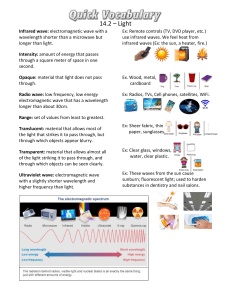
Name: WAVES STUDY GUIDE Labeling Label the image with the common properties of waves. Label 1: crest Label 2: wavelength Label 3: amplitude Label 4: trough Matching Write the letter of the electromagnetic wave next to the description. 1. Absorbed by bones. d 2. The only visible wave on the electromagnetic spectrum. a 3. The wave with the longest wavelength. b 4. The most dangerous wave with the highest frequency. f 5. Used in GPS and radar. e 6. Felt as heat by humans. c 7. Responsible for sun burns. g a) b) c) d) e) f) g) Visible Radio Infrared X-ray Microwave Gamma Ultraviolet Ordering In the space below, write the electromagnetic waves in the order that they occur on the spectrum from large wavelength to small wavelength. Radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-ray, gamma Name: Fill in the blank Fill in the blanks using the word bank. Each word will only be used once. ROY G BIV Refraction Opaque Transmitted Amplitude Wavelength Reflects Absorbs Frequency Translucent Speed Echo Transparent Hertz Pitch 1. To remember the order of wavelengths of visible light, we can use the abbreviation ROY G BIV (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet). 2. For sound waves, a high frequency results in a high pitch. 3. The volume of sound is determined by the amplitude of the wave. 4. The color of light is determined by the wavelength of the light wave. 5. When sound waves are reflected, it is called an echo. 6. The unit used to measure frequency is hertz. 7. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency. 8. An object is opaque because it absorbs light. 9. A window is an example of a transparent object. 10. A wall is an example of an opaque object. 11. A thin, white piece of paper is an example of a translucent object. 12. An object is transparent or translucent when some light is transmitted. 13. A banana appears yellow because that is the wavelength that the banana reflects. 14. The equation for wave speed is wavelength divided by frequency. 15. An pencil appearing distorted in water is an example of refraction. Name: Matching Write the letter of the light property next to the description. 8. When light bends. b 9. When light energy is transferred into something else. c 10. An object that is not see through. g 11. An object that is fully see through. e 12. When light bounces off a surface. a 13. When light travels throughs something. d 14. An object that is partially see through. f a) b) c) d) e) f) g) Reflection Refraction Absorption Transmission Transparent Translucent Opaque Sorting Sort the terms as describing either light or sound waves. Transverse wave Requires matter Longitudinal wave Mechanical wave Travels fastest in empty space Compression LIGHT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE TRANSVERSE WAVE TRAVELS FASTEST IN EMPTY SPACE Electromagnetic wave Travels fastest in a solid Pitch SOUND Mechanical wave Longitudinal wave Compression Requires matter Travels fastest in a solid Pitch Name: Things to Know The definition of a wave The properties of waves and how to identify or measure them o Wavelength o Amplitude o Crest o Trough o Frequency o Speed Be able to identify a transverse wave and longitudinal wave o Compression o Rarefaction Sound Waves o Type of mechanical wave o Longitudinal wave o Needs a medium o Travels fastest in solids o Can be reflected and absorbed Electromagnetic spectrum o Know that they do not need a medium (matter) o Know the order of the waves o Know examples for each wave Properties of Light o Type of electromagnetic wave o Transverse wave o Does not need a medium o Travels fastest in empty space (vacuum) o Refraction o Reflection o Absorption o Transmission o Transparent objects o Translucent objects o Opaque objects o Know how we see color Name: