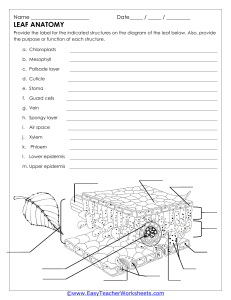
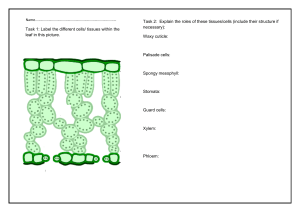
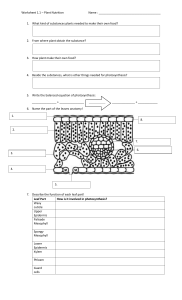
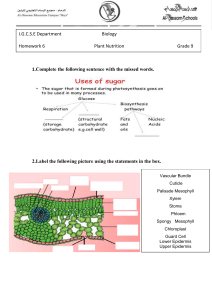
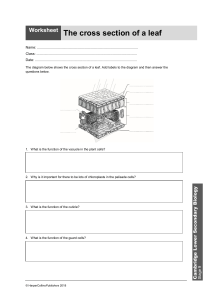
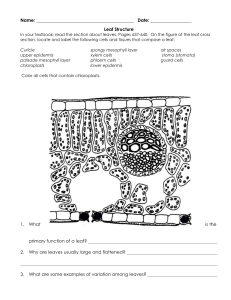
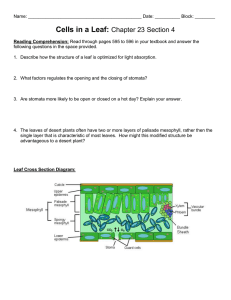
Name_________________________________________ Ms. Sameroff Class__________ Date______________ Objective: SWBAT describe how the structures of a leaf enables it to carry out photosynthesis. DO NOW ACTIVITY #1 Activity #2 Exit DO NOW Salad ingredients include lettuce, tomatoes, radishes, cucumbers, onions, bean sprouts, carrots, and celery. Botanists might look at a fresh salad and see plant organs. Think of salad ingredients you are familiar with. Decide whether they are roots, stems, or leaves and list them on the appropriate line below. Roots: __________________________________________________________________________________________ Stems: __________________________________________________________________________________________ Leaves: _________________________________________________________________________________________ VOCABUALARY- Use your worksheet to define the words below. Blade Thin, flatten portion of the leaf Petiole Mesophyll Palisade Mesophyll Spongy Mesophyll 1 ACTIVITY #1 Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. The leaf is the primary photosynthetic organ of the plant. It consists of a flattened portion, called the blade, that is attached to the plant by a thin stalk called the petiole. Sometimes leaves are divided into two or more sections called leaflets. Leaves with a single undivided blade are called simple, those with two or more leaflets are called compound leaves. The outer surface of the leaf has a thin waxy covering called the cuticle (A), this layer's primary function is to prevent water loss within the leaf. (Plants that leave entirely within water do not have a cuticle). Directly underneath the cuticle is a layer of cells called the epidermis (B). The vascular tissue, xylem and phloem are found within the veins of the leaf. Veins are actually extensions that run from to tips of the roots all the way up to the edges of the leaves. The outer layer of the vein is made of cells called bundle sheath cells (E), and they create a circle around the xylem and the phloem. In the picture, xylem is the upper layer of cells (G) and is shaded a little lighter than the lower layer of cells - phloem (H). Recall that xylem transports water and phloem transports sugar (food). Within the leaf, there is a layer of cells called the mesophyll. The word mesophyll is greek and means "middle" (meso) "leaf" (phyllon). Mesophyll can then be divided into two layers, the palisade layer (D) and the spongy layer (F). Palisade cells are more column-like, and lie just under the epidermis, the spongy cells are more loosely packed and lie between the palisade layer and the lower epidermis. The air spaces between the spongy cells allow for gas exchange. Mesophyll cells (both palisade and spongy) are packed with chloroplasts, and this is where photosynthesis actually occurs. Epidermis also lines the lower area of the leaf (as does the cuticle). The leaf also has tiny holes within the epidermis called stomata. Specialized cells, called guard cells (C) surround the stomata and are shaped like two cupped hands. Changes within water pressure cause the stoma (singular of stomata) to open or close. If the guard cells are full of water, they swell up and bend away from each other which opens the stoma. During dry times, the guard cells close. Questions: 1. What two tissues are found within a vein? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does the word "mesophyll" mean? _____________________________ 3. What two layers of the plant contain chloroplasts? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. The outermost layer of cells: ________________________________ 5. The waxy covering of the leaf: _______________________________ 6. These cells function to open and close stomata. _________________________ 7. Outer layer of the vein: ______________________________ 8. Column shaped cells that lie just under the epidermis. __________________________ 9. Openings that allow for gas exchange. _______________________________ 10. The stalk that connects the leaf to the stem. ______________________ 2 Activity #2 Part 1: Label the diagram of a leaf below, using the following information Part Description Stoma Vein Spongy Mesophyll Waxy Cuticle Upper Epidermis Palisade Cells Pores on the underside of the leaf. (opening for gas exchange) Contains the tissues that transport food and water. (Round) Layer of cells with air-spaces between them. Transparent layer on the top of the leaf. Single layer of flat cells covering the top surface of the leaf. Layer of long cylindrical cells just under the upper epidermis. (Contain Chloroplasts) Control the closing and opening of the stomatal pores. Single layer of flat cells covering the bottom surface of the leaf. Small structures within the cells where photosynthesis takes place. (oval shaped) Guard Cells Lower Epidermis Chloroplast HINT: Water goes into leaf from veins Oxygen and water vapor go out PART 2 – Which arrow shows… The movement of water in the leaf? ( A / B / C) The movement of oxygen and water vapour in the leaf? ( A / B / C) The movement of carbon dioxide in the leaf? ( A / B / C) 3 Regents Questions 1. Photosynthesis is the process by which A. the potential energy of simple sugars is transferred to ATP molecules B. simple sugars are gradually broken down to form lactic acid or alcohol C. two simple sugar molecules combine to form maltose and water D. light energy is converted into the chemical energy of simple sugars 2. Most of the oxygen gas present in the atmosphere is produced as a result of A. photosynthesis B. cellular respiration C. dehydration synthesis D. decomposition 3. Which phrase is an example of autotrophic nutrition? A. a cow eating grass in a field B. a mushroom digesting a dead log C. an apple tree making its own food D. a tapeworm feeding in the body of a dog EXIT TICKET After the lesson, now I understand… Something I still need help with… 4 5 EXIT TICKET After the lesson, now I understand… ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Something I still need help with… ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 6 7