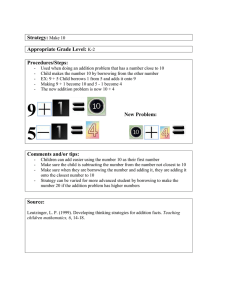
Borrowing Cost Answer Let’s Check (ULO o) Activity 1. Now that you know most of the essential terms in the study of accounting for borrowing costs, let us try to check your understanding of the topic. True or False: Write true if wrong, write false. the statement is correct and if the statement is ________1. Borrowing costs are incurred in connection with borrowing of funds and include all of the following: a. Interest expense calculated using the effective interest method. b. Finance charge in respect of finance lease. c. Exchange difference arising from foreign currency borrowing to the extent that the exchange difference is regarded as an adjustment to interest costs. d. All of these are included in borrowing costs. ___True___2. If the qualifying asset is financed by specific borrowing, the capitalizable borrowing cost is equal to actual borrowing cost incurred up to completion of asset minus any investment income from the temporary investment of the borrowing. _False____3. If the qualifying asset is financed by general borrowing, the capitalizable borrowing cost is equal to average expenditures on the asset multiplied by a capitalization rate or actual borrowing cost incurred, whichever is higher. _False___4. Inventory that is manufactured or produced in large quantity on a repetitive basis and takes a substantial period of time to get ready for use or sale could be treated as qualifying asset for the purpose of capitalizing borrowing costs. ___False__5. Borrowing costs can be capitalized when the asset is a qualifying asset and it is probable that the borrowing costs will result in future economic benefit to the entity but the costs cannot be measured reliably. _False_____6. All of the following should be considered a qualifying asset: a. A power generation plant that normally takes two years to construct. b. An expensive jet that can be purchased from a vendor. c. A toll bridge that usually takes more than a year to build. d. A ship that normally takes one to two years to complete. __False__7. Cessation of capitalisation is provided for in IAS 23 par. 20 _True____8. The IAS 23 on borrowing cost does not deal with actual or imputed cost of equity including preferred capital, not classified as a liability. _False___9. An entity is required to apply the standard on borrowing cost to a qualifying asset measured at fair value, for example a biological asset within the scope of IAS 41. __False__ 10. Paragraph 20 of IAS 23 provides that during extended period where companies suspend active developments of a qualifying asset, it shall continue the capitalisation of borrowing cost. Let’s Analyze (ULO m) Answer the following adapted problems: Activity 1. Getting acquainted with the essentials in computing and accounting treatment of borrowing costs, what also matters is you should also be able to solve and analyze problems on borrowing costs. Now, I will require you to answer this problem. Problem 2 (Adapted C. Valix, J. Peralta, C. Valix 2017 page 1169 Mildred Company borrowed 5,200,000 on a 10% note payable to finance a new warehouse which the entity is constructing for own use. The only other debt of the entity is a 7,800,000, 12% mortgage payable on an office building. At the end of the current year, average accumulated expenditures on the new warehouse totalled 6,175,000. What amount of interest should be capitalized for the current year? a. 520,000 b. 617,500 c. 637,000 d. 679,250 Problem 2.(Adapted C. Valix, J. Peralta, C. Valix 2017 page 1163) On January 1, 2017, Sheena Company borrowed 2,800,000 at an interest rate of 12% specifically for the construction of a new building. The actual interest cost on this specific borrowing was 336,000 but interest of 14,000 was earned from the temporary investment of the borrowing proceeds. Sheena company also had the following other loans in 2017 for general purposes but the proceeds were used in part for the construction of the building. 10% bank loan 12% long term loan Principal 4,200,000 7,000,000 Interest 420,000 840,000 The construction began on January 1, 2017 and was completed on December 31, 2017. The expenditures on the construction were 2,800,000 on Jan. 1, 1,400,000 on March 31 and 4,200,000 on Sept.30. Required: Compute the cost of the new building. 336,000-14000= 322,000 2800*12 =33,600,000 1,400,000*9 =12,600,000 4200,000*3 =12600,000 58,800,000/12=4900,000-2800,000=2100,000*.1125=236,250 1,260,000/11,200,000=.1125 = 2,800,000+1,400,000+4,200,000+ 322,000+ 236,250=8,958,250 Problem 3.(Adapted C. Valix, J. Peralta, C. Valix 2017 page 1163)Milott Company had the following borrowings during 2017. The borrowings were made for general purposes but the proceeds were used to finance the construction of a new building. 12% bank loan 14% long term loan Principal 3,900,000 6,500,000 Interest 468,000 910,000 The construction began on January 1, 2017 and was completed on Dec. 31, 2017. Expenditures on the building were 2600,000 on June 30 and 1,300,000 on December 31. Required: Compute the cost of the building. 1378000/10,400,000 2600*6 = 1300* =0 = 13.25 * 15,600,000/12 = 1300,000 = 172,250 1300,000 Answer= 172,250+2600,000+1300,000=4,072,250 Problem 4.(Adapted C. Valix, J. Peralta, C. Valix 2017 page 1164) Jewelry Company had the following outstanding loans during 2017 and 2018. Specific construction loan 3,600,000 10% General loan 30,000,000 12% The entity began the self-construction of a new building on January 1, 2017 and the building was completed on June 30, 2018. The following expenditures were made: January 1, 2017 April 1, 2017 December 1, 2017 March 1, 2018 4,800,000 6,000,000 3,600,000 7,200,000 Required: Compute for the cost of the building on December 31, 2017 and on June 30, 2018. 1. December 31, 2017 = 14400,000+ 1,080,000=15,480,000 4800*12 = 57600,000 6000*9 = 54,000,000 SB 3600,000*.10=360,000 3600*1 = 3600,000 115,200,000 /12= 9600,000 - 3600,000 =6000,000*.12 = 720,000 1,080,000 2. June 30, 2018 15,480,000*6/6 7200,000*4/6 = 15480,000+7,200,000+1,180,800=23,860,800 =15,4800,000 = 4800,000 20,280,0003600,000=16,680,000*.12=2,001,600*6/12=1000,800 SBC .10 *3600,000*6/12 = 180,000 1180,800 Problem 5.(Adapted C. Valix, J. Peralta, C. Valix 2017 page 1164)Macy company had the following loans outstanding for the entire year 2017. Specific construction loan 2,000,000 10% General Loan 40,000,000 12% The entity began the self construction of a building on January 1, 2017 and the building was completed on Dec.31, 2017. The following expenditures were made during the current year. January 1 2,000,000 July 1 4,000,000 November 1 6,000,000 Total 12,000,000 Required: Compute the cost the new building. 2000*12 = 24,000,000 4,000*6 = 24,000,000 6000*2 = 12,000,00 = 60,000,000/12=5,000,000 (2000,000) =3,000,000*.12=360,000+200, 000 = 560,000 +12,000,000 12,560,000 Intangible Assets Answer key Let’s Check (ULO a&b) Answer the following adapted problems: 1. An intangible asset is defined as a non monetary asset without physical substance. (True or False) True 2. All of the following should be capitalized as cost of trademark. a. Cost of successful litigation of the trademark b. Registration with Intellectual property code c. Design cost d. Legal fee Answer: False 3. When an entity develops a trademark, the costs directly related to securing it should generally be capitalized. All of the following costs associated with a trademark should be capitalized. (True or False) a. Attorney fees b. Consulting fees c. Research and development fees d. Design costs 4. A trademark is an example of which general category of intangible asset? Market Related 5. When a patent is amortized, the credit is usually made to the patent account. True 6. When an entity successfully defended a patent from infringement by a competitor, the cost of successful litigation should be charged to patent and amortized over the remaining useful life of the patent. False 7. It refers any creation or product of the human mind or intellect such as an invention, original design, practical application of a good idea, trademark, literary or artistic works. Intellectual Proprty 8. When normal earnings exceed future earnings, it is an indication of an unidentifiable intangible asset. False 9. A franchise is a market based type of intangible whereby there are two parties in a franchise agreement, the franchisee and the franchisor. (True or False) 10. On January 1, year 1, Leslie Company purchased a patent with a 5,200,000 and a useful life of 10 years. On December 31, year 2, determined that impairment indicators were present. The fair value less cost of disposal of the patent was estimated to be 3,600,000. The value in use is estimated to be 3,800,000. What amount should be reported as impairment loss for year 1? Answer: 5,200,000/10=520,000*2=1,040,000-5,200,000=4,160,0003,800,000=360,000IL 11. Young Company purchased for cash at 50 per share all 150,000 ordinary shares outstanding of another entity. The statement of financial position of the acquiree on the date of acquisition showed net assets with a carrying amount of 6,000,000. The fair value of property, plant and equipment on same date was 800,000 in excess of carrying amount. What amount should be recorded as goodwill on the date purchase? Answer: 50*150,000=7,500,000-6,800,000=700,000 12. At year end, Vans Company showed the following account balances: Patent 500,000 Deposit with advertising agency used to promote goodwill 400,000 Bond sinking fund 1,000,000 Excess of cost over fair value of identifiable net assets of acquired subsidiary 4,000,000 Trademark 900,000 What total amount should be reported as intangible assets? 5,400,000 Let’s Analyze (ULO c) Answer the following adapted problems: On January 1, year 1, Suzette Company signed a franchise agreement for a period of 20 years for an initial fee of 6,000,000. On the same date, the entity paid 2,000,000 which is not refundable and agreed to pay the balance in four equal annual payments of 1,000,000 at each year end. No future services are required are required of the franchisor. borrow at 14% for a loan of this type. Present value of 1 at 14% for 4 periods 0.59 Future amount of 1 at 14% for 4 periods Present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 at 14% for 4 periods The entity can 1.69 2.91 The agreement further provides that the franchisee shall pay a periodic fee of 5% based on the annual gross sales. During the current year, Suzette Company realized gross sales of 25,000,000 Prepare the journal entries for two years in connection with the franchise on the books of the franchisee. Required: Determine the initial measurement of the franchise and prepare the entries for the company for the first two years. Answer: Franchise 4,910,000 Initial measurement Discount on N/P 1,090,000 Cash Note payable 2,000,000 4,000,000 2.91*1,000,000=2,910,000+2,000,000=4,910,000 2,910,000-4,000,000=1,090,000 Cash 25,000,000 Sales 25,000,000 Franchise fee expense 1,250,000 Cash 1,250,000 Amortization of Franchise 245,500 Franchise Interest Expense 245,500 407,400 Discount on N/P 407,400 2,910,000*.14=407,400 YEAR 2 Amortization of Franchise 245,500 Franchise Interest expense 245,500 82,964 Discount on N/P 82,964 2,910,000-407,400=592,600*.14=82,964 Research And Development Let’s Check (ULO d) In each item below, put a checkmark if it is a research and development expense. Equipment acquired for use in various research __________ Depreciation on the equipment __________ Materials used __________ Compensation costs of personnel __________ Outside consulting fees __________ Indirect costs appropriately allocated __________ Modification to the formulation of a chemical product __________ Trouble-shooting in connection with breakdowns during Commercial production __________ Design of tools, jigs, molds and dies involving new technology__________ Seasonal or other periodic design changes to existing products __________ Laboratory research aimed at discovery of new technology __________ Let’s Analyze (ULO e) Answer the following adapted problems: 1. During the current year, Dangerous company incurred the following costs: Research and development services performed by another entity for Luminous 300,000 Design, construction and testing of preproduction prototype And model 400,000 Testing in search for new product or process alternative 350,000 What total amount should be reported as research and development expense in the current year? Answer: 1,050,000 2. Milby company incurred the following research and development costs during the current year: Equipment purchased for current and future projects 150,000 Equipment purchased for current project only 300,000 Research and development salaries of current project 600,000 Legal fees to obtain patent 75,000 Material and labor costs for prototype product 900,000 The equipment has a five-year useful life and is depreciated using the straight line method. What total amount should be recognized as research and development expense for current year? Answer: 300,000+900,000 + 600,000 + 150,000/5= 1,830,000 3. Squarepants company made the following expenditures relating to product Y. Legal costs to file a patent on Product Y. Production of the finished Product would not have been undertaken without the patent 75,000 Special equipment to be used solely for the development of Product Y The equipment has no other use and has an estimated useful life of 4 yrs 450,000 Labor and materials costs incurred in producing a prototype 1,500,000 Cost of testing the prototype 600,000 What total amount should be expensed when incurred? Answer: 450,000+ 1,500,000 + 600,000 =2,550,000