Lawyer Ethics Rules Chart: Competence, Conflicts, Confidentiality
advertisement
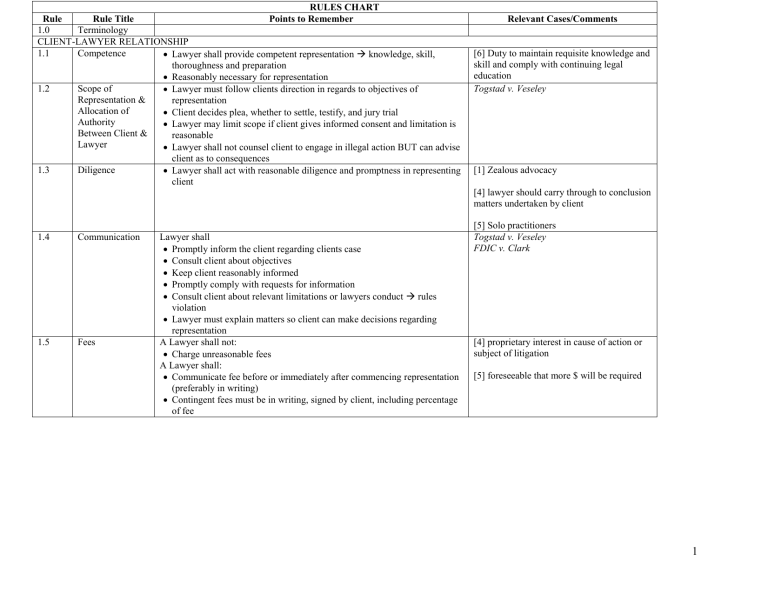
RULES CHART Rule Rule Title Points to Remember 1.0 Terminology CLIENT-LAWYER RELATIONSHIP 1.1 Competence Lawyer shall provide competent representation knowledge, skill, thoroughness and preparation Reasonably necessary for representation 1.2 Scope of Lawyer must follow clients direction in regards to objectives of Representation & representation Allocation of Client decides plea, whether to settle, testify, and jury trial Authority Lawyer may limit scope if client gives informed consent and limitation is Between Client & reasonable Lawyer Lawyer shall not counsel client to engage in illegal action BUT can advise client as to consequences 1.3 Diligence Lawyer shall act with reasonable diligence and promptness in representing client Relevant Cases/Comments [6] Duty to maintain requisite knowledge and skill and comply with continuing legal education Togstad v. Veseley [1] Zealous advocacy [4] lawyer should carry through to conclusion matters undertaken by client 1.4 Communication 1.5 Fees Lawyer shall Promptly inform the client regarding clients case Consult client about objectives Keep client reasonably informed Promptly comply with requests for information Consult client about relevant limitations or lawyers conduct rules violation Lawyer must explain matters so client can make decisions regarding representation A Lawyer shall not: Charge unreasonable fees A Lawyer shall: Communicate fee before or immediately after commencing representation (preferably in writing) Contingent fees must be in writing, signed by client, including percentage of fee [5] Solo practitioners Togstad v. Veseley FDIC v. Clark [4] proprietary interest in cause of action or subject of litigation [5] foreseeable that more $ will be required 1 1.6 Confidentiality of Information Communicate which expenses the client is responsible for A lawyers shall not: Contingent fee in criminal matter, domestic relations matters Division of a fee to lawyer not in firm permissible if: Proportionate to work, client agrees in writing, total fee is reasonable Lawyer shall not reveal Info relating to client unless informed consent Lawyer may reveal Info to prevent reasonably certain death or injury Prevent committing a crime or fraud services used Prevent, mitigate, rectify substantial injury services used Secure legal advice in compliance with rules Establish claim or defense in action btw. Lawyer and client Comply with other law or court order [3] work product doctrine, attorney client privilege [4] use of hypothetical’s [6] substantial harm rule [9] complying with rules of Professional Conduct [12] If request for confidential information lawyer must discuss with client before disclosure [13] When ordered to reveal conf. info. consult client, appeal, comply [16] lawyer must act competently to preserve confidentiality [17] reasonable precautions to prevent client info from getting in wrong hands 1.7 Conflict of Interest: Current Clients Lawyer shall not represent client in concurrent conflict Directly adverse to another client Representation could limit lawyer’s zeal May represent if: Reasonably believes can be competent and diligent Not prohibited by law Togstad v. Veseley Hickman v. Taylor—undue hardship [2] Steps to determine conflict [23] representing multiple defendants in criminal matters grave risk of conflict [24] Zeal of advocacy of a client because of duties to another client 2 Does not involve conflicted clients (π v. ∆) Informed consent given by each client (writing) [25] class actions [26] conflicts of interest can arise in contexts other than litigation; depends on whether there is a significant potential for material limitation [30] attorney-client privilege does not attaché between commonly represented clients [34] & [35] Organization as a client 1.8 Conflict of Interest: Current Clients Specific Rules Shall not enter into adverse business transaction with client unless: Fair and reasonable, in writing Advised in writing to get other counsel Informed consent given in writing Shall not use info to disadvantage of client unless given informed consent Shall not solicit substantial gift, prepare document that gives substantial gift unless related to client Prior to termination of rep. no agreement for literary or media rights Lawyer shall not: Provide financial assistance in pending or contemplated case except: advancement of court costs or litigation expenses Poor client can pay for expenses Lawyer shall not accept payment from one other than client unless: Informed consent No interference with independent judgment Attorney-client info protected No aggregated settlement claims in criminal cases expect informed consent A lawyer shall not: Prospectively limit malpractice suits unless client indep. Represented or Advised in writing to seek counsel and given time Togstad v. Veseley Pentnwalt Corp. v. Slough, Inc. [2] lawyer should discuss both material risks and existence of reasonable alternatives [5] use of information relating to the representation to the disadvantage of the client violates the lawyer’s duty of loyalty [6] small tokens are acceptable gifts and even large gifts as long as not solicited. Lawyer may not suggest that a client give a substantial gift [7] conveyance of a substantial gift REQUIRES detached advice of another lawyer [9] literary rights [16] Acquiring proprietary interest in subject of litigation [17] & [18] Sexual Relationships between 3 1.9 1.10 Duties to Former Clients Imputation of Conflicts of Interest: General Rules 1.11 Special Conflicts of Interest for Former & Current Government Officers & Employees 1.12 Former Judge, Arbitrator, Mediator or Other A lawyer shall not: Acquire proprietary interest in case except: Lien to get paid Contingent fee in civil case No sexing unless predates lawyer-client relationship Lawyer shall not represent another client in matter substantially related to a matter of a former client in which interests are materially adverse unless informed consent given in writing Lawyer shall not represent new client when old firm represented client that: Materially adverse interests Acquired confidential information (unless informed consent in writing) Lawyer and firm shall not use old clients information to that clients disadvantage unless info becomes generally known Lawyers firm shall not represent client prohibited by 1.7 or 1.9 unless lawyer personally adverse to representation lawyers and clients [2] clearly prohibited representation of new client when directly and substantially involved with old client with materially adverse interests [3] defines substantially related matters Hickman v. Taylor [4] does not apply when person with information is a paralegal or secretary or law student as long as they are timely screened Old firm can represent new client with interests adverse to previous client as long as The matter is not the same or substantially related Lawyers at the firm has no material information Can be waived with informed consent in writing Lawyer who has served as a public officer or employee of the government Title 18 U.S.C.A. §207 - Restrictions on former officers, employees, and elected Subject to 1.9(c) officials of the executive and legislative Shall not represent a client in a matter which the lawyer participated in branch materially and substantially as a public officer unless government gives informed consent in writing When a lawyer is disqualified from representation no lawyer at the firm can represent the client unless (1) disqualified lawyer is screened, (2) written notice is given to gov’t agency and no part of fee is given to disqualified lawyer Lawyer recently serving as a public officer or employee shall not – negotiate for private employment unless law clerk A lawyer shall not: (1) represent anyone in connection with a matter in which the lawyer participated in personally and substantially as a judge unless all parties give informed consent in writing; (2) negotiate for employment if served as a judge 4 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 Third-Party Neutral Organization as a Client Client with Diminished Capacity Safekeeping Property Declining or Terminating Representation If lawyer knows officer of organization is engaged in detrimental conduct that relates to the representation and the conduct would be imputed to the corporation the lawyer shall: Proceed as reasonably necessary in the best interests of org. highest authority If highest authority fails to take action AND the violation will result in substantial injury lawyer may reveal information to the extent necessary to prevent substantial injury This does not apply to investigations relating to lawyer’s representation or in defending employee/officer in alleged violation [3] policy decisions are not within lawyers duty [5] highest authority = board of independent directors Pentnwalt Corp. v. Slough, Inc. IBM v. Levin FDIC v. Clark If discharged due to reporting lawyer shall act to assure highest authority is informed of discharge Lawyer has duty to inform client with diminished capacity as much as possible regarding case Lawyer can take action on behalf of diminished clients when there is risk of substantial physical, financial or other harm Lawyer shall keep property of client separate from their own ($$), maintained in the same state as the lawyers office, appropriately identified and safe guarded. Appropriate records shall be kept for 5 years Look here also for rules regarding FEES and maintaining fiduciary duties Lawyer shall promptly inform client of received funds and promptly deliver to 3rd person property/funds they are entitled to receive When property is in dispute by 2 or more persons lawyer shall keep property separate until dispute is resolved. Lawyer must promptly return any undisputed funds/property Lawyer shall not represent client (or shall withdraw) if: Rep. = violation of professional conduct Physical or mental impairment Lawyer fired Lawyer may withdraw if: No materially adverse affect on client Client wants to do criminal acts Client has used lawyer’s services to perpetuate crime or fraud Repugnant or fundamental disagreement [3] handling disputed funds N.Y Code of Prof. Responsibility §1200.46[DR 9-102.] Preserving Identity of Funds and Property of Others, Fiduciary Responsibility… [2] ordinarily must decline or withdraw if client demands lawyer engage in unlawful conduct [4] client has right to discharge lawyer at any time [9] even when unfairly discharged lawyer must take steps to mitigate consequences to 5 Client doesn’t pay lawyer gives warning Unreasonable financial burden on lawyer Lawyer must request withdrawal from tribunal their ruling governs 1.17 1.18 Sale of Law Practice Duties to Prospective Clients Lawyer must take steps to protect client’s interest reasonable notice, time to procure other representation, surrendering papers/property, refunding advanced monies. Lawyer may retain papers to extent permitted by other law Lawyer can sell or buy a practice if: Seller ceases to engage in private practice or in the area of practice sold Entire practice sold to one or more lawyers Seller gives written notice to clients regarding: (1) proposed sale; (2) clients right to retain other counsel; (3) clients consent presumed if the client does not take action in 90days Fees charged to client shall not be increased by reason of the sale Lawyer shall not use or reveal information learned in consultations Lawyer shall not represent a client with interests materially adverse to those of a prospective client in the same/substantially related matter No lawyer in firm can represent client except if: (1) both prospective and client give informed consent in writing or (2) lawyer took measures to only receive as much information as necessary to determine whether to represent the client and (2)(a) disqualified lawyer is screened and (2)(b) written notice given to prospective client client [3] return due to unforeseen circumstances allowed [14] retirement plans do not constitute sale of practice [2] a person who communicates information to a lawyer without any reasonable expectation that the lawyer is willing to discuss the possibility of forming a clientlawyer relationship is not a prospective client [4] Initial interview should be held to determine whether there is a conflict. If so, representation should be declined or lawyer should inform client of conflict [5] lawyer may condition conversations with prospective clients on informed consent [6] Not prohibited if prospective clients information will not significantly harm Togstad v. Veseley COUNSELOR 2.1 Advisor Lawyer shall give candid advice law, economics, morals, political factors 6 2.3 Evaluation for Use by Third Party A lawyer may provide an evaluation for use by 3 rd party if making evaluation is compatible with duties to client if bad effect on client likely lawyer shall not provide evaluation unless informed consent given [3] when 3rd party will rely on evaluation legal duty to that person may arise [4] under no circumstances may lawyer make false statement of material fact in evaluation ADVOCATE 3.1 Meritorious Claims & Contentions 3.3 Candor Toward the Tribunal Lawyer shall not bring or defend non meritorious claims EXCEPT in criminal proceeding A lawyer shall not knowingly: Make a false statement of fact to a tribunal or fail to correct a false statement of material fact previously made Fail to disclose controlling legal authority that is directly adverse or not disclosed by opposing counsel Knowingly offer false evidence Lawyer shall: Take remedial measures when they later find out a witness has lied Lawyer may: Refuse to offer evidence reasonably believed to be false (excluding criminal matters) If the lawyer knows person intends to engage, is engaging, or has engaged in criminal or fraudulent conduct related to proceeding the lawyer shall take remedial measures disclose to tribunal This includes disclosures of confidential material under 1.6 duty ends when proceeding is concluded 3.4 Fairness to Opposing Party & Counsel In an ex parte proceeding a lawyer shall inform the tribunal of all material facts known to the lawyer to enable tribunal to make informed decision (adverse + beneficial facts), including the existence of witness. EX: filing a TRO A Lawyer shall not: Unlawfully obstruct another parties access to evidence or alter, destroy or conceal a document having potential evidentiary value Falsify evidence Knowingly disobey an obligation under court rules [2] lawyer must not allow tribunal to be mislead [6] Steps to take if lawyer knows that the client intends to testify falsely or introduce false evidence [8] Lawyer is only prohibited from offering evidence known to be false. Knowledge can be inferred from the circumstances [10] Remedial Measures – steps that constitute remedial measures [13] Duration of Obligation In re Seelig Penthouse Int’l Ltd. V. Playboy U.S. v. Litchfield People v. Andrades United States v. Thoreen [2] handling evidence, temporary custody for investigatory purposes [3] it is not improper to pay a witnesses expenses or an compensate an expert witness 7 3.5 Impartiality & Decorum of the Tribunal 3.6 Trial Publicity Make frivolous discover request or fail to produce discoverable materials At trial, allude to irrelevant matters, assert personal knowledge of facts except when testifying as a witness, or state a personal opinion Request a person to refrain from voluntarily giving relevant info unless: (1) person is a relative/employee/agent and (2) reasonably believes persons interests will not be adversely affected Lawyer shall not: Seek to influence a judge, juror, or prospective juror by means prohibited by law Communicate ex parte with judge/juror during proceeding Communicate with juror or prospective juror after discharge of jury if: (1) the juror has made it known they don’t want to talk; (2) the communication involves misrepresentation, coercion, duress or harassment Engage in conduct intended to disrupt a tribunal Lawyer shall not make extrajudicial statements regarding a proceeding if lawyer reasonably knows it will be disseminated to public and will materially prejudice adjudicative process A lawyer may state: The claim or defense, identity of persons Information in public record Investigation is in progress Scheduling of litigation Request for assistance to get information Warning of danger where likelihood of substantial harm is present In criminal cases (can state above and): Identity, residence, occupation and family status If accused has been apprehended or information to aid in apprehension Fact, time, place of arrest Identity of investigation or arresting officers Lawyer can make statement to press to counter recent statement that prejudices client (must limit information to that necessary to mitigate damage) 3.8 Special No lawyer in firm or agency can make prohibited statements Prosecutor in a criminal case shall: In re Zawada [4] belligerence – decorum [3] the rule applies only to lawyers who are or have been involved in the investigation or litigation of a case, and their associates. The rule precludes legal analysts [5] Subjects more likely than not to have prejudicial affect on a proceeding review 1-6 [7] Extrajudicial statements made in response to other parties adverse statements Gentile v. Nevada State Bar [1] Prosecutor responsible for the 8 Responsibilities of a Prosecutor Refrain from prosecuting charges without probable cause Make reasonable efforts to get accused counsel Not seek a waiver of important pretrial rights from an unrepresented person Make timely disclosure of all evidence tending to negate guilt of accused or mitigate offense Disclose to defense and tribunal all known unprivileged mitigating information Not subpoena a lawyer in criminal case about past or present client unless: (1) the information is not protected; (2) evidence is essential to case or ongoing investigation; and (3) no other feasible alternative to obtain info. Refrain from making unnecessary extrajudicial statements that have a substantial likelihood of heightening public condemnation of the accused and take reasonable care to ensure that investigators, law enforcement, employees, and other persons in their control make no such statements When new, credible material evidence that tends to show convicted ∆ is innocent prosecutor shall: Promptly disclose evidence to appropriate court/authority If conviction obtained in prosecutors jurisdiction: (1) promptly disclose evidence to ∆; (2) undertake further investigation to determine whether ∆ is innocent administration of justice when lawyer systematic abuse of prosecutorial discretion constitute an 8.4 [2] should not attempt to obtain waivers of preliminary hearings or other important pretrial rights [5] Prejudicial statements in relation to 3.6 [6] Duty to control investigators, etc. “even when such persons are not under direct supervision of the prosecutor” [8] Prosecutor must seek to remedy conviction Gentile v. Nevada State Bar Atty essentially called the police (potential witnesses) corrupt. NV SC called it prejudicial of material witness…brought charges after conclusion of trial When prosecutor knows ∆ was falsely convicted he shall seek to remedy the conviction TRANSACTIONS WITH PERSONS OTHER THAN CLIENTS 4.1 Truthfulness in In the course of representing a client a lawyer shall not knowingly Statements to Make a false statement of material fact or law to a third person Others Fail to disclose a material fact when disclosure is necessary to avoid criminal or fraudulent act by a client (unless 1.6) 4.2 Communication In representing a client a lawyer shall not: [4] parties to a matter may communicate with Persons directly with each other Communicate about the subject of representation with a person known to Represented by be represented by another lawyer in the matter; unless: Counsel The lawyer has consent of the other lawyer or is authorized by law or court [7] constituent of organization order 9 4.3 When dealing on behalf of a client with a person who is not represented by counsel a lawyer shall not: State or imply that the lawyer is disinterested If lawyer knows or reasonably should know that person misunderstands lawyers role lawyer shall make reasonable efforts to correct the misunderstanding The lawyer shall not give legal advice to an unrepresented person other than to secure counsel if interests of person are adverse to client 4.4 Respect for Lawyer shall not: [2] Prompt notification required but not Rights of Third additional steps to return information Use means with no substantial purpose other than to embarrass, delay, or Persons burden a third person, or Use methods of obtaining evidence that violate persons legal rights A lawyer who knows or should know that they have received documents by mistake shall promptly notify sender. LAW FIRMS & ASSOCIATES 5.1 Responsibilities A partner in a law firm (or equivalent lawyer) shall make reasonable efforts to [5] Duty to remedy of Partners, ensure that reasonable measures are in place to ensure conformity with the Managers, & rules of professional conduct Supervisory Lawyers A lawyer directly supervising another lawyer shall make reasonable efforts to ensure conformity with these rules 5.2 5.3 5.5 Dealing with Unrepresented Persons Responsibilities of a Subordinate Lawyer Responsibilities Regarding Nonlawyer Assistants Unauthorized Practice of Law; Multijurisdictiona l Practice of Law A lawyer shall be responsible for another’s violation of the RPC if: Lawyer orders or with knowledge ratifies conduct Lawyer is a partner or manager with direct supervisory control and knows of the conduct at a time when its consequences can be avoided or mitigated but fails to take reasonable remedial action A lawyer is bound by the rules of professional conduct notwithstanding that the lawyer acted in direction of another person Not in violation if follows reasonable decision regarding arguable question of professional duty Lawyer shall make: reasonable assurance that the persons conduct is compatible with the professional obligations of the lawyer A lawyer shall be responsible for conduct of such a person that would violate RPC if : (1) lawyer knowing orders or ratifies specific conduct; (2) knows of conduct and can mitigate damages Lawyer shall not practice law in jurisdiction where not licensed [6] Temporary and recurring basis allowed Say that they can practice in a jurisdiction that they are not barred in Lawyer may temporarily practice in a jurisdiction that they are not barred in if: 10 5.6 Restrictions on Right to Practice PUBLIC SERVICE 6.2 Accepting Appointments Associate with licensed lawyer Reasonably related to pending or potential matter before tribunal in jurisdiction and granted authorization by law to practice Pending or potential arbitration, mediation, or other alternative dispute resolution proceeding arising out of practice in barred jurisdiction Not above but arising out of practice in barred jurisdiction Lawyer not barred in jurisdiction may provide legal services if: Works for an organization (in-house counsel) and does not need pro hac vice admission; or Lawyer authorized by federal law to provide services Lawyer shall not enter into agreement limiting right to practice unless Retirement benefits, or Restriction as apart of settlement of a client controversy Lawyer shall not seek to avoid appointment by tribunal expect for showing of good cause: Representation likely to result in violation of RPC or law Financial burden too great Repugnant Look at 1.16 – declining or terminating representation A lawyer who provides short term legal services (not-for-profit or court appointment) with no expectation of continued representation: Is subject to rule 1.7 and 1.9(a) only if lawyer knows conflict exists and Subject to rule 1.10 only if lawyer knows another lawyer associated with the lawyer is disqualified under rule 1.7 or 1.9(a) Except as provided in paragraph (a)(2), Rule 1.10 is inapplicable to a representation governed by this rule INFORMATION ABOUT LEGAL SERVICES 7.1 Communications Lawyer shall not make a false or misleading communication about the lawyer Concerning a or lawyer’s services. Lawyer’s False/Misleading statements omit facts necessary to make the statement Services truthful 7.2 Advertising Lawyer may advertise using public media 6.5 Nonprofit CourtAnnexed Limited Legal Services Programs [2] Good cause exists if lawyer can not handle matter competently [1] In programs like legal advice hotlines there is no expectation that the lawyer-client relationship will continue after the limited consultation Florida Bar v. Went For It, Inc. Florida Bar v. Went For It, Inc. 11 7.3 Direct Contact with Prospective Clients Lawyer shall not give anything of value for a person recommending lawyer services except that a lawyer may: Pay reasonable advertising costs N.Y Code of Prof. Responsibility Pay usual charges for not-for-profit or qualified referral service §1200.38[DR 7-107.] Trial Publicity Pay a law practice (1.17) Refer clients to another lawyer or Nonlawyer professional pursuant to a reciprocal agreement that is: (1) not exclusive and (2) informed consent given by client All ads must contain name and office of at least one lawyer or firm responsible for its content A lawyer shall not in-person, telephone, real-time electronic contact solicit professional employment from prospective client when significant motive for solicitation is lawyers pecuniary gain; unless person contacted: Is a lawyer Family, close personal, or prior professional relationship Lawyer shall not solicit employment by any means if: Prospective client has made it clear they do not want solicitations Solicitation involves coercion, duress or harassment Every solicitation to a person known to be in need of representation must include the words “Advertising Materials” on outside envelope (at beginning and end of recorded communication) unless recipient is lawyer, family, etc. Lawyer may participate in prepaid or group legal services that uses otherwise prohibited means of communication for persons not known to need legal services MAINTAINING THE INTEGRITY OF THE PROFESSION 8.1 Bar Admission & [1] material false statement in connection Lawyer shall not lie on bar examination or application Disciplinary with an application for admission it may be Fail to disclose fact necessary to correct misapprehension known to have Matters basis of subsequent disciplinary action arisen Knowingly fail to respond to a lawful demand for information; except for confidential info protected by 1.6 8.3 Reporting A lawyer who knows that another lawyer has committed a violation shall inform the appropriate professional authority Professional Misconduct A lawyer who knows that a judge has committed a violation that raises substantial question as to judges fitness shall inform appropriate authority 8.4 Misconduct This rule does not require disclosure of information protected by 1.6 gained during lawyer assistance program It is professional misconduct for a lawyer to: [2] Pattern of repeated offenses, even ones of minor significance when considered Violate or attempt to violate the rules of professional conduct or 12 knowingly assist or induce another to do so Commit a criminal act that reflects adversely on honesty, etc. Engage in conduct that is prejudicial to the administration of justice Engage in conduct involving dishonesty, fraud, deceit, or misrepresentation State or imply the ability to improperly influence gov’t agency or to achieve results by means that violate these rules Knowingly assist a judge or judicial officer in conduct that violates rules or law 8.5 separately, can indicate indifference to legal obligation [3] a lawyer who, in the course of representing a client, knowingly manifests words/conduct, bias or prejudice based on race, sex, religion, national origin, disability, age, sexual orientation or SES, violates paragraph (d) Cincinnati Bar Ass’n v. Statzer – 8.4(c) In re Gatti – 8.4(c) Disciplinary Authority, Choice of Law Lawyer is subject to discipline in jurisdictions where: Lawyer is barred Provides or offers to proved legal services Lawyer can be subject in both jurisdiction for the same conduct Choice of law When conduct involves pending case rules of that jurisdiction apply For any other conduct the rules for that jurisdiction apply unless predominate affect of conduct is in a different jurisdiction Lawyer shall not be subject to discipline if follows laws of jurisdiction where reasonably believes predominate affect will occur. CODE OF JUDICIAL CONDUCT Rule 2.15 – Responding to D. A judge who receives information indicating a substantial likelihood that a lawyer has committed a violation of the Rules Judicial and Lawyer of Professional Conduct shall take appropriate action Misconduct Rule 1.2 - Promoting A judge shall act at all times in a manner that promotes pubic confidence in the independence, integrity, and impartiality of Confidence in the Judiciary the judiciary, and shall avoid impropriety and the appearance of impropriety. 18 U.S.C.A. §207(a)(1)— Permanent Restrictions on Former Officers, employees of Executive & Legislative Branches 18 U.S.C.A. §207(a)(2)—2 yr Restrictions for former managers Permanent restriction to knowingly influence via communication or appearance before any agency, court, or court-martial of the US or DC in connection with a particular matter that US or DC has a direct and substantial interest Which the person has participated personally and substantially and Which involved a specific party or specific parties at the time of such participation 2yr ban on appearing before any agency, court, court- martial US or DC on behalf of any other person in connection w/particular matter In which US or DC has a direct and substantial interest That one knows or reasonably should know was actually pending under his or her official responsibility 1 yr prior 13 18 U.S.C.A. §207 (c) –1 yr ban Restrictions for ANY employee ending employ w/US or DC Which involved a specific party or parties at the time it was so pending 1 year ban on appearing before the agency, court, court- martial of US or DC where you worked on behalf of any other person for any reason 14






