactly the set data into two parts. Mode • Value that occurs most frequently. • Ungrouped Data Type of Data • 4, 8, 10, 14, 18, 19, 23, 24 • 4, 6, 9, 10, 12, 15, 17, 20 28 • Grouped Data •𝑥= Mean Ungrouped 𝑥𝑖 𝑛 ( Mean) • Weighted Mean • 𝑥 = 𝑤𝑥/ 𝑤 • Where: • 𝑥 = 𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑛 • n = number of observation • w = weight of each observation • 𝑥 = 𝑥𝑛+1 (odd number of data) 2 Median •𝑥= 𝑥𝑛 + 𝑥𝑛 2 +1 2 2 𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑑𝑎𝑡𝑎 • Where: • 𝑥 = 𝑚𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛 • 𝑥𝑖 = 𝑜𝑏𝑠𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑒𝑑 𝑑𝑎𝑡𝑎 Mode •𝑥=𝑥 • Where: • 𝑥 = 𝑚𝑜𝑑𝑒 • x = observed data which most frequently occur •𝑥= Mean Grouped 𝑓𝑥𝑖 𝑛 ( Mean) • Where: • 𝑥 = 𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑛 • f = frequency • n = number of observation • By coding or deviation • 𝑥 = 𝑥0 + 𝑓𝑑 𝑛 𝑐 • Where: • xo = class mark • d = code or deviation • c = class interval 𝑛 • 𝑥 = L𝑏 + Median ( 2 − ≺𝐶𝐹) 𝑓𝑚 𝑐 • WHERE: • 𝑥 = 𝑚𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛 • 𝑛 = 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎l 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑏𝑠𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 • Lb = lower limit • <CF = cumulative frequency before the median class • fm = frequency of the median class • c = class interval •𝑥= Mode • • • • • 𝑓𝑚𝑜 −𝑓1 𝐿𝑚𝑜 + ( )𝑐 2𝑓𝑚𝑜 −𝑓1− 𝑓2 Where: 𝑥 = 𝑚𝑜𝑑𝑒 Lmo = Lower limit of the modal class fmo = frequency of the modal class f1 = frequency of the class before the modal class • f2 = frequency of the class after the modal class • • Quartile, Decile & Percentile Ungrouped • 𝑛𝑁 𝑄𝑛 = 4 𝑛𝑁 𝐷𝑛 = 10 𝑛𝑁 𝑃𝑛 = 100 • Where: • Qn = Quartile • Dn = Decile • Pn = Percentile • N = number of observed data • n = nth quartile, decile or percentile • 𝑄𝑛 = 𝐿𝑏 + • 𝐷𝑛 = 𝐿𝑏 + Quartile, Decile & Percentile Grouped • 𝑃𝑛 = 𝐿𝑏 + 𝑁 4 ( −<𝑐𝑓) 𝑓𝑄𝑛 𝑐 𝑁 10 ( −<𝑐𝑓) 𝑓𝐷𝑛 ( 𝑁 −<𝑐𝑓) 100 𝑓𝑃𝑛 𝑐 𝑐 • Where: • Qn = Quartile • Dn = Decile • Pn = Percentile • N = number of observed data • n = nth quartile, decile or percentile • Lb = lower limit • <cf = cumulative frequency before the quartile, decile and percentile class • f(Qn, Dn, Pn) = frequency of quartile, decile or percentile class. • c = class interval Example • From the given data determine the mean, median, mode, quartile, decile and percentile. • 53, 48,76, 64, 79, 81, 62, 43, 63, 76, 41, 53 • 53, 48,76, 64, 79, 81, 62, 43, 63, 76, 41, 53, 72 • From the given data determine the mean, median, mode, quartile, decile and percentile. Example Class F 48 – 52 7 53 – 57 4 58 – 62 5 63 – 67 12 68 – 72 16 73 – 77 9 78 – 82 11 83 – 87 2 88 – 92 13 93 – 97 1 Lb Ub < cf Xc --