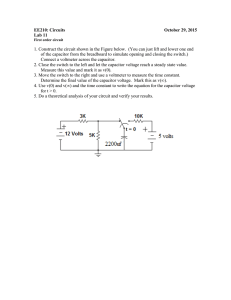
Electricity Review Packet – AP Physics 2 1. A heating coil is placed in a thermally insulated tank of negligible heat capacity. The tank contains 0.1 kilogram of water and 0.01 kilogram of ice, both initially at a temperature of 0°C. The resistance of the coil is 25 ohms, independent of temperature, and there is a current of 2 amperes in the coil. Calculate each of the following quantities. (a) The heat transferred to the water and ice by the heating coil in time t (b) The time t1 necessary to melt all the ice (The latent heat of fusion of ice is 3.34 x 106 joules per kilogram.) (c) The additional time t2 necessary to bring the water to a boil (The specific heat of water is per kilogram • Kelvin.) 4.19 x 103 joules Electricity Review Packet – AP Physics 2 5. (15 points) Four lightbulbs are connected in a circuit with a 24 V battery as shown above. (a) i. Determine the average potential energy change of an electron as it moves from point Z to point X. ii. Indicate whether the electron gains or loses potential energy as it moves from point Z to point X. ____ Gains energy ____ Loses energy (b) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit. (c) i. Calculate the magnitude of the current through point Y. ii. Indicate on the diagram the direction of the current through point Y. (d) Calculate the energy dissipated in the 12 W bulb in 5 s. (e) Rank the bulbs in order of brightness, with 1 being the brightest. If any bulbs have the same brightness, give them the same ranking. ____ Bulb A ____ Bulb B ____ Bulb C ____ Bulb D Basic Circuits with Identical Capacitors—Charge on a Capacitor 159 Shown below are eight capacitor circuits. All of the capacitors are identical, and all are fully charged. The batteries are also identical. In each circuit, one capacitor is labeled X. Rank these circuits in terms of the charge on capacitor X. That is, put first the circuit in which capacitor X has the largest charge, and put last the circuit in which capacitor X has the smallest charge. If two or more circuits result in identical charges on capacitor X, give these circuits equal ranking. A B X C D X X X E G F H X X X X Largest 1____ 2____ 3____ 4____ 5____ 6____ 7____ 8____ Smallest Or, all of these capacitors have the same charge on them. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 159 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 L. Takahashi, D. Maloney, C. Hieggelke Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 171 Electricity and Magnetism Circuits with Identical Capacitors—Charge on a Capacitor 160 Shown below are eight capacitor circuits. All of the capacitors are identical, and all are fully charged. The batteries are also identical. In each circuit, one capacitor is labeled X. Rank these circuits in terms of the charge on capacitor X. That is, put first the circuit in which capacitor X has the largest charge, and put last the circuit in which capacitor X has the smallest charge. If two or more circuits result in identical charges on capacitor X, give these circuits equal ranking. A B C D X X X X E G F X H X X X Largest 1____ 2____ 3____ 4____ 5____ 6____ 7____ 8____ Smallest Or, all of these capacitors have the same charge on them. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 160 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 L. Takahashi Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 172 Electricity and Magnetism Simple Capacitor Circuits—Charge on a Capacitor 161 Shown below are eight capacitor circuits. All of the capacitors are either 1 µF or 2 µF, and all are fully charged. The batteries are also identical. In each circuit, one capacitor is labeled X. Rank these circuits in terms of the charge stored in capacitor X. That is, put first the circuit in which capacitor X has the largest charge stored, and put last the circuit in which capacitor X has the smallest charge stored. If two or more circuits result in identical charge stored for capacitor X, give these circuits equal ranking. A 2 µF B 1 µF 2 µF C D 1 µF 2 µF 1 µF X X F E 2 µF 2 µF 1µF X X G H X X 1 µF 1 µF 2 µF X X Largest 1 µF 1 µF 1 µF 1____ 2____ 3____ 4____ 5____ 6____ 7____ 8____ 2 µF Smallest Or, the capacitors marked X all have the same charge stored. _______ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 161 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 L. Takahashi, C. Hieggelke Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 173 Electricity and Magnetism Basic Circuits with Identical Capacitors—Voltage Across a Capacitor162 Shown below are eight capacitor circuits. All of the capacitors are ,and all are fully charged. The batteries are also identical. In each circuit, one capacitor is labeled X. Rank these circuits in terms of the voltage across capacitor X. That is, put first the circuit in which capacitor X has the largest voltage, and put last the circuit in which capacitor X has the smallest voltage. If two or more circuits result in identical voltages for capacitor X, give these circuits equal ranking. A B X C D X X X E G F H X X X X Largest 1____ 2____ 3____ 4____ 5____ 6____ 7____ 8____ Smallest Or, the capacitors marked X all have the same voltage drop. _______ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 162 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 L. Takahashi, C. Hieggelke, D. Maloney Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 174 Electricity and Magnetism Circuits with Resistors and Capacitors—Current 163 The circuit shown below has circuit elements α, β, γ , and δ, which are either a 1 F capacitor or a 1, 2, or 4 ohm resistor. Rank the arrangements of circuit elements given below in order from largest to smallest magnitude of current that flows after a long time through the 6 volt battery connected as shown. α 6V γ β Arrangements δ α β γ δ Arrangement A 1F=1 Farad 4Ω = 4 ohms 1Ω = 1 ohm 2Ω = 2 ohms Arrangement B 1Ω 1F 2Ω 4Ω Arrangement C 2Ω 1Ω 4Ω 1F Arrangement D 4Ω 2Ω 1F 1Ω Arrangement E 1F 1Ω 2Ω 4Ω Arrangement F 1Ω 4Ω 2Ω 1F Arrangement G 2Ω 4Ω 1F 1Ω Ranking of arrangements by magnitude of current through the battery: Largest 1_____ 2_____ 3_____ 4_____ 5_____ 6_____ 7_____ Smallest Which of these arrangements have the same magnitude of current, if any? ________________________________________________________________________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 163 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 K. Wetz Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 175 Electricity and Magnetism Current Carrying Wires with Different Lengths—Net Charge 164 The figures below show six segments of wires that are carrying electric currents. In all six cases, the currents are flowing to the right (into the page). As you can see from the values in the figures, the pieces of the wires shown have different lengths, and they are carrying different currents. For the ranking below, we are only interested in the segments of the wires actually shown in the figures. Rank these segments from greatest to least on the basis of the net electric charge, i.e., the difference in number of positive charges and negative charges in each segment. That is, put first the segment that has the greatest net electric charge on it, and put last the segment that has the smallest net electric charge on it. 5A 3A B A 30 cm 12 cm 2A C 45 cm 2A 4A Greatest E D 12 cm 5A F 30 cm 1______ 2______ 3_______ 4______ 5______ 6______ Or, all of these segments have the same net charge. _______ Or, the net charge is zero for all of these segments. Please carefully explain your reasoning. _______ How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 164 7 20 cm Smallest 8 Very Sure 9 10 D. Maloney Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 176 Electricity and Magnetism Batteries and Bulbs—Bulb Brightness165 Identical batteries are connected in different arrangements to the same light bulb. Rank these items on the basis of bulb brightness. + - + A - + + - - + - + - C B + + + - + - + - - - D E Brightest 1_________ 2_________ 3________ 4_________ 5_________ Least Bright Or, all bulbs have the same brightness. _______ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 165 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 C. Hieggelke, D. Maloney, T. O’Kuma Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 177 Electricity and Magnetism Simple Resistor Circuits—Current 166 All the resistors in the circuits below are identical at 2Ω each. The batteries are ideal with voltages of 6 or 12 volts as shown below. All connecting wires have negligible resistance. Rank the current passing through the upper right hand corner of each circuit from greatest to least. A 12V B 6V C 12V D 6V E 12V F 6V Greatest 1_______ 2________ 3________ 4________ 5________ 6________ Least Or, the current is the same in each situation. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 166 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 C. Hill, C. Lam, M. Mann Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 178 Electricity and Magnetism Current Carrying Wires with Different Resistances—Net Charge 167 Shown below are six segments of wires that are carrying electric currents. All of these segments have the same length and the same diameter, but the wires are made of different materials so they have different resistances. The currents flowing in these segments also vary. Specific values for each of these properties are given in the figures. Rank these situations from highest to lowest on the basis of the net electric charge on each segment, i.e., on the basis of the difference between the number of positive and negative charges in the wire segment. Put first the situation that has the greatest net charge, and put last the situation with the smallest net charge, i.e., the smallest difference between the number of positive and negative charges. I=2A R = 5Ω R = 3Ω A R = 3Ω B C I=4A I=3A I=3A R = 7Ω R = 5Ω D Largest I=4A I=7A R = 3Ω E F 1______ 2______ 3______ 4______ 5______ 6______ Smallest Or, all of these segments have the same net charge. __ Approximate value: Or, all of these segments have zero net charge. _____ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 167 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 D. Maloney Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 179 Electricity and Magnetism Simple Series Circuit—Voltage Across Bulb X 168 + , and three light bulbs, shown as The eight circuits below all have one battery, shown as . All of the batteries are identical. The bulbs can have different resistances (resistance is the opposition a circuit element presents to the flow of current) given in units of ohms, Ω . The specific values for these resistances are given in the figures. One of the three bulbs in each circuit is designated by an X. This is the bulb we are interested in. All of the wires in these circuits are identical and of equal length. Rank these circuits, from greatest to least, on the basis of the voltage drop across the bulb marked X. That is, put first the circuit where the voltage drop across bulb X is the largest of any of the X bulbs, and put last the circuit where the voltage drop across bulb X is the smallest of all of the X bulbs. We are not interested in the voltage drops across any of the other bulbs. A B + X 10 Ω C + + X Ω 20 Ω 30 Ω 10 Ω X 10 Ω 20 Ω 10 Ω 20 Ω 10 Ω D E + + X 10 Ω X 20 Ω 30 Ω F 30 Ω G + Greatest H + X 10 Ω 20 Ω 10 Ω + X 10 Ω 20 Ω X 10 Ω 20 Ω 10 Ω 1_____ 2_____ 3_____ 4_____ 5_____ 6_____ 7_____ 8_____ Or, all of these circuits have the same voltage drop across bulb X. Or, all of these have zero voltage drop across bulb X. ____ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 168 10 Ω 7 20 Ω 30 Ω Least _____ 8 Very Sure 9 10 D. Maloney Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 180 Electricity and Magnetism Simple Resistor Circuits—Voltage Drop 169 All the resistors in the circuits below are identical at 2Ω each. The batteries are ideal with voltages of 6 or 12 volts as shown. All connecting wires have negligible resistance. Rank the voltage at the upper righthand corner relative to the ground. Place the highest voltage first and the lowest voltage last. A 12V B 6V C 12V D 6V E 12V F 6V Highest 1_______ 2________ 3________ 4________ 5________ 6________ Lowest Or, all of the voltages are the same. _______ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 169 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 C. Hill, C. Lam, M. Mann Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 181 Electricity and Magnetism Parallel Circuits—Voltmeter Readings Across Open Switches I 170 All resistors shown are identical in the circuits below. The switches in each case are open. Rank the voltmeter readings from highest to lowest. 2V 7V VA VB 3V 9V VC VD Highest 1___________ 2____________ 3____________ 4____________ Lowest Or, all of the readings are zero. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 170 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 M. Nelson Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 182 Electricity and Magnetism Parallel Circuits—Voltmeter Readings Across Open Switches II 171 All resistors shown are identical in the circuits below. The switches in each case are open. Rank the voltmeter readings from highest to lowest. 3V 3V VA VB 3V 3V VC VD Highest 1___________ 2____________ 3____________ 4____________ Lowest Or, all readings are zero. __________ Or, all readings are 3 V. __________ Or, not enough information is given to be able to rank these readings. ___________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 171 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 M. Nelson Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 183 Electricity and Magnetism Circuit with Two Open and Closed Switches—Ammeter Readings 172 Shown below is a DC circuit that contains two switches. Each switch is resistanceless when closed. All of the connecting wires should be considered to have zero resistance. All of the resistors shown are identical. The circuit contains an ideal ammeter and an ideal voltmeter. The diagram shows the switches open. Below the diagram are four different switch configurations for the circuit. A V S1 S2 Configuration S1 S2 A open open B open closed C closed open D closed closed Rank these configurations in terms of the ammeter reading. Largest 1 ______ 2 ______ 3 ______ 4 ______ Smallest Or, all configurations produce the same ammeter reading. __________ Or, all configurations produce a zero ammeter reading. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 172 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 L. Takahashi, C. Hieggelke Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 184 Electricity and Magnetism Circuit with Two Open and Closed Switches—Voltmeter Readings 173 Shown below is a DC circuit that contains two switches. Each switch is resistanceless when closed. All of the connecting wires should be considered to have zero resistance. All of the resistors shown are identical. The circuit contains an ideal ammeter and an ideal voltmeter. The diagram shows the switches open. Below the diagram are four different switch configurations for the circuit. A V S1 S2 Configuration S1 S2 A open open B open closed C closed open D closed closed Rank these configurations in terms of the voltmeter reading. Largest 1 ______ 2 ______ 3 ______ 4 ______ Smallest Or, all configurations produce the same voltmeter reading. __________ Or, all configurations produce a zero voltmeter reading. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 173 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 L. Takahashi, C. Hieggelke Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 185 Electricity and Magnetism Circuit with Three Open and Closed Switches—Voltmeter Readings I 174 Shown below is a DC circuit that contains a number of switches. Each switch is resistanceless when closed. All of the connecting wires may be considered to have zero resistance. All of the resistors shown are identical. The circuit contains an ideal voltmeter. The diagram shows all of the switches open. Below the diagram are eight different switch configurations for the circuit. Rank these configurations in terms of the voltmeter reading. That is, put first the configuration for which the voltmeter gives the largest reading, and put last the configuration for which the voltmeter gives the smallest reading. If two or more configurations produce the same voltmeter reading, give these configurations equal ranking. V S1 S2 S3 Configuratio S1 S2 S3 A open open open B open closed closed C open closed open D open open closed E closed closed closed F closed open open G closed open closed H closed closed open n Largest 1_____ 2_____ 3_____ 4_____ 5_____ 6_____ 7_____ 8_____ Smallest Or, all configurations produce the same voltmeter reading. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure Very Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 174 L. Takahashi Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 186 Electricity and Magnetism Circuit with Three Open and Closed Switches—Voltmeter Readings II 175 Shown below is a DC circuit that contains a number of switches. Each switch is resistanceless when closed. All of the connecting wires may be considered to have zero resistance. All of the resistors shown are identical. The circuit contains an ideal voltmeter. The diagram shows all of the switches open. Below the diagram are eight different switch configurations for the circuit. Rank these configurations in terms of the voltmeter reading. That is, put first the configuration for which the voltmeter gives the largest reading, and put last the configuration for which the voltmeter gives the smallest reading. If two or more configurations produce the same voltmeter reading, give these configurations equal ranking. S1 V S2 S3 Configuration S1 S2 S3 A open open open B open closed closed C open closed open D open open closed E closed closed closed F closed open open G closed open closed H closed closed open Largest 1_____ 2_____ 3_____ 4_____ 5_____ 6_____ 7_____ 8_____ Smallest Or, all configurations produce the same voltmeter reading. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 175 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 L. Takahashi Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 187 Electricity and Magnetism Circuit with Three Open and Closed Switches—Ammeter Readings 176 Shown below is a DC circuit that contains a number of switches. Each switch is resistanceless when closed. All of the connecting wires may be considered to have zero resistance. All of the resistors shown are identical. The circuit contains an ideal ammeter. The diagram shows all of the switches open. Below the diagram are eight different switch configurations for the circuit. Rank these configurations in terms of the ammeter reading. That is, put first the configuration for which the ammeter gives the largest reading, and put last the configuration for which the ammeter gives the smallest reading. If two or more configurations produce the same ammeter reading, give these configurations equal ranking. A S1 S2 S3 Configuration S1 S2 S3 A open open open B open closed closed C open closed open D open open closed E closed closed closed F closed open open G closed open closed H closed closed open Largest 1_____ 2_____ 3_____ 4_____ 5_____ 6_____ 7_____ 8_____ Smallest Or, all configurations produce the same ammeter reading. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 176 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 L. Takahashi Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 188 Electricity and Magnetism Simple Series Circuit with Various Resistors—Current I 177 In the circuit below, there are seven possible combinations of R1, R 2, and R3. Rank the combinations, in terms of the current measured by the ammeter, from highest to lowest. R3 A 10V R2 R1 R2 R3 A 1 2 3 B 2 1 3 R1 C 3 2 1 D 2 2 2 E 4 1 1 F 1 1 4 G 0 5 1 Highest 1______ 2______ 3______ 4______ 5______ 6______ 7______ Lowest Or, all of the combinations have the same current. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 177 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 P. D’Alessandris, J. Taylor, R. Krupp Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 189 Electricity and Magnetism Simple Series Circuit with Various Resistors—Voltmeter 178 In the circuit below, there are seven possible combinations of R1, R 2, and R3. Rank the combinations, on the basis of the reading on the voltmeter, from highest to lowest. R3 A 10V R2 V R1 R2 R3 A 1 2 3 B 2 1 3 C 3 2 1 R1 D 2 2 2 E 4 1 1 F 1 1 4 G 0 5 1 Highest 1______ 2______ 3______ 4______ 5______ 6______ 7______ Lowest Or, all of the combinations have the same voltage. __________ Please carefully explain your reasoning. How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure 1 2 3 4 5 6 178 7 8 Very Sure 9 10 P. D’Alessandris, J. Taylor, R. Krupp, D. Maloney Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 190 Electricity and Magnetism