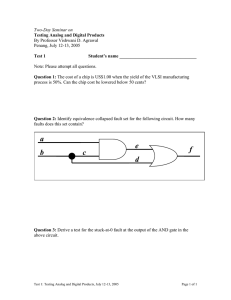
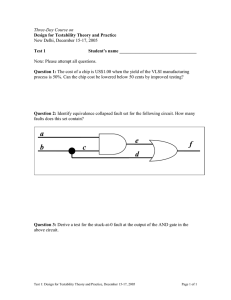
RMIT University © School of Engineering Power System Protection Tutorial Problem Sheet 2 Problem 1 Consider the system shown in Fig. 1. Circuit breakers Q12, Q21, Q23, Q32, Q34 and Q43 are tripped by directional overcurrent relays. Circuit breakers Q1 and Q4 are tripped by overcurrent relays only. a. Which relays will not pick up if a fault occurs at P1? b. Repeat the above for a fault at P2. c. Repeat the above for a fault at P3. d. What is the relationship between the operating times of all relays, if the relays are properly coordinated? e. Illustrate the above with plots of the relay operating time v. the fault location. Assume that all relays have definite-time trip characteristics. The minimum trip time is 0.2 s. The coordination time is 0.3 s. f. Is the system protected against bus faults? Justify your answer. 1 Q1 Q21 Q12 Q32 Q23 P1 L1 4 3 2 P2 Q43 Q4 Q34 P3 L3 L2 L4 Fig. 1 Problem 2 A bus protective zone is shown in Fig. 2. The zone is protected by three numerical differential relays, one for each phase. All current transformers are the same and have a ratio of 100/5. If a fault occurs inside the zone or close to it, the feeder fault currents are of the same phase and their magnitudes are as follows: IAF = 1000 A, IBF = 1200 A, ICF = 800A, IDF = 900 A, IEF = 1000A, IFF = 800 A. 1. Show how the current transformers in one phase are connected to the relay. Indicate the dotted ends of the primary and the secondary of each current transformer. 2. During the normal operation of the system, the feeder currents are IA = 90 A, IB = 100 A, IC = 95 A, ID = 90 A, IE = 95 A, IF = 90 A. What are the values of the differential current Idiff and the restraint current Irest, as a multiple of the CT rated current In during normal operation? 3. Calculate the differential current and the restraint current, as a multiple of the CT rated current, if a fault occurs at point F1. Assume ideal CT-s. 4. Calculate the differential current and the restraint current, as a multiple of the CT rated current, if a fault occurs at point F2. Assume ideal CT-s. 5. On a graph of Idiff/In vs. Irest/In, indicate the points of operation of the relay corresponding to normal operation, a fault at F1 and a fault at F2. 1 RMIT University © School of Engineering ID IE I1 IF I2 I3 I4 Differential Protection Relay F1 I5 IA F2 IC IB I6 Fig. 2 Problem 3 The circuit breakers in the power system shown in Fig. 3 are set to provide zone protection. 1. Draw the boundaries of protective zones in the power system shown in Fig. 3. 2. Which circuit breakers should open as primary protection for a fault at P1? 3. Which circuit breakers should open as primary protection for a fault at P2? 4. Which circuit breakers should open as primary protection, for a fault at P3? 1 4 2 Q21a Q12a Q24a Q1 P1 Q12b Q42a Q46 Q21b Q13 Q24b 1 Q23 Q42b 1 P3 P2 Q31 Q32 3 Q35 5 Q5 Fig. 3 2