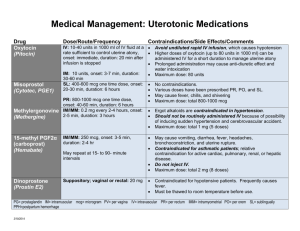
Onslow County - Camp Lejeune EMS System Medication Formulary D 1|Page Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 Contents 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE ..................................... 3 ACETAMINOPHEN ................................................. 6 ACTIVATED CHARCOAL ..................................... 7 ADENOSINE ............................................................ 8 ALBUTEROL SULFATE ......................................... 9 ALTEPLASE ........................................................... 10 AMIODARONE HCL ............................................. 11 ASPIRIN .................................................................. 13 ATROPINE SULFATE ........................................... 14 CALCIUM CHLORIDE.......................................... 15 CALCIUM GLUCONATE ..................................... 16 CEFAZOLIN ........................................................... 17 CEFTRIAXONE ..................................................... 18 ORAL GLUCOSE .................................................. 19 DEXTROSE 5% IN WATER ................................ 20 DEXTROSE 10% ................................................... 21 DILTIAZEM ........................................................... 22 DIPHENHYDRAMINE .......................................... 23 ENALAPRILAT ...................................................... 24 EPINEPHRINE ....................................................... 25 EPI 1:1,000 ............................................................. 26 EPI 1:10,000 ........................................................... 27 EPI 1:100,000 ......................................................... 28 EPI 1:500,000 ......................................................... 29 ETOMIDATE .......................................................... 30 FAMOTIDINE ........................................................ 31 FENTANYL CITRATE .......................................... 32 GLUCAGON ........................................................... 34 HEPARIN ................................................................ 35 HYDROMORPHONE HCL.................................... 36 HYDROXOCOBALAMIN ..................................... 37 IBUPROFEN ........................................................... 38 IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE ................................... 39 Revised April 2020 KETAMINE HCL ....................................................40 KETOROLAC TROMETHAMINE ........................42 LABETALOL HCL .................................................43 LACTATED RINGERS ..........................................44 LEVALBUTEROL HCL .........................................45 LEVETIRACETAM ................................................46 LIDOCAINE HCL ...................................................47 LOPERAMIDE HCL ...............................................48 LORAZEPAM .........................................................49 MAGNESIUM SULFATE ......................................50 METHYLPREDNISOLONE ...................................51 METOCLOPRAMIDE ............................................52 MIDAZOLAM HCL ................................................53 NALOXONE HCL ..................................................55 NERVE AGENT KIT ..............................................56 PRALIDOXIME CHLORIDE ................................ 57 NICARDIPINE HCL ...............................................58 NITROGLYCERIN .................................................59 NITROGLYCERIN SL .......................................... 60 NITROGLYCERIN PASTE ................................... 60 NITROGLYCERIN DRIP ...................................... 60 NITROUS OXIDE ...................................................61 NOREPINEPHRINE BITARTRATE .....................62 ONDANSETRON....................................................63 OXYGEN .................................................................64 OXYMETAZOLINE HCL ......................................65 OXYTOCIN .............................................................66 PROMETHAZINE HCL .........................................67 PROPOFOL .............................................................68 RANITIDINE HCL .................................................69 ROCURONIUM BROMIDE ...................................70 SODIUM BICARBONATE ....................................71 SUCCINYLCHOLINE CHLORIDE .......................72 TRANEXAMIC ACID ............................................73 Color code: Green=Adult Protocol/Dose; Orange=Pediatric Protocol/Dose; Blue=All Ages Protocol/Dose D 2|Page Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE Common names: Class: Action: Normal Saline, NS, 0.9%NaCl Isotonic Crystalloid Solution Contains 9 g/L sodium chloride, 154 mEq/L sodium and 154 mEq/L chloride, utilized as fluid and electrolyte replacement. Indications: Hypovolemia of numerous origins. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Pulmonary edema Side Effects: +Pulmonary/peripheral edema +Hypertension Special Considerations: In large amounts, other physiological electrolytes may become depleted. Large amounts of NS may contribute to acidosis Onset & Duration: Immediate Protocols & Dose: D Adult Asystole (AC1): 250mL IV/IO, qPRN, maximum 2L Bradycardia (AC2): 250mL-2L IV/IO, unless acute CHF, maximum 2L Chest Pain/STEMI (AC4): *pearl: 250-500mL as pre-cath hydration Allergic Reaction (AM1): 500mL IV/IO, qPRN, maximum 2L Adult Diabetic (AM2): 250mL IV/IO, qPRN. Then infuse 150mL/hr Dialysis/Renal Failure (AM3): 250mL, qPRN, max 1L if lungs remain clear Hypotension/Shock (AM5): Bolus 250mL IV, repeat to effect SBP > 90, 2L Maximum Hemorrhagic Shock?: 250mL each bolus, 1L maximum Newly Born (AO2): 10mL/kg IV/IO, may repeat x 1 Pediatric Asystole (PC1): 20mL/kg IV/IO, qPRN, maximum 60mL/kg Pediatric Bradycardia (PC2): 20mL/kg IV/IO, qPRN x3, max 60mL/kg Pediatric Allergic Reaction (PM1): *pearl: Fluids titrated to maintain a SBP >70 + (2xAge) Pediatric Diabetic (PM2): 10-20mL/kg IV/IO, if s/s of metabolic compromise, maximum 20ml/kg Pediatric Hypotension/Shock (PM3): *Cardiogenic 5-10mL/kg IV/IO, titrate to age appropriate SBP ≥ 70 + (2xAge) Maximum 10mL/kg *Hypovolemic/Distributive/Obstructive 20mL/kg IV/IO, titrate to age appropriate SBP ≥ 70 + (2xAge) *Hypovolemic Shock 20mL/kg IV/IO, qPRN 3|Page Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 Revised April 2020 Scene Rehabilitation Responder (SO2): 500mL IV/IO, Maximum 2L, Titrate to HR ≤ 100 and SBP ≥ 100mmHg Radiation Incident (TB7): *Eye involvement Irrigate involved eye(s) for 15-30 min, qPRN *Chemical exposure/burn Flush contact area for 15 min Hyperthermia (TE4): (Adult) 500mL IV/IO, repeat to SBP> 90; Maximum 2L (Pedi) 20mL/kg IV/IO, repeat to SBP> 70+ (2xAge) Maximum 60mL/kg Hypothermia (TE5): (Adult) 500mL IV/IO, repeat to SBP > 90, Maximum 2L (Pedi) 20mL/kg IV/IO, repeat to SBP ≥ 70 + (2xAge) Maximum 60mL/kg Abdominal Pain/Vomiting & Diarrhea (UP3): (Adult) 250mL, qPRN to SBP ≥ 90; Maximum 2L (Pedi) 20mL/kg, qPRN to SBP ≥ 70 + (2xAge); Maximum 60mL/kg Syncope (UP16): (Adult) 250mL Bolus, qPRN, Titrate SPB ≥ 90mmHg, Maximum 2L (Pedi) 20mL/kg IV/IO, qPRN to SBP ≥ 70 + (2xAge), Maximum 60mL/kg Back Pain (UP5): (Adult) Bolus 250mL IV, Titrate to SBP ≥ 90, Maximum 2L (Pedi) 20mL/kg IV/IO, Titrate to SBP ≥ 70 + (2xAge) Maximum 60mL/kg Behavioral (UP6): (Adult) 500mL Bolus IV/IO, then 150-200mL/hr, May repeat 500mL Bolus as needed, Maximum 2L (Pedi) 20-60mL/kg IV/IO, Maximum 60mL/kg Suspected Sepsis (UP15): (Adult) 30ml/kg, qPRN to SBP ≥ 90mmHg, MAP > 65mmHg (Pedi) 30mL/kg IV/IO, qPRN to SBP ≥ 70 + (2xAge) D 4|Page Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 3% SODIUM CHLORIDE Common Names: Class: Action: Hypertonic Saline, 3% NaCl Hypertonic Crystalloid Solution Hypertonic fluids contain a higher concentration of solute compared to plasma and interstitial fluid; this creates an osmotic gradient and drives fluid from the interstitial space into the intravascular space. This increase in intravascular volume increases mean arterial pressure (MAP), stroke volume (SV), and cardiac output (CO) when compared with equal volumes of normal saline or other isotonic fluids. There is also a significant increase in end-diastolic pressure and a subsequent decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance. Hypertonic saline requires less overall volume administered to achieve similar plasma volumes as larger volumes of normal saline. Hypertonic saline increases the osmolarity of the blood, which allows fluid from the extravascular space to enter the intravascular space, which leads to decreases in brain edema, improved cerebral blood flow, and decreased CSF production. Indications: -Hyponatremia -Increased ICP Contraindications: -Pediatrics -Administered IV ONLY, NO IO administration Side Effects: +Hypernatremia +Metabolic Acidos +Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome Considerations: Caution is necessary with hypertonic saline in patients with congestive heart failure or renal insufficiency due to their already increased fluid and sodium loads. Pregnancy Category C. Onset & Duration: Immediate onset with estimated duration of 2-4 hours. Protocols & Dose: Head Trauma (TB5) 100mL infused over 10 minutes, IV ONLY Follow on infusion of 400mL over 50 minutes D 5|Page Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ACETAMINOPHEN Common names: Class: Action: Tylenol®, APAP, MAPAP Non-narcotic analgesic, antipyretic Inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins that may serve as mediators of pain, antipyretic effect via direct action on the hypothalamus. Indications: Used for fever ≥ 100.4* F and pain of mild, moderate, or severe intensity (alone or in combination with opioids). May be preferred over NSAIDs due to fewer hematologic, gastrointestinal, and renal effects. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Liver impairment/failure, -Active hepatitis infection Side Effects: +Nausea/vomiting +Constipation +Allergic reactions +Abdominal pain Special Considerations: Use caution in patients with obstructive pulmonary disease Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, peaking 1-2 hours, duration 3-4 hours Protocols & Dose: Scene Rehabilitation Responder (SO2): 1000mg PO Fever/Infection (UP10): (Adult) 325-1000mg PO, Liver Disease: Max 600mg (Pedi) 15mg/kg PO/PR *PR Tylenol Dosing (Adult) 1000mg (Pedi) 15mg/kg Pain Control (UP11): 15mg/kg (325-1000mg typical adult) Maximum 1000mg Repeat & Max: D May repeat every 4-6 hours as needed Max 1000mg/dose or 4000mg/day if pt is ≥ 60kg Max 1000mg/dose or 75mg/kg/day if pt is ≤ 60kg 6|Page Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ACTIVATED CHARCOAL Class: Action: Absorbent Activated charcoal is a fine black powder that binds and adsorbs ingested toxins within the GI tract. It is commonly combined with a laxative, such as sorbitol, which increases gastric motility, so the body may excrete the toxin quickly and reduce constipation. Indications: Used for pts who have overdosed on oral medications/substances, or ingested oral poisons/toxins less than one hour ago, that pose potential harm. Use in intubated pts via NG tube is only advised when ingestion confirmed ≤ 1 hour and substance is lethal. Contraindications: -Ingestion of strong corrosive, caustic, or petroleum solutions. Side Effects: +Nausea/vomiting +constipation/diarrhea Special Considerations: Will stain any surface including skin and clothing. Precipitous within bottle may settle into a mass when stored upright, making it difficult to administer. Shake well prior to administering, consider storing on its side. Onset & Duration: Immediate within the GI tract until excreted, typically within 6-8 hours Protocols & Dose: D Overdose/Toxic Ingestion (TE7): 1g/kg PO *pearl: Give NG if substance is KNOWN to be adsorbed, and airway secured by intubation 7|Page Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ADENOSINE Common names: Class: Action: Adenocard® Antiarrhythmic Adenosine produces electrophysiologic changes by stimulating adenosine-sensitive potassium channels in the atrial and sinoatrial node, causing an outward flow of potassium from the cardiac myocytic membrane, which also reduces the action potential of atrioventricular cells, resulting in atrioventricular nodal blockade and reduction of accessory-pathway antegrade refractoriness. Indications: Symptomatic tachycardic rhythms with a pulse. While adenosine is effective at converting SVT rhythms due to accessory pathways, it can also be an effective "diagnostic aid" in wide complex and atrial tachycardias, although it is ineffective at managing them. Contraindications: -Sick sinus syndrome -Bradycardia -Hypersensitivity -2nd and 3rd degree heart block Side Effects: +Facial flushing +Lightheadedness +Arrhythmias +Headache +Diaphoresis +Palpitations +Chest Pain +Hypotension +Shortness of breath +Nausea +Transient/Prolonged asystole Special Considerations: May produce bronchoconstriction in patients with severe asthma or bronchopulmonary disease. The half-life is relatively short, ≤ 10 seconds. Therefore, a proximal, large-bore IV site is preferred, followed by a 20 mL flush to assist in timely delivery to myocardial cells. Onset & Duration: Successful administration will result in rhythm changes within seconds. Although the drug’s half-life is short, successful conversion to a sinus rhythm usually lasts. Other atrial/ventricular rhythms may slow enough to allow a diagnostic view before resuming the initial rate. Protocols & Dose: Adult Tachycardia (narrow/reg:AC6)(wide/reg:AC7): 6mg IV/IO Rapid push with flush, May repeat 12mg IV/IO May repeat 12mg IV/IO Pediatric Tachycardia (PC5): 0.1mg/kg IV/IO, Maximum 6mg, May repeat 0.2mg/kg IV/IO, Maximum 12mg D 8|Page Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ALBUTEROL SULFATE Class: Action: Sympathomimetic bronchodilator Selective beta2-adrenergic agonist that stimulates receptors of the smooth muscle in the lungs, uterus, and vasculature supplying skeletal muscle. Indications: Acute bronchospasms associated with obstructive airway disease; moderate to severe allergic reaction; symptomatic hyperkalemia with peaked T-waves and widened QRS, secondary to renal failure or crush syndrome. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Severe Tachycardia Side Effects: +Restlessness +Anxiety +Palpitations +Transient rise in BP +Tachycardia +Dry mouth +Nausea/Vomiting Special Considerations: Sympathomimetics may precipitate adverse cardiovascular effects Onset & Duration: Onset 5-15 minutes, peak 60-90 minutes, duration 3-6 hours Protocols & Dose: Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis (AM1): Pediatric Allergic Reaction (PM1): 2.5-5mg via nebulizer, qPRN Adult COPD/Asthma (AR4): 2.5-5mg via nebulizer, qPRN Pediatric Asthma (AR7): 1.25-2.5mg via nebulizer, qPRN x3 *pearl (≤1yr=1.25mg; 1–6yrs=1.25–2.5mg; 6–14yrs=2.5mg; ≥ 15yrs=2.5–5mg) Dialysis/Renal Failure (AM3): 2.5-5mg via nebulizer Crush Syndrome (TB3): 2.5-5mg via nebulizer, qPRN x3 D 9|Page Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ALTEPLASE Common names: Class: Action: Activase®, t-PA Fibrinolytic Alteplase exerts its action on the endogenous fibrinolytic system to convert plasminogen to plasmin by directly hydrolyzing the arginine-valine bond in plasminogen. Plasmin degrades fibrin and fibrinogen as well as the procoagulant factors V and VIII. Unlike streptokinase or urokinase, most of the activity of alteplase is dependent on the presence of fibrin. Minimal amounts of plasminogen are converted to plasmin in the absence of fibrin. Upon binding to fibrin, the one-chain form of t-PA is converted to the two-chain form. Both forms have similar fibrinolytic and plasminogen-activating potential; however, the one-chain t-PA is considerably less active in the absence of fibrin. Alteplase that is bound to fibrin acquires a high affinity for plasminogen, which is responsible for an increased activity at the fibrin surface compared to the circulation. Indications: t-PA is utilized when conducting interfacility transfer of suspected stroke pts only when the referring facility has initiated bolus and/or maintenance infusion. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Angioedema +Bleeding +Bradycardia +Arrhythmia +Laryngeal edema +Pulmonary edema +AV block Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with severe, uncontrolled hypertension. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, duration 10 min after cessation of infusion. Protocols & Dose: D Suspected Stroke Activase/t-PA- Interfacility (AM6): Verify bolus dose, Verify total dose. Stop/Continue infusion as appropriate. 10 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 AMIODARONE HCL Common names: Class: Action: Cordarone® Antiarrhythmic Although the exact mechanism is unknown, amiodarone is known to act on the myocardium to delay repolarization and increase the duration of the action potential without significantly altering conduction. Eliminated by hepatic metabolism. Indications: Ventricular arrhythmias or wide complex tachycardia with or without a pulse Contraindications: Iodine sensitivity as amiodarone incorporates iodine into its chemical structure -Cardiogenic shock -Hypotension/Hypovolemia -Bradycardia -Prolonged QT -Second/Third degree heart block Side Effects: +Peripheral vasodilation +Hypotension +Bradycardia +Prolonged QT +Respiratory Distress +Arrhythmias +Angioedema +Headache +Dizziness +Nausea/Vomiting Special Considerations: Use with caution in pts already on beta-blocker therapy as it may cause severe bradycardia. When diluting, amiodarone should be mixed with D5W and not NS due to its incompatibility. Diluted concentrations are safe to store and administer in polyvinyl chloride or polyolefin tubing/bags for up to 24 hours, causing no concern for prehospital administration. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, short duration with serum concentrations dropping to 10% within 30-45 minutes D 11 | P a g e Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 Protocols & Dose: Revised April 2020 Adult Tachycardia (Narrow/Reg:AC6): 150mg in 100mL of D5W, IV/IO, Infuse over 10 minutes May repeat if narrow complex tachycardia recurs. 450mg in 250mL of D5W, 1mg/min (33mL/hr) Adult Tachycardia (Wide/Reg/Mono:AC7) 150mg in 100mL of D5W, IV/IO, Infuse over 10 minutes. May repeat if wide complex tachycardia recurs. 450mg in 250mL of D5W, 1mg/min (33mL/hr) Adult Tachycardia (Wide/Irreg/Monomorphic:AC7): 150mg in 100mL of D5W IV/IO, Infuse over 10 minutes May repeat if wide complex tachycardia recurs. 450mg in 250mL of D5W, 1mg/min (33mL/hr) V-Fib /Pulseless V-Tach (AC8): 300mg IV/IO If refractory: May repeat 150mg IV/IO Pediatric Tachycardia (PC5): 5mg/kg IV/IO over 20-60 minutes Maximum single dose 300mg May repeat x2, Maximum total dose of 15mg/kg. Pediatric V-Fib/Pulseless V-Tach (PC6): Pediatric Post Arrest (PC7): 5mg/kg IV/IO (single dose Maximum 300mg) May repeat x2 Maximum total dose of 15mg/kg D 12 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ASPIRIN Common names: Class: ASA, Acetylsalicylic acid Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID), anti-platelet aggregator, analgesic, antipyretic Action: Inhibits cyclooxygenase, which is responsible for prostaglandin synthesis associated with pain, fever and inflammation. Inhibits platelet aggregation by acetylating cyclooxygenase permanently disabling cellular function so that it cannot synthesize prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Since thromboxane is important in clotting, its absence does not allow blood to clot effectively. Indications: Chest pain/STEMI, treatment of mild pain. Contraindications: -Not for pediatrics ≤ 15 yrs old due to risk of Reye’s Syndrome -GI Bleed/Ulcer -Bleeding disorders -Hypersensitivity -Pregnancy -Head trauma/stroke -Renal failure Side Effects: +Abdominal Pain +Nausea/Vomiting +Prolonged bleeding +Heartburn +Shortness of breath Special Considerations: Use with caution with pts known to have ASA/NSAID sensitive asthma Onset & Duration: Onset 5-30 min, peak in 15 min-2 hrs, duration 1-4 hrs Protocols & Dose: Chest Pain: Cardiac/STEMI (AC4): 81mg x 4 PO (chewed) Or 325mg PO Pain Control (UP11): (≥16 only) 324-650mg PO D 13 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ATROPINE SULFATE Class: Action: Parasympatholytic/Anticholinergic Atropine is a potent parasympatholytic, that inhibits the actions of acetylcholine at the postganglionic parasympathetic neuroeffector sites. Small doses inhibit salivary and bronchial secretions; moderate doses decrease GI motility, inhibit gastric acid secretion, and may block nicotinic receptor sites at the autonomic ganglia and at the neuromuscular junction. Blocks vagal impulses, thereby increasing SA node discharge and enhancing AV conduction resulting in positive chronotropic and dromotropic effects without and inotropic effects. Indications: Symptomatic bradycardia Contraindications: -A-Fib/A-Flutter -Tachycardia -Glaucoma -Cardiovascular compromise due to hypovolemia -Second/third degree heart block due to ineffectiveness Side Effects: +Pupil dilation +Tachycardia +Headache +Dry mouth Special Considerations: Use caution in suspected MI as increased cardiac demand will precipitate increased injury of the myocardium. Adverse effects may be seen when administered with other cholinergic agents, digitalis, antihistamines, procainamide, antidepressants, and benzodiazepines. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, peak in 2-4 min, half-life 2-3 hrs Protocols & Dose: Bradycardia (AC2): 0.5mg IV/IO, q3-5 minutes, maximum 3mg Pediatric Bradycardia (PC2): 0.02mg/kg IV/IO, May repeat x 1 Minimum single dose: 0.1mg Maximum single dose: 0.5mg WMD-Nerve Agent (TE8): *See nerve agent kit for dosing instructions *If nerve agent kit is unavailable, dose atropine accordingly (Adult) 2mg IV/IO/IM, q3-5 min until symptoms resolve (Pedi) See Pearls, IV/IO/IM, q3-5 minutes until symptoms resolve *pearl: ≤ 40 lbs (18 kg) = 0.5mg 40-90 lbs (18-40 kg) = 1mg ≥ 90 lbs (≥ 40 kg) = 2mg D 14 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 CALCIUM CHLORIDE Class: Action: Electrolyte Replaces elemental calcium, which is essential for regulating excitation threshold of nerves and muscles. Calcium is also essential for blood clotting mechanisms, maintenance of renal function, and bone tissues. Calcium increases myocardial contractile force and ventricular automaticity making it a strong inotropic agent. Additionally, it serves as an antidote for magnesium sulfate and calcium channel blocker toxicity. Calcium chloride has three times as much elemental calcium than calcium gluconate. Indications: Calcium channel blocker overdose, cardiac arrest in pts with known renal failure/dialysis, acute hyperkalemia/hypocalcemia with peaked T-waves w/ widened QRS in dialysis and crush syndrome pts, Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Renal/cardiac insufficiency -Patients taking digitalis -Hypercalcemia -V-fib Side Effects: +Arrhythmias including bradycardia or cardiac arrest +Syncope +Nausea/vomiting +Hypotension +Necrosis with extravasation Special Considerations: Calcium chloride will precipitate when used in conjunction with sodium bicarbonate, Toxicity with digitalis, and may antagonize the effects of calcium channel blockers. Onset & Duration: Onset and peak are immediate. Protocols & Dose: Dialysis/Renal Failure (AM3): 1g IV/IO Crush Syndrome (TB3): (Adult) 1g IV/IO (Pedi) 20mg/kg IV/IO Give over 2-3 minutes Overdose/Toxic Ingestion (TE7): (Adult) 1g IV/IO (Pedi) 20mg/kg IV/IO Give over 2-3 minutes D 15 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 CALCIUM GLUCONATE Class: Action: Electrolyte Replaces elemental calcium, which is essential for regulating excitation threshold of nerves and muscles. Calcium is also essential for blood clotting mechanisms, maintenance of renal function, and bone tissues. Calcium increases myocardial contractile force and ventricular automaticity making it a strong inotropic agent. Additionally, it serves as an antidote for magnesium sulfate and calcium channel blocker toxicity. Calcium gluconate has three times less elemental calcium than calcium chloride. Indications: Calcium channel blocker overdose, cardiac arrest in pts with known renal failure/dialysis, acute hyperkalemia/hypocalcemia with peaked T-waves w/ widened QRS in dialysis and crush syndrome pts, Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Renal/cardiac insufficiency -Patients taking digitalis -Hypercalcemia -V-fib Side Effects: +Arrhythmias including bradycardia or cardiac arrest +Syncope +Nausea/vomiting +Hypotension +Necrosis with extravasation Special Considerations: Calcium gluconate will precipitate when used in conjunction with sodium bicarbonate, Toxicity with digitalis, and may antagonize the effects of calcium channel blockers. Onset & Duration: Onset and peak are immediate. Protocols & Dose: Dialysis/Renal Failure (AM3): 2g IV/IO Crush Syndrome (TB3): 2g IV/IO Overdose/Toxic Ingestion (TE7): 2g IV/IO D 16 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 CEFAZOLIN Common names: Class: Action: Ancef® Cephalosporin antibiotic It inhibits the third and final stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis by preferentially binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) that are located inside the bacterial cell wall. Like all beta-lactam antibiotics, its ability to interfere with PBPmediated cell wall synthesis ultimately leads to cell lysis. Indications: Adult pts (≥18 years old) presenting with open fractures. Contraindications: -Severe penicillin allergy -Cephalosporin/Cephamycin hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Angioedema +Dizziness +Anaphylaxis +Nausea/Vomiting +Diarrhea +Bleeding Special Considerations: Provider should attempt to collect blood labs prior to administering the antibiotic if such action won’t delay care. Cephalosporins may precipitate increased bleeding, use caution when administering to pts on anticoagulant therapies. Reconstitute vial with 10 mL of NS. May be given IV over 3-5 minutes or added to 100 mL NS bag for infusion over 5 minutes. Onset & Duration: Peak serum levels are reached soon after IV administration, elimination half-life ~1.8 hours. Protocols & Dose: D Extremity Trauma (TB4): (≥18 years old) 1g IV/IO over 3-5 minutes 17 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 CEFTRIAXONE Common names: Class: Action: Rocephin® Cephalosporin antibiotic It inhibits the third and final stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis by preferentially binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) that are located inside the bacterial cell wall. Like all beta-lactam antibiotics, ceftriaxone's ability to interfere with PBP-mediated cell wall synthesis ultimately leads to cell lysis. Indications: Pts presenting with symptoms of sepsis or CNS infections, meeting systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) criteria, extremity amputation and/or open fractures. Contraindications: -Severe penicillin allergy -Cephalosporin/Cephamycin hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Bronchospasms +Angioedema +Anaphylaxis +Nausea/Vomiting +Shortness of breath +Diarrhea +Flushing +Abdominal pain +Rash +Bleeding Special Considerations: Cannot be administered/reconstituted with any calcium products including LR Provider should attempt to collect blood labs prior to administering the antibiotic if such action won’t delay care. Ceftriaxone may precipitate an elevated INR in pts on warfarin, consider risk/benefit prior to administration. Onset & Duration: IM route delayed peak 1.5-4 hrs while IV route has rapid onset, peak 30 min; elimination exceeds 24 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Repeat & Max: D Suspected Sepsis (UP15): 50mg/kg up to 1g, IV/IO/IM *CNS Infections: 100mg/kg, Maximum 2g **Reconstitute in 3ml NS. Administer IM route in deep gluteal** Pt can receive a repeat dose in 12-24 hrs, not to exceed 4g/day for adults, and 2-4 g/day for infant through adolescents. 18 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ORAL GLUCOSE Class: Action: Carbohydrate Dextrose (aka. glucose) is one of the basic building blocks of all sugars. Glucose is a monomer and is therefore readily processed in the blood. Through glycolysis glucose is turned into pyruvate giving off a small amount of chemical energy (ATP). Insulin turns excess glucose into glycogen when blood sugars are high. Glucose is a large molecule that forms a ring, this structure is incapable of being absorbed into a cell without a mediator (insulin) and therefore increases damage to epithelium as it floats through the blood stream. It also causes an osmotic pressure as concentrations vary across membranes, the pressure is less with lower concentrated solutions. Indications: Blood glucose ≤ 69 in an awake pt with the ability to protect their airway. Contraindications: -Hyperglycemia -Inability to swallow Side Effects: +Hyperglycemia +Airway compromise Special Considerations: Disable/disconnect pt’s insulin pump prior to administering glucose solutions to correct hypoglycemia. When hypoglycemia is corrected, pt must consume protein/carbohydrate foods to maintain blood glucose levels. Onset & Duration: Rapid absorption. Protocols & Dose: Adult Diabetic (AM2): Consider Oral Glucose Solution if available (1 tube=15 grams) Pediatric Diabetic (PM2): ½ to 1 Tube If age appropriate D 19 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 DEXTROSE 5% IN WATER Common names: Class: Action: D5W Carbohydrate Dextrose (aka. glucose) is one of the basic building blocks of all sugars. Glucose is a monomer and is therefore readily processed in the blood. Through glycolysis glucose is turned into pyruvate giving off a small amount of chemical energy (ATP). Insulin turns excess glucose into glycogen when blood sugars are high. Glucose is a large molecule that forms a ring, this structure is incapable of being absorbed into a cell without a mediator (insulin) and therefore increases damage to epithelium as it floats through the blood stream. It also causes an osmotic pressure as concentrations vary across membranes. The pressure is less with D5 and D10, therefore they are used in pediatrics. Indications: For use in the administration and dilution of medications not compatible with other agents. Contraindications: -Hyperglycemia -Suspected stroke Side Effects: +Hyperglycemia +Tissue necrosis with extravasation Special Considerations: Ensure patent IV/IO site to avoid tissue necrosis. Onset & Duration: Rapid absorption Protocols & Dose: Adult Tachycardia (Narrow/Reg: AC6): Adult Tachycardia (Wide/Reg/Monomorphic: AC7): Adult Tachycardia (Wide/Irreg/Monomorphic: AC7): *as adjunct for amiodarone administration only 100mL of D5W IV/IO (initial and repeat dose) 250mL of D5W (maintenance dose) Pediatric Tachycardia (PC5) Pediatric V-fib/Pulseless V-tach (PC6) Pediatric Post Resuscitation (PC7) *as adjunct for amiodarone administration only 100mL of D5W IV/IO (initial and repeat dose) 250mL of D5W (maintenance dose) D 20 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 DEXTROSE 10% Common names: Class: Action: D10 Carbohydrate Dextrose (aka. glucose) is one of the basic building blocks of all sugars. Glucose is a monomer and is therefore readily processed in the blood. Through glycolysis glucose is turned into pyruvate giving off a small amount of chemical energy (ATP). Insulin turns excess glucose into glycogen when blood sugars are high. Glucose is a large molecule that forms a ring, this structure is incapable of being absorbed into a cell without a mediator (insulin) and therefore increases damage to epithelium as it floats through the blood stream. It also causes an osmotic pressure as concentrations vary across membranes. The pressure is less with D5 and D10, therefore they are used in pediatrics. Indications: Blood glucose ≤ 69 with the inability to consume oral solutions. Contraindications: -Hyperglycemia -Suspected stroke Side Effects: +Hyperglycemia +Tissue necrosis with extravasation Special Considerations: Ensure patent IV/IO site to avoid tissue necrosis. Disable/disconnect pt’s insulin pump prior to administering glucose solutions to correct hypoglycemia. When hypoglycemia is corrected, pt must consume protein/carbohydrate foods to maintain blood glucose levels. Onset & Duration: Rapid absorption Protocols & Dose: Adult Diabetic (AM2): 100mL IV/IO D10 repeat doses: 150mL IV/IO May repeat until Blood Glucose is ≥ 80mg/dL or patient’s normal range Pediatric Diabetic (PM2): 2.5ml/kg IV/IO Repeat as needed until mental status improves or Patient’s normal range D 21 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 DILTIAZEM Common names: Class: Action: Cardizem® Calcium channel blocker Calcium channels in myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes are selective and allow a slow, inward flow of calcium that contributes to excitationcontraction coupling and electrical discharge (plateau phase of the action potential) of conduction cells in the heart and vasculature. Diltiazem inhibits this influx, possibly by deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The resultant decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells, resulting in dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries and improved oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue. In addition, total peripheral resistance, systemic blood pressure, and afterload are decreased. Indications: Symptomatic atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, or SVT Contraindications: -Sick sinus syndrome -Hypotension -Second/Third degree heart block -WPW and other accessory pathway reentry tachycardias Side Effects: +Headache +Constipation +Rash +Nausea +Nausea +Flushing +Edema +Drowsiness +Hypotension +Dizziness Special Considerations: Diltiazem prolongs AV node refractory periods without significantly prolonging sinus node recovery time, except in patients with sick sinus syndrome. Concomitant use of diltiazem with beta-blockers or digitalis may result in additive effects on cardiac conduction Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, half-life 4-6 hours Protocols & Dose: D Adult Tachycardia (Narrow/Reg:AC6)(Narrow/Irreg:AC6): 0.25mg/kg IV/IO, Over 2-3 minutes, Maximum 25mg *If no improvement: 5-15mg/hr IV/IO Infusion *If No Improvement in 15 minutes: 0.35mg/kg IV/IO Bolus; Maximum 25mg 22 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 DIPHENHYDRAMINE Common names: Class: Action: Benadryl® Antihistamine, anticholinergic Diphenhydramine blocks the effects of Histamine (H1 histamine) on the H1 receptor site through a competitive competition for the peripheral H1 site. When diphenhydramine is bound the H1 site cannot be stimulated preventing the effects of histamines (swelling, etc...). As an H1 blocker diphenhydramine blocks the effects of H1 on its receptor in the cortex as well this causes a change in the cortex neural potassium channels causing neurons in the cortex to have a higher threshold to depolarize. This results in an increase in sedation as a result of the H1 block. As an antihistamine, diphenhydramine one of the most effective antihistamine. Indications: Mild to severe allergic reactions and dystonia; nausea/vomiting refractory to antiemetics; Behavioral emergencies where the pt has aggression, violence, or agitation that creates a threat to themselves or others. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Seizures +Hypotension +Sinus tachycardia +Sedation Special Considerations: Can be a powerful CNS depressant and work to potentiate other sedatives. Onset & Duration: Onset within 15 min when given IV, peak 1-4hrs, half-life 2-10hrs Protocols & Dose: Allergic Reaction (AM1): 25-50mg PO/IV/IM/IO, if not already given PO Pediatric Allergic Reaction (PM1): 1mg/kg IV/IM/IO/PO, if not already given PO Abdominal Pain Vomiting & Diarrhea (UP3): (Adult) 25-50mg IV/IM (Pedi) 1mg/kg IV/IM; (Must be ≥ 3 months old) Behavioral (UP6): *pearl: for extrapyramidal reactions (dystonia) (Adult) 50mg IV/IO/IM/PO (Pedi) 1mg/kg IV/IO/IM/PO D 23 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ENALAPRILAT Common names: Class: Action: Vasotec®, Enalapril Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor Enalapril competes with the natural substrate, angiotensin I, thereby inhibiting its conversion to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor and a negative feedback mediator for renin activity. Thus, when enalapril lowers angiotensin II plasma levels, blood pressure decreases and plasma renin activity increases. Indications: Moderate to severe pulmonary edema secondary to hypertension. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -History of angioedema with any ACE inhibitor -Pregnancy -Hypotension Side Effects: +Bradycardia +Angioedema +Bronchospasms +Tachycardia +Anaphylaxis +Hypotension +Chest pain +Shortness of breath Special Considerations: Toxicity is more likely in pts suffering from renal impairment. Pts suffering severe volume depletion, on high dose diuretic therapy, hyponatremia, or recent dialysis may suffer excessive hypotension after administration, use caution. Onset & Duration: Effects seen within 15 min, peak occurring 1-4 hrs with effects lasting up to 6 hrs, half-life approximately 11 hrs. Protocols & Dose: D CHF/Pulmonary Edema (AC5): 1.25mg IV/IO, given over 5 minutes 24 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 EPINEPHRINE Class: Action: Sympathomimetic, endogenous catecholamine Epinephrine has complex target organ effects. It is a potent agonist at both alpha- and beta- receptors throughout the body except for the sweat glands and facial arteries. Epinephrine is a nonselective adrenergic agonist; it stimulates alpha1-, alpha2-, beta1, and beta2-adrenergic receptors, although the degree of stimulation at these receptors may vary depending on the dose administered. Stimulation of alpha1-receptors by epinephrine leads to arteriolar vasoconstriction. Stimulation of presynaptic alpha2receptors inhibits norepinephrine release via negative feedback while stimulation of post-synaptic alpha2-receptors also leads to arteriolar vasoconstriction. Stimulation of beta1-receptors induces a positive chronotropic and inotropic response. Stimulation of beta2-receptors by epinephrine leads to arteriolar vasodilation, bronchial smooth muscle relaxation, and increased glycogenolysis. Indications: Cardiac arrest, bradycardia, moderate to severe allergic reaction, severe hypotension, reactive airway disease refractory to bronchodilators, and stridor/croup. Contraindications: -None in life threatening situations Side Effects: +Tachycardia +Hypertension +Arrhythmia +Palpitations +Chest pain +Anxiety +Diaphoresis +Myocardial infarction Special Considerations: Use caution in pts suffering hypertension/tachycardia, those with a history of cardiovascular disease, or elderly pts > 65, consider reducing IM dose by half. Onset & Duration: IV route has immediate onset with short half-life < 5 min, continuous infusion achieves steady peak state within 10-15 min. IM route offers rapid onset, peak at 6-10 min, half-life 15-20 min. Study shows IM absorption is more rapid at anterolateral thigh as opposed to deltoid due to increased blood flow. Nebulized/inhaled epi causes bronchodilation in under 1 min. ET absorption is unpredictable. D 25 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 EPI 1:1,000 Concentration: 1mg/mL = 1000mcg/mL Protocols & Dose: Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis (AM1): Autoinjector if available 0.3-0.5mg if available IM; q5 minutes x1 if no improvement *EMTB* Contact Med Control for repeat doses of Epi 1:1 Pedi Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis (PM1): ≥30kg: Adult Epi Pen IM if available <30kg: Epi Pen Jr IM if available ≥30kg: 0.3-0.5 mg IM <30kg: 0.01mg/kg Repeat x1 in 5 minutes if no improvement *EMTB* Contact Med Control for repeat doses of Epi 1:1 Adult COPD/Asthma (AR4): 0.3-0.5mg IM *Stridor Nebulize 1mg in 2mL NS, May repeat x 1 Pedi Asthma/Respiratory Distress (AR7):) 0.01mg/kg IM, Maximum 0.3mg *Stridor Nebulize 1mg in 2mL NS, May repeat x 1 Pedi Asystole/PEA (PC1): Pedi V-Fib/Pulseless V-Tach (PC6): 0.1mg/kg ETT, Maximum 2.5mg, q3-5 minutes D 26 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 EPI 1:10,000 Concentration: Mixing instructions: 1mg/10 mL = 0.1mg/mL = 100mcg/mL -Waste 1mL from a 10mL NS flush -Draw up 1mg (1mL) of epi 1:1,000 into same NS flush -Shake well to create 10mL (0.1mg/mL) of epi 1:10,000 Protocols & Dose: Adult Asystole/PEA (AC1): V-Fib/Pulseless V-Tach (AC8): 1mg IV/IO; q3-5 minutes as needed Pedi Asystole/PEA (PC1): Pedi V-Fib/Pulseless V-Tach (PC6): 0.01mg/kg IV/IO Maximum Single Dose 1mg, q3-5 minutes as needed Newly Born (AO2): 0.01mg/kg IV/IO, q3-5 minutes as needed D 27 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 EPI 1:100,000 Concentration: Mixing instructions: Protocols & Dose: 1mg/100mL = 1000mcg/100mL = 10mcg/mL Push-dose, Epi Push -Draw up 0.1mg (0.1mL) of epi 1:1,000 -Inject into 10mL NS flush -Shake well to create 10mL (10mcg/mL) of epi 1:100,000 or -With 10mL syringe, draw up 0.1mg (1mL) of epi 1:10,000 -With same syringe, draw up 9mL NS -Shake well to create 10mL (10mcg/mL) of epi 1:100,000 or Drip -Draw up 1mg (1mL) of epi 1:1,000 -Inject into 100mL NS bag or buretrol -Shake well to create 100mL (10mcg/mL) of epi 1:100,000 Bradycardia (AC2): “Push-dose” 10mcg IV/IO, q3-5 minutes, Titrate to SBP ≥ 90 mmHg Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis (AM1): “Epinephrine Drip” 1ml each minute over 10 minutes or until symptoms resolve; IV/IO Pedi Allergic Reaction (PM1): “Epinephrine” IV/IO Per Agency Medical Director, see page 2 for instructions *Info box: 1mL each minute over 10 minutes or until symptoms resolve Hypotension/Shock (AM5): “Epi Push” 1ml of Epi 1:100,000 *Info box: IV Push/IO Push: 1ml Epinephrine 1:100,000 q3-5 minutes Airway, Drug Assisted (AR3): 2-5mcg/min IV/IO D 28 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 EPI 1:500,000 Concentration: Mixing instructions: Protocols & Dose: 1mg/500 mL = 1000mcg/500mL = 2mcg/mL Drip -Draw up 1mg (1mL) of epi 1:1,000 -Inject into 500mL NS bag -Shake well to create 500mL (2mcg/mL) of epi 1:500,000 drip or -Draw up 2mg (2mL) of epi 1:1,000 -Inject into 1000mL NS bag -Shake well to create 1000mL (2mcg/mL) of epi 1:500,000 drip Bradycardia (AC2): “Epinephrine Drip” 1-10mcg/min IV/IO, Titrate to SBP ≥ 90mmHg Pedi Bradycardia (PC2): “Epinephrine” 0.1-1mcg/kg/min IV/IO, Titrate to age appropriate SBP ≥ 70 + (2 x Age) Pedi Asystole/PEA (PC1): “Epinephrine” Pedi Hypotension/Shock (PM3): “Epinephrine” 0.1-1mcg/kg/min IV/IO D 29 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ETOMIDATE Common names: Class: Action: Amidate® Hypnotic It appears to facilitate GABAminergic neurotransmission by increasing the number of available GABA receptors, possibly by displacing endogenous inhibitors of GABA binding. Etomidate produces clinical responses such as hypnosis. Based on animal studies, etomidate induces neocortical sleep. These studies suggest the effects of etomidate are at least partially due to depression of the brainstem reticular formation. Indications: Airway compromise/impending compromise requiring anesthesia to secure intubation. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Sepsis Side Effects: +Hypoventilation/Apnea +Anaphylaxis +Dysrhythmia +Nausea/Vomiting +Laryngospasm Special Considerations: Only for pts >12. May cause adverse reaction in pts with liver/renal impairment, consider reduced dose. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset < 1 min, half-life 75 min Protocols & Dose: Temperature Management-Interfacility (AC10): 10-20mg IV/IO Airway, Drug Assisted (AR3): 0.3mg/kg IV/IO D 30 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 FAMOTIDINE Common names: Class: Action: Pepcid® Histamine (H2) Antagonists Competitively inhibits the binding of histamine to H2-receptors on the gastric basolateral membrane of parietal cells, reducing basal and nocturnal gastric acid secretions. It also decreases the gastric acid response to stimuli such as food, caffeine, insulin, betazole, or pentagastrin. Famotidine reduces the total volume of gastric juice, thus indirectly decreasing pepsin secretion. The drug does not appear to alter gastric motility, gastric emptying, esophageal pressures, biliary secretions, or pancreatic secretions. Indications: Mild to severe allergic reaction. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Angioedema +Bronchospasms +Prolonged QT +Excitation +Headache +Dizziness +Anaphylaxis Special Considerations: Pt’s hypersensitive to any H2 antagonist may experience cross-reaction. Onset & Duration: Onset 5-15 min, half-life 2.5-3.5 hrs Protocols & Dose: Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis (AM1): 20mg IV/IO/IM Pedi Allergic Reaction (PM1): 0.5mg/kg IV/IO/IM, Maximum 20mg D 31 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 FENTANYL CITRATE Class: Action: Narcotic analgesic, opiate agonist Opiates do not alter the pain threshold of afferent nerve endings to noxious stimuli, nor do they affect the conductance of impulses along peripheral nerves. Analgesia is mediated through changes in the perception of pain at the spinal cord (mu2-, delta-, kappa-receptors) and higher levels in the CNS (mu1- and kappa3 receptors). The actions of fentanyl are similar to those of morphine, although fentanyl has a more rapid onset. Clinically, stimulation of mu-receptors produces analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, miosis, decreased gastrointestinal motility, and physical dependence. Kappa-receptor stimulation also produces analgesia, miosis, respiratory depression, as well as, dysphoria and some psychomimetic. Indications: Acute moderate/severe pain, sedation for multiple purposes. Contraindications: -Hypotension -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Respiratory depression +Apnea +Euphoria +Hyper/Hypotension +Tachy/Bradycardia +Nausea/vomiting +Chest wall rigidity +Dizziness +Laryngospasm +CNS depression Special Considerations: Rapid administration IV/IO may result in muscle rigidity of the chest/abd wall Onset & Duration: IV route: Onset immediate with peak within minutes, duration 30-60 min. IM route: Onset 7-8 min, lasting 1-2 hrs. IN route: Onset 10 min, peak 15-21 min, duration 30-60 min. D 32 | P a g e Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 Protocols & Dose: Revised April 2020 Bradycardia (AC2): Adult Tachycardia (narrow/reg:AC6)(narrow/irreg:AC6)(wide/reg:AC7)(wide/irreg:AC7): 50mcg IV/IO/IM/IN, q5 minutes, Max 100mcg **Sedation** Chest Pain/STEMI (AC4): 1mcg/kg IV/IO/IM/IN, Repeat 25mcg q20 minutes as needed, Maximum 200mcg Target Temperature Management-Interfacility (AC10): 1mcg/kg IV/IO, q5 minutes as needed, Maximum 200mcg Post-intubation/BIAD Management (AR8): (Adult) 1mcg/kg IV/IO/IM/IN, q5 minutes as needed, Maximum 300mcg (Pedi) 1mcg/kg IV/IO/IM/IN, MAY repeat 0.5mcg/kg q5 minutes as needed, Maximum 2mcg/kg Pediatric Pulmonary Edema/CHF (PC3): *pearl: 1mcg/kg IV/IO, Max single dose 50mcg. **Must speak with Medical Control** Crush Syndrome Trauma (TB3): (Adult) 50mcg IV/IO/IM/IN, q5 minutes, Max 100mcg (Pedi) 1mcg/kg IV/IO/IM/IN, If no improvement after 5 minutes 0.5mcg/kg IV/IO Pain Control (UP11): (Adult) 50-100mcg IV/IO/IM/IN, Repeat 50mcg q5 minutes as needed, Maximum 200mcg (Pedi) 1mcg/kg IV/IO/IM/IN, Repeat 0.5mcg/kg q5 minutes as needed, Maximum 2mcg/kg D 33 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 GLUCAGON Common names: Class: Action: GlucaGen® Hormone Increases blood glucose, causes relaxation of smooth muscle of the GI tract, and positive inotropic and chronotropic effect on the heart. Increases in blood glucose are secondary to stimulation of glycogenolysis. In liver and adipose tissue, glucagon increases the production of adenylate cyclase, which catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cAMP. Cyclic AMP then initiates a series of enzymatic reactions that include activation of phosphorylase, which promotes the breakdown of glycogen to glucose. As a result, blood glucose levels are increased within minutes of glucagon administration. Indications: Symptomatic hypoglycemia when IV/IO access is delayed or not possible, esophageal spasms secondary to food bolus. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Tachycardia +Nausea/vomiting +Anaphylaxis +Hypotension Special Considerations: The degree to which glucagon increases blood glucose is dependent on the liver glycogen reserves and the presence of phosphorylases, increase is not as great in patients with type I diabetes as compared to those with type II diabetes. Use caution in pts with known cardiovascular disease due to inotropic effects. Glucagon causes glycogen depletion, pts should consume carbohydrates asap. Onset & Duration: Onset 5-20, peak 30 min, duration 1-2 hrs. Half-life 45 min. Protocols & Dose: Adult Diabetic (AM2): 1-2mg IM, q15 min if needed Pediatric Diabetic (PM2): 0.1mg/kg IM (Maximum 1mg), q15 minutes as needed to keep Blood glucose > 60mg/dL Overdose/Toxic Ingestion (TE7): (Adult) 2-4mg IV/IO/IM (Pedi) 0.1mg/kg IV/IO/IM, q15 minutes as needed D 34 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 HEPARIN Class: Action: Glycosaminoglycan anticoagulant Heparin exerts its anticoagulant action by accelerating the activity of antithrombin III (ATIII) to inactivate thrombin; however, heparin does not lyse existing clots. The inability of heparin to inactivate surface-bound thrombin and factor Xa may explain its limited efficacy in patients with unstable angina, high-risk coronary angioplasty, and coronary thrombolysis. High doses of heparin also interfere with platelet aggregation, which, in turn, prolongs the bleeding time, although commonly used therapeutic doses heparin do not affect bleeding time. High-molecular-weight heparin fractions have a greater effect on platelet function. It has been shown that the plateletaggregating activity of heparin can be directly related to its molecular weight. Indications: Acute and symptomatic MI with ST segment elevation that has been confirmed with the receiving PCI center. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Aneurysm -Head trauma -Clotting disorders -Recent significant trauma -Active/suspected bleeding of any kind -History of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Bleeding +Bronchospasm +Injection site reaction Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with known renal/hepatic disease Use caution in pts already on anti-coagulant therapy due to increased bleeding risk, consider consulting medical control. Onset & Duration: Immediate onset, half-life 2.5-5 hrs Protocols & Dose: Chest pain/STEMI (AC4): 60units/kg IV/IO, Maximum 4000units **Must confirm STEMI via medical consult with receiving facility prior to administration** D 35 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 HYDROMORPHONE HCL Common names: Class: Action: Dilaudid® Narcotic analgesic, opioid agonist Hydromorphone is a potent µ-opiate receptor agonist. Opiates do not alter the pain threshold of afferent nerve endings to noxious stimuli nor do they affect the conductance of impulses along peripheral nerves. Analgesia is mediated through changes in the perception of pain at the spinal cord and higher levels in the CNS. The emotional response to pain is also altered. Clinically, stimulation of µ-receptors produces analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, miosis, decreased gastrointestinal motility, and physical dependence. Indications: Acute moderate/severe pain. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Active asthma -Labor/Delivery -Hypovolemia/Hypotension -Respiratory depression Side Effects: +Nausea/vomiting +Respiratory depression/apnea +Hypotension +Bronchospasm +Bradycardia +Anaphylaxis +Sedation Special Considerations: Will potentiate the effects of other CNS/respiratory depressants, including alcohol. Consider reducing the initial dose in elderly pts. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, peak 15 min, duration 1-4 hrs. Protocols & Dose: D Pain Control (UP11): Chest Pain/STEMI (AC4): 1mg IV/IO, q20 minutes x1 36 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 HYDROXOCOBALAMIN Common names: Class: Action: CyanoKit®, Hydroxycobalamin, Vitamin B12 Antidote Cyanide binds rapidly with cytochrome a3, a component of the cytochrome c oxidase complex in mitochondria. Inhibition of cytochrome a3 prevents the cell from using oxygen and forces anaerobic metabolism, resulting in lactate production, cellular hypoxia and metabolic acidosis. The action of hydroxocobalamin in the treatment of cyanide poisoning is based on its ability to bind cyanide ions. Each hydroxocobalamin molecule can bind one cyanide ion by substituting it for the hydroxo ligand linked to the trivalent cobalt ion, to form cyanocobalamin, which is then excreted in the urine. Indications: Known or suspected symptomatic cyanide poisoning. Contraindications: -None in emergency situations Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Renal failure +Hypertension +Rash +Nausea +Headache +Peripheral edema +Pulmonary edema +Dizziness +Skin/Eye irritation Special Considerations: May be incompatible with numerous medications, should be administered through dedicated IV line. Should be administered slowly over 15 minutes. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, half-life 26-31 hrs Protocols & Dose: D Carbon Monoxide/Cyanide (TE2): 70mg/kg IV/IO, Maximum 5g 37 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 IBUPROFEN Common names: Class: Action: Advil® Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID), analgesic, antipyretic Ibuprofen competitively inhibits both cyclooxygenase (COX) isoenzymes, COX-1 and COX-2, by blocking arachidonate binding resulting in analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory pharmacologic effects. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of ibuprofen is due to decreased prostaglandin synthesis via inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2. Ibuprofen is effective in cases where inflammation has caused sensitivity of pain receptors (hyperalgesia). It appears prostaglandins, specifically prostaglandins E and F, are responsible for sensitizing the pain receptors; therefore, ibuprofen has an indirect analgesic effect by inhibiting the production of further prostaglandins and does not directly affect hyperalgesia or the pain threshold. Ibuprofen promotes a return to a normal body temperature set point in the hypothalamus by suppressing the synthesis of prostaglandins, specifically PGE2, in circumventricular organs in and near the hypothalamus. Indications: Used for fever ≥ 100.4* F and mild pain. Contraindications: -Renal Impairment/Failure/Transplant -Hypersensitivity -NSAID sensitive asthma -GI bleeding -Gastric ulcer -Clotting disorders Side Effects: +Angioedema +Pulmonary edema +Bronchospasm +Anaphylaxis +Shortness of breath +Bradycardia +Hypo/hypertension +Bleeding +Nausea/vomiting Special Considerations: Avoid use in pts with severe heart failure or hypertension. NSAID use should be avoided after the second/third trimester of pregnancy. Will increase effects of anticoagulants, use caution in pts undergoing anticoagulant therapy. NSAIDs should be avoided in pts undergoing chemotherapy Many pts are aware if they have been instructed not to use NSAIDs by their doctor, it is good practice to ask. Onset & Duration: Onset 15-45 min, peak 1-2 hr, half-life ~2 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Scene Rehabilitation Responder (SO2): 400mg PO Fever/Infection (UP10): (Adult) 400-800mg PO, Liver Disease: 600mg Maximum (Pedi) 10mg/kg PO (if age > 6 months) Pain Control (UP11): 10mg/kg PO (400-800mg typical adult), Maximum 800mg D 38 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE Common names: Class: Action: Atrovent® Anticholinergic, Parasympatholytic bronchodilator Ipratropium antagonizes the action of acetylcholine by blocking muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Blockade of cholinergic receptors decreases the formation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). When administered by oral inhalation, ipratropium exhibits antimuscarinic activity on the bronchial smooth muscle; systemic effects are minimal. Compared with atropine, ipratropium is roughly twice as potent as a bronchodilator, and it exhibits a more favorable ratio of bronchodilation to inhibition of salivary secretion. Bronchodilation following inhalation of ipratropium is secondary to local effects rather than a systemic effect. Ipratropium does not possess anti-inflammatory properties. Indications: Acute bronchospasms associated with reactive or obstructive airway disease. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity to ipratropium or atropine -Narrow angle glaucoma Side Effects: +Bronchospasm +Angioedema +Anaphylaxis +laryngospasm +Tachycardia +Hypotension +Dry mucosa +Palpitations Special Considerations: Use caution in elderly pts and those already suffering from cardiac arrhythmia. Onset & Duration: Onset 15-30 min, peak 1-2 hrs, duration of effects 4-5 hrs, half-life 2 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Adult COPD/Asthma (AR4): Pediatric Asthma (AR7): 0.5mg, qPRN x3 Repeat & Max: FDA recommends no more than 4 doses/day (2mg max) as no benefit is noted at higher doses. D 39 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 KETAMINE HCL Common names: Class: Action: Ketalar® Sedative hypnotic, nonbarbiturate dissociative anesthetic Ketamine-induced analgesia is obtained without the induction of deep levels of anesthesia. Increasing doses of ketamine result in anesthesia. The state of unconsciousness it produces is trancelike and cataleptic in nature and has been referred to as dissociative anesthesia. Ketamine appears to selectively interrupt association pathways of the brain before producing somatesthetic sensory blockade. It may selectively depress the thalamoneocortical system before significantly obtunding more ancient cerebral centers and pathways. Ketamine non-competitively blocks Nmethyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. The activity on NMDA receptors may be responsible for the analgesic as well as psychiatric (psychosis) effects. It is also a potent bronchodilator due to its sympathomimetic activity, with no effects on pharyngeal or laryngeal reflexes, leaving the pts airway intact. Indications: +Sedation during RSI +Dangerously combative +Behavioral emergencies +Pain control +Post intubation sedation Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Hypertension Side Effects: +Tachy/Bradycardia +Arrhythmia +Laryngospasm +Anaphylaxis +Respiratory depression/apnea +Nystagmus Special Considerations: Give over 60 seconds to reduce pressor effects and subsequent rise in BP/ICP. May exacerbate acute psychosis in pts with psychiatric history, such as schizophrenia. Utilize low end of dosing ranges for elderly pts. Use caution in pts with chronic cardiac diseases (angina, CHF, MI), as ketamine causes substantial increase in myocardial oxygen demand. Onset & Duration: IV route onset of dissociation 15 seconds, anesthesia effects 30 seconds, duration 510 minutes. Analgesic effects last 20-45 min. IM route rapid absorption, delayed effects with anesthesia occurring in 3-4 min, lasting 12-25 min. D 40 | P a g e Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 Protocols & Dose: Revised April 2020 Airway, Drug Assisted (AR3): 1.5-2mg/kg IV/IO, May repeat x1 *Hypoxic/Hypotension/Dangerously Combative: Airway Management: 1.5-2mg/kg IV/IO Airway Management+Dangerously Combative: 4mg/kg IM, max 400mg (behavioral) 1.5-2mg/kg IV/IO Post-Intubation/BIAD Management (AR8): 2mg/kg IV/IO Behavioral (UP6): 4mg/kg IM, max 400mg Pain Control (UP11): 0.2mg/kg IV/IO, max 20mg. Mix in 250mL NS, infuse over 10 minutes, q30 minutes D 41 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 KETOROLAC TROMETHAMINE Common names: Class: Action: Toradol® Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID), analgesic Ketorolac competitively inhibits both cyclooxygenase (COX) isoenzymes, COX-1 and COX-2, by blocking arachidonate binding resulting in analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory pharmacologic effects. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of ketorolac is due to decreased prostaglandin synthesis via inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2. Ketorolac is effective in cases where inflammation has caused sensitivity of pain receptors (hyperalgesia). It appears prostaglandins, specifically prostaglandins E and F, are responsible for sensitizing the pain receptors; therefore, ketorolac has an indirect analgesic effect by inhibiting the production of further prostaglandins and does not directly affect hyperalgesia or the pain threshold. Indications: Moderate to severe pain Contraindications: -Renal Impairment/Failure/Transplant -Hypersensitivity -NSAID sensitive asthma -GI bleeding -Clotting disorders -Active bleeding -Headaches -Abd Pain -Open fractures/obvious deformity Side Effects: +Angioedema +Pulmonary edema +Bronchospasm +Anaphylaxis +Shortness of breath +Bradycardia +Hypo/hypertension +Bleeding +Nausea/vomiting Special Considerations: Avoid use in pts with severe heart failure or hypertension. NSAID use should be avoided after the second/third trimester of pregnancy. Will increase effects of anticoagulants, use caution in pts undergoing anticoagulant therapy. NSAIDs should be avoided in pts undergoing chemotherapy Many pts are aware if they have been instructed not to use NSAIDs by their doctor, it is good practice to ask. Onset & Duration: Onset 30 min, peak 1-2 hrs, effect duration 4-6 hrs Protocols & Dose: D Pain Control (UP11): (Adult) 30mg IV/IO, 60mg IM, Maximum 60mg (Pedi) 0.5mg/kg IV/IO/IM, Maximum 30mg 42 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 LABETALOL HCL Class: Action: Beta-blocker Labetalol blocks beta1-receptors in the heart, beta2-receptors in bronchial and vascular smooth muscle, and alpha1-receptors in vascular smooth muscle. The betablocking activity is three to seven times as potent as the alpha-blocking ability. In contrast to other beta-blockers such as propranolol, labetalol does not appear to decrease the glomerular filtration rate or renal blood flow, probably because of the drug's balanced actions on both alpha- and beta-receptors and its minimal effect on cardiac output. The result of labetalol's actions at alpha- and beta-receptors leads to vasodilation and decreased total peripheral resistance, which results in decreased blood pressure without a substantial decrease in resting heart rate, cardiac output, or stroke volume. Indications: Narrow complex, symptomatic tachycardia that is stable in nature and refractory to adenosine. Labetalol is also used for hypertension, defined as SBP ≥ 180 and/or DBP ≥ 105, that develops during interfacility (hospital to hospital) transfer of suspected stroke pts only. Contraindications: -AV block -Sick sinus syndrome -Shock/Hypotension -CHF/pulmonary edema -Severe bradycardia -AMI -Acute/chronic asthma -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Brady/Tachycardia +Bronchospasm +Anaphylaxis +Laryngospasm +Angioedema +Hypotension +Wheezing +Shortness of breath Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with liver disease, dosage reduction may be necessary. Onset & Duration: Onset 2-5 min, peak 5-15 min, duration 2-4 hrs. Half-life 2.5-8 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Adult Tachycardia (narrow/reg:AC6)(narrow/irreg:AC6): 10mg IV push over 5 minutes, If no improvement in 5 minutes, 10mg IV push over 5 minutes Suspected Stroke: Activase/t-PA Interfacility (AM6): *if transferring hospital DID NOT initiate antihypertensive infusion: 10mg IV/IO *if transferring hospital DID initiate antihypertensive infusion: Increase drip 2mg/min, every 10 minutes, Titrate SBP<180mmHg, DBP<105mmHg, Maximum 8mg/min D 43 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 LACTATED RINGERS Common names: Class: Action: LR Isotonic crystalloid Each 100 mL contains 300 mg sodium chloride, 310 mg sodium lactate, 30 mg potassium chloride, 20 mg calcium chloride, with a pH 6.5 utilized as fluid and electrolyte replacement. Indications: Volume replacement in the presence of thermal burns. Contraindications: -Pulmonary edema Side Effects: +Edema Special Considerations: Excessive administration may lead to metabolic alkalosis. Cannot be administered with ceftriaxone (Rocephin®). Onset & Duration: Immediate within vesicular. Protocols & Dose: Chest Pain/STEMI (AC4): *pearl: 250-500mL as pre-cath hydration Thermal Burn (TB9): 0.25mL/kg x (% TBSA) / hr, for up to the first 8 hours Crush Syndrome Trauma (TB3): Entrapped < 2 hours: (Adult): 1L/hour IV/IO (Pedi): 3x Maintenance rate Entrapped > 2 hours: (Adult): 500mL/hour IV/IO (Pedi): Maintenance fluid rate D 44 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 LEVALBUTEROL HCL Common Names: Xopenex Class: Bronchodilator/Beta2-Adrenergic Agonist Action: Activation of beta2-adrenergic receptors in smooth muscles, relaxing smooth muscles in all airways from trachea to terminal bronchioles. Increased cyclic AMP are also associated with the inhibition of release of mediators from mast cells in the airway. Acts as a functional antagonist to relax the airway irrespective of the spasmogen involved, thus protecting against all bronchoconstrictor challenges. Indications: Treatment of bronchospasm in patients with reversible obstructive airway disease. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity to Levalbuterol or racemic Albuterol Side Effects: -Palpitations -Chest pain -Dizziness -Tremors Considerations: -Paradoxical Bronchospasm -Worsening of Asthma -Renal patients Onset & Duration: Onset time of <10 minutes with peak at 1.5 hours. Duration can last up to 6 hours. Protocols & Dose: Adult COPD/Asthma Respiratory Distress (AR4) 1.25mg via nebulizer -Tachycardia -Headache -Nervousness -Hypokalemia Pediatric Asthma/Respiratory Distress (AR7) 1.25mg via nebulizer D 45 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 LEVETIRACETAM Common names: Class: Action: Keppra® Anticonvulsant The precise mechanism of action of levetiracetam is not known. Its antiepileptic effect does not appear to involve known mechanisms relating to inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmission. In vitro studies show that levetiracetam, up to 1700 mcg/ml, did not result in significant ligand displacement at known receptor binding sites. Second messenger systems, ion channel proteins, glutamate receptor-mediated neurotransmission, muscimol-induced chloride flux, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-transaminase and glutamate decarboxylase activities were unaffected by levetiracetam. Benzodiazepine receptor antagonists (e.g., flumazenil) had no effect on levetiracetam's protection against seizures. Conversely, a stereoselective binding site for the drug has been demonstrated to exist exclusively in synaptic plasma membranes in the CNS, but not in peripheral tissue. In vitro and in vivo recordings of epileptiform activity from the hippocampus have shown that levetiracetam inhibits burst firing without affecting normal neuronal excitability. This suggests that levetiracetam may selectively prevent hypersynchronization of epileptiform burst firing and propagation of seizure activity. Indications: Status epilepticus refractory to two doses of benzodiazepines. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Angioedema +Hallucinations +Psychosis +Hypertension +Nausea/vomiting +Abd pain Special Considerations: May cause acute psychosis in pts with history of psychosis or schizophrenia. Can potentiate other CNS depressants. Concomitant use with tricyclic antidepressants may lower seizure threshold. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, peak ~1 hr, half-life 6-8 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Seizure (UP13): (Adult): 500mg IV/IO, Over 15 minutes (Pedi): 15mg/kg; IV/IO, Over 15 minutes **MUST administer 2 doses of Benzodiazepines prior to administration** Repeat & Max: Max 3000mg/day IV/PO D 46 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 LIDOCAINE HCL Class: Action: Antidysrhythmic, Sodium channel blocker Lidocaine's antiarrhythmic effects result from its ability to inhibit the influx of sodium through the "fast" channels of the myocardial cell membrane, thereby increasing the recovery period after repolarization. It suppresses automaticity and decreases the effective refractory period and the action potential duration in the HisPurkinje system, while not suppressing automaticity at the SA node. It suppresses spontaneous depolarizations in the ventricles by inhibiting reentry mechanisms. Its analgesics effects are through a reversible nerve conduction blockade by diminishing nerve membrane permeability to sodium, decreasing the rate of membrane depolarization, and increasing the threshold for electrical excitability. Indications: Monomorphic, wide-complex tachycardia, pulseless v-tach and v-fib. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -WPW/Adam-Stokes syndrome -Severe SA block -Any AV block -Bifascicular block Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Angioedema +Hypotension +Bradycardia/Asystole +Respiratory depression/arrest +Laryngospasm +Malignant hyperthermia +Skin flushing/hot flashes Special Considerations: A bifascicular block is defined when two or more fascicles are involved in any combo. LBBB is bifascicular because it involves both the L anterior and posterior fascicles. RBBB alone is singular, but in the presence of either L anterior or L posterior fascicular block, the combo is considered bifascicular. Onset & Duration: Immediate onset, duration of effects 10-20 min. Protocols & Dose: Adult Tachycardia (Wide/Reg/Monomorphic:AC7) 1mg/kg bolus IV/IO. Repeat 1mg/kg bolus q15 minutes if needed. Adult Tachycardia (Wide/Irreg/Monomorphic:AC7): 1mg/kg bolus IV/IO. Repeat 1mg/kg bolus q15 minutes if needed. V-Fib /Pulseless V-Tach (AC8): 1.5mg/kg IV/IO, may repeat if refractory at 0.75 mg/kg IV/IO Pediatric Tachycardia (PC5): 1mg/kg IV/IO, Maximum 100mg, Repeat 0.5mg/kg, Maximum 3mg/kg total Pediatric V-Fib/Pulseless V-Tach (PC6): Pediatric Post Arrest (PC7): 1mg/kg IV/IO. Repeat 1mg/kg bolus q15 minutes, if needed. *IO placement: Paramedics may give 10-20mg of 2% lidocaine through an established IO for adult pts with IO infusion-related pain per state procedure guidelines. May repeat up to 3x for a maximum of 60mg. D 47 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 LOPERAMIDE HCL Common names: Class: Action: Imodium® Anti-diarrheal Loperamide interferes with peristalsis by a direct action on the circular and longitudinal muscles of the intestinal wall to slow motility. It also may directly inhibit fluid and electrolyte secretion and/or increase water absorption by increasing the transit time of the intestinal contents. Indications: +Control of nonspecific diarrhea +Chronic diarrhea from IBS +Reduce discharge from ileostomies Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -GI bleeding/bloody stools -Abd pain -Constipation/GI obstruction Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Angioedema +Prolonged QT +Arrhythmia +Abd pain +Nausea/vomiting +Dizziness +Headache Special Considerations: Should not be used for bacterial gastroenteritis, food poisoning, as diarrhea is the body’s protective process to reduce exposure to the infecting bacteria. Not approved for use in pediatric pts <2 yrs Not for use by nursing mothers Onset & Duration: Delayed onset PO 30-60 min, peak 5 hrs, duration 24 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Scene Rehabilitation Responder (SO2): 4mg PO Repeat & Max: Max 8mg/day PO, pediatric max dosage varies by age 3-6mg/day D 48 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 LORAZEPAM Common names: Class: Action: Ativan® Benzodiazepine, anticonvulsant, sedative Benzodiazepines act at the level of the limbic, thalamic, and hypothalamic regions of the CNS, and can produce any level of CNS depression required. The action of these drugs is mediated through the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Central benzodiazepine receptors interact allosterically with GABA receptors, potentiating the effects of GABA and thereby increasing the inhibition of the ascending reticular activating system. Benzodiazepines block the cortical and limbic arousal that occurs following stimulation of the reticular pathways. As an anticonvulsant lorazepam is preferred, because even though it has a shorter half-life than diazepam, lorazepam persists in the CNS longer. Indications: Seizure activity; For sedation during cardioversion/cardiac pacing procedures; And behavioral emergencies where the pt has aggression, violence, or agitation that creates a threat to themselves or others. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Respiratory depression/arrest +Cardiac arrest +Pulmonary edema +Bradycardia +Hypo/hypertension +Dizziness +Drowsiness +Nausea/Vomiting +Delirium/confusion Special Considerations: May potentiate other CNS depressants, including alcohol. Use caution in pts with acute exacerbation of reactive/obstructive airway diseases, due to respiratory depression. Avoid in pts with neuromuscular disease and late-stage Parkinson’s. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, half-life 12 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Bradycardia (AC2): 0.5-1mg IV/IO/IM, Maximum 10mg (Sedation) Adult Tachycardia (narrow/reg:AC6)(narrow/irreg:AC6): 0.5-1mg IV/IO, Maximum 2mg (Sedation) Adult Tachycardia (wide/reg:AC7)(wide/irreg:AC7): 0.5-1mg IV/IO, May repeat as needed, Max 2mg (Sedation) Obstetrical Emergency (AO3): 0.5-1mg IV/IO, max 2mg Seizure (UP13): (Adult) 2mg IV/IO, repeat 2mg q2 minutes as needed, max dose 10mg (Pedi) 1mg IV/IO, repeat 1mg q2 minutes as needed, max dose 5mg. Behavioral (UP6): (Adult) 2mg IV/IO (Pedi) 0.1mg/kg IV/IO D 49 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Class: Action: Electrolyte, anticonvulsant, It is the second most plentiful cation of the intracellular fluids. It is essential for the activity of many enzyme systems and plays an important role with regard to neurochemical transmission and muscular excitability. Magnesium sulfate reduces striated muscle contractions and blocks peripheral neuromuscular transmission by reducing acetylcholine release at the myoneural junction. Additionally, Magnesium inhibits Ca2+ influx through dihydropyridine-sensitive, voltage-dependent channels. This accounts for much of its relaxant action on vascular smooth muscle. Indications: Used for immediate control of life-threatening convulsions due to preeclampsia/eclampsia during pregnancy; Also indicated for magnesium deficiency as indicated by persistent ventricular fibrillation or torsades de pointes; Acute exacerbation of reactive/obstructive pulmonary disease with impending failure and/or refractory to bronchodilators. Contraindications: -AV block -Hypotension -AMI -Hypocalcemia Side Effects: +Flushing/sweating +Eye/Skin irritation +Weakness/paralysis +CNS depression +Respiratory paralysis +Hypocalcemia +Hypotension +High degree heart block Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with renal insufficiency. Onset & Duration: IV route provides immediate onset, duration ~30 min. IM route is significantly delayed, onset ~1 hr, duration 3-4 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Adult Tachycardia (wide/irreg/polymorphic:AC7): *pearl: 2g slow IV/IO Pediatric Tachycardia (PC5): *pearl: 40mg/kg IV/IO over 10 minutes. Cardiac arrest given over 2 minutes. Ventricular Fibrillation/Pulseless V-Tach (AC8): 2g IV/IO Pediatric V-Fib/Pulseless V-Tach (PC6): 40mg/kg IV/IO over 10-20 minutes. *Persistent VF/VT or Torsades de Points: 40mg/kg IV/IO over 1-2 minutes, q5 minutes, Max 2g Obstetrical Emergency (AO3): 4g IM in each buttock (Total of 8g) THEN: 4g IV/IO over 3-5 minutes Adult COPD/Asthma (AR4): 2g IV/IO, infuse over 10 minutes Pediatric Asthma/Respiratory Distress (AR7): 40mg/kg IV/IO, infuse over 10-20 minutes D 50 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 METHYLPREDNISOLONE Common names: Class: Action: Solu-Medrol® Systemic Corticosteroids, glucocorticoid Glucocorticoids are naturally occurring hormones that prevent or suppress inflammation and immune responses. At the molecular level, unbound glucocorticoids readily cross cell membranes and bind with high affinity to specific cytoplasmic receptors. This binding induces a response by modifying transcription and, ultimately, protein synthesis to achieve the steroid's intended action: inhibition of leukocyte infiltration at the site of inflammation, interference in the function of mediators of inflammatory response, and suppression of humoral immune responses. Indications: Moderate to severe allergic reactions; hypotension/shock secondary to possible adrenal insufficiency; Respiratory distress secondary to reactive/obstructive pulmonary diseases. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Systemic fungal infection -Acute pulmonary edema -Acute hypertension Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Increased blood coagulation +Brady/Tachycardia +Pulmonary edema +Angioedema +Hypertension +Palpitations +Nausea/vomiting +Anxiety/restlessness +Syncope +Hyperglycemia Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with recent MI due to possibility of left ventricular rupture. Use caution in pts with thyroid disorders. Monitor pts with diabetes for signs of hyperglycemia. Consider diluting prior to administering IV/IO to avoid pt discomfort. Onset & Duration: Onset 1 hr, half-life 6-9 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis (AM1): 125mg IV/IO Pediatric Allergic Reaction (PM1): 2mg/kg IV, Maximum 125mg Hypotension/Shock (AM5): Pediatric Hypotension/Shock (PM3): *pearl: In suspicion of acute adrenal insufficiency/congenital adrenal hyperplasia 125mg IM/IV/IO Adult COPD/Asthma (AR4): 125mg IV/IO/IM Pediatric Asthma/Respiratory Distress (AR7): 2mg/kg IV/IO/IM, Maximum 125mg D 51 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 METOCLOPRAMIDE Common names: Class: Action: Reglan® Antiemetic Metoclopramide enhances gastric motility without stimulating gastric secretions. Peripherally, metoclopramide augments cholinergic activity either by causing release of acetylcholine from postganglionic nerve endings or by sensitizing muscarinic receptors on smooth muscle. Centrally, metoclopramide blocks dopaminergic receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone by antagonizing the actions of apomorphine, a known central dopamine agonist. Antiemetic effects of are the result of both the central dopamine antagonism and increased gastric motility. Indications: Nausea Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Hypersensitivity to procainamide -GI bleeding/bloody stools -GI obstruction/perforation -Acute pulmonary edema Side Effects: +Laryngospasm +AV block +Brady/Tachycardia/SVT +Bronchospasm +Angioedema +Hypo/Hypertension +Nausea/vomiting +Headache +Drowsiness Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with existing hypertension, especially with history of CHF Should be avoided in pts with history of dystonic/extrapyramidal reactions Onset & Duration: Onset 1-3 min, duration 1-2 hrs. Protocols & Dose: D *None in current protocols. 52 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 MIDAZOLAM HCL Common names: Class: Action: Versed® Benzodiazepine, anticonvulsant, sedative Benzodiazepines act at the level of the limbic, thalamic, and hypothalamic regions of the CNS, and can produce any level of CNS depression required. The action of these drugs is mediated through the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Unlike barbiturates, which augment GABA responses by increasing the length of time that chloride channels are open, benzodiazepines enhance the effects of GABA by increasing GABA affinity for the GABA receptor. Binding of GABA to the site opens the chloride channel resulting in a hyperpolarized cell membrane that prevents further excitation of the cell. Midazolam has twice the affinity for these benzodiazepine receptors, than does diazepam. Indications: Seizure activity; For sedation during various emergencies; And behavioral emergencies where the pt has aggression, violence, or agitation that creates a threat to themselves or others. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Shock/Hypotension -Acute closed-angle glaucoma Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Respiratory depression/arrest +Cardiac arrest +Laryngospasm +Bradycardia +Significant hypotension +Bronchospasm +Amnesia +Nausea/Vomiting +Hiccups Special Considerations: May potentiate other CNS depressants, including alcohol. Use caution in pts with acute exacerbation of reactive/obstructive airway diseases, due to respiratory depression. Avoid use in pts with neuromuscular disease and late-stage Parkinson’s. IV administration should be done slowly to diminish adverse respiratory symptoms. Onset & Duration: Onset 1.5-5 min, peak 20-60 min, duration 2-6 hrs. D 53 | P a g e Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 Protocols & Dose: Revised April 2020 Bradycardia (AC2): 2-2.5mg IV/IO/IM/IN, Maximum 10mg Adult Tachycardia (narrow/reg:AC6)(narrow/irreg:AC6): 2-2.5mg IV/IO, qPRN, Maximum 5mg Adult Tachycardia (wide/reg:AC7)(wide/irreg:AC7): 2-2.5mg IV/IO, qPRN, Maximum 10mg Pediatric Tachycardia (PC5): 0.1-0.2mg/kg IV/IO/IN, May repeat if needed, Maximum Single Dose 2mg, Maximum Total Dose 5mg Obstetrical Emergency (AO3): 2.5mg IV/IO, q3-5 minutes as needed 5mg IM, 2mg IN, Maximum 10mg Post-intubation/BIAD Management (AR8): (Adult) 2-2.5mg IV/IO, q3-5 minutes as needed, Maximum 10mg (Pedi) 0.1-0.2mg/kg IV/IO/IN Crush Syndrome Trauma (TB3): (Adult) 0.5-2mg IV/IO, 1-2mg IN, Maximum 5mg (Pedi) 0.1-0.2mg/kg IV/IO/IM/IN, Maximum 2mg, Over 2-3 minutes as needed Bites & Envenomations (TE1): (Adult) 2.5mg IV/IO/IM, Over 2-3 minutes, 1-2mg IN, Maximum 5mg (Pedi) 0.1-0.2mg/kg IV/IO/IM/IN, Maximum 2mg, over 2-3 minutes Behavioral (UP6): (Adult) 2.5mg IV/IO/IN, 5 mg IM (Age ≥ 65) 1mg-2.5mg IV/IO/IN, 2.5mg IM (Pedi) 0.1mg-0.2mg/kg IV/IO/IM/IN, q2-3 minutes as needed Seizure (UP13): (Adult) 2-2.5mg IV/IO/IN, 5mg IM; q3-5min, Max 10mg (Pedi) 0.1-0.2mg/kg IV/IO/IM/IN, q3-5 minutes as needed, Maximum 10mg D 54 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 NALOXONE HCL Common names: Class: Action: Narcan® Opioid antagonist Naloxone competitively antagonizes opiate receptors (mu, responsible for analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, and miosis; kappa, responsible for analgesia, dysphoria, some psychomimetic effects, and sedation; and delta, responsible for analgesia, sedation, and possibly hormonal and neurotransmitter release) thus inhibiting both the toxic and clinical effects of opiates. It’s quick action produces almost an immediate reversal to respiratory depression, hypotension, sedation, and analgesia. Indications: Used as a reversal agent for respiratory depression secondary to suspected opioid intoxication. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Pulmonary edema +Ventricular Tach/Fib +Hypotension +Tachycardia +Nausea/vomiting +Withdrawal symptoms +Agitation +Pain Special Considerations: Titrate to achieve adequate respiratory drive/oxygenation, not given to restore consciousness. Use caution in opioid-dependent pts as naloxone use may precipitate withdrawal symptoms. Onset & Duration: IV/IN route has onset 2-3 min, duration 45-90 min. IM onset 15 min, duration 45-90 min. Protocols & Dose: Adult Asystole/PEA (AC1): Cardiac Arrest (AC3): *pearl: 2mg IM/IV/IO/IN Pediatric Cardiac Arrest (PC4): *pearl: 0.1mg/kg IM/IV/IO/IN Overdose/Toxic Ingestion (TE7): (Adult) 0.4-2mg, Max10mg, IV/IO/IM/IN/ETT (Pedi) 0.1mg/kg, Max 2mg, IV/IO/IM/IN/ETT Titrate to adequate ventilation and oxygenation, NOT GIVEN TO RESTORE CONSCIOUSNESS D 55 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 NERVE AGENT KIT Common names: Class: Action: DuoDote® Two-part antidote kit comprised of atropine and pralidoxime. Both medications work to reverse the toxic effects of organophosphate on the body that lead to symptoms of salivation, lacrimation, urination, diarrhea, gastric upset, and emesis. See individual medication for information regarding specific actions. Indications: Organophosphate toxicity/nerve agent exposure accompanied by SLUDGE symptoms. Contraindications: None in emergency situations. Side Effects: Consult individual medications for specific side effects. Special Considerations: None in emergency situations. Special Considerations: None in emergency situations. Protocols & Dose: WMD-Nerve Agent (TE8): (Adult) Minor: 2 Doses Rapidly IM Major: 3 Doses Rapidly IM (Pedi) *pearl: ≤ 7 yrs = 1 kit 8-14 yrs = 2 kit ≥ 15 yrs = 3 kit *Each nerve agent kit includes 2mg atropine and 600mg pralidoxime auto-injectors D 56 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 PRALIDOXIME CHLORIDE Common names: 2-PAM® Class: Action: Antidote, cholinesterase reactivator Pralidoxime is a cholinesterase reactivator that reverses muscle paralysis after organophosphate poisoning. Organophosphate compounds inhibit cholinesterase via phosphorylation of the enzyme. The inhibited cholinesterase is unable to metabolize acetylcholine resulting in an accumulation of the neurotransmitter. Acetylcholine is present in the central nervous system, parts of the autonomic nervous system, and at the skeletal muscle end plates; therefore, accumulation of this neurotransmitter after organophosphate poisoning adversely affects each of these systems. In the somatic nervous system, acetylcholine accumulation leads to paralysis. The clinical effects of pralidoxime are most evident at skeletal neuromuscular junctions. Pralidoxime reverses the paralysis by removing the phosphoryl group from the inhibited cholinesterase molecule, reactivating the enzyme and restoring the body's ability to metabolize acetylcholine, thereby decreasing blood pressure, reducing salivation, muscle twitching, cramps, weakness, tachycardia, and facial pallor. Indications: Organophosphate toxicity/nerve agent exposure accompanied by SLUDGE symptoms. Contraindications: -None in emergency situations Side Effects: +Laryngospasm +Tachycardia +Hypertension +Blurred vision +Hyperventilation +Headache +Nausea/vomiting +Dizziness +Flushing Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with myasthenia gravis receiving anticholinesterase agents for treatment. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, peak in 10-20 min, half-life ~75 mins. Protocols & Dose: D WMD-Nerve Agent (TE8): *If nerve agent kit is unavailable, dose pralidoxime accordingly (Adult) 600mg IV/IO/IM (Pedi) 15-25mg/kg IV/IO/IM, Over 30 minutes 57 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 NICARDIPINE HCL Common names: Class: Action: Cardene® Calcium-channel blocker Nicardipine inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium across the cell membranes of myocardial and vascular smooth muscle without altering serum calcium concentrations and inhibits intracellular phosphodiesterase. Unlike other calciumchannel blockers, nicardipine has greater selectivity for vascular smooth muscle than for cardiac muscle relaxing the peripheral vasculature without affecting inotropy. These effects elicit an increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, and a decreased total peripheral resistance, systemic blood pressure, and afterload. Indications: Used for hypertension, defined as SBP ≥ 180 and/or DBP ≥ 105, that develops during interfacility (hospital to hospital) transfer of suspected stroke pts only. Contraindications: -AV block -Sick sinus syndrome -Hypotension -Left ventricular dysfunction -Severe bradycardia -Cardiogenic shock -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +AV block +Arrhythmia +Hypotension +Angina +Tachycardia +Palpitations +Wheezing +Flushing +Headache +Nausea/vomiting Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with history of CHF as pulmonary edema may develop Onset & Duration: Rapid onset with continuous effects for duration of drip, after discontinuation, effects last ~3. Protocols & Dose: D Suspected Stroke: Activase/t-PA Interfacility (AM6): Increase 2.5mg/hr, every 5 minutes, Titrate SBP<180mmHg, DBP<105mmHg, Maximum 15mg/hr 58 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 NITROGLYCERIN Common names: Class: Action: Nitro Bid®, Nitrostat®, NitroMist® Nitrate vasodilator Nitroglycerin is converted to nitric oxide, a reactive free radical. Nitric oxide activates the enzyme guanylate cyclase, thereby stimulating the synthesis of cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cGMP). This second messenger then activates a series of protein kinase-dependent phosphorylations in the smooth muscle cells, eventually resulting in the dephosphorylation of the myosin light chain of the smooth muscle fiber and the subsequent release, or extrusion, of calcium ions. The contractile state of smooth muscle is normally maintained by a phosphorylated myosin light chain (stimulated by an increase in calcium ions). Thus, the nitrite- or nitrate-induced dephosphorylation of the myosin light chain signals the cell to release calcium, thereby relaxing the smooth muscle cells and producing vasodilation. Indications: Chest pain thought to be cardiac in nature. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Head trauma -Hypotension -Severe brady/tachycardia -Phosphodiesterase inhibitor (erectile disfunction medication) use in past 24-36 hrs. Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Brady/Tachycardia +Pulmonary edema +Hypo/Hypertension +Dyspnea +Palpitations +Headache +Blurred vision +Dizziness/vertigo +Syncope Special Considerations: Not indicated for use during pregnancy. Use in pts with acute R sided MI may cause profound hypotension, use caution. Onset & Duration: SL route onset 1-3 min, duration 30 min. Paste transdermal route onset 40-60 min, duration 18-24 hrs. D 59 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 NITROGLYCERIN SL Protocols & Dose: Chest Pain/STEMI (AC4): 0.3/0.4mg SL, q5 minutes as needed *Info box: When treating suspected/confirmed MI, continue NTG even if pt relates they are pain free and the systolic BP is manageable CHF/Pulmonary Edema (AC5): 0.3/0.4mg SL, q5 minutes as needed Pediatric Pulmonary Edema (PC3): *pearl: Dose determined after consultation of Medical Control. NITROGLYCERIN PASTE Protocols & Dose: Chest Pain/STEMI (AC4): CHF/Pulmonary Edema (AC5): SBP >100 1 inch SBP >150 1.5 inch SBP >200 2 inch NITROGLYCERIN DRIP Protocols & Dose: D Chest Pain/STEMI (AC4): CHF/Pulmonary Edema (AC5): 10mcg/min, IV/IO Increase by 10mcg/min at 10 minute intervals, keeping systolic BP > 100 **Remember to vent tubing** 60 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 NITROUS OXIDE Class: Action: Analgesic, anesthetic gas The exact mechanism of action of nitrous oxide is unknown. Findings indicate that the analgesic effect of N2O is opioid in nature, and, like morphine, may involve a myriad of neuromodulators in the spinal cord. The anxiolytic effect of N2O, on the other hand, resembles that of benzodiazepines and may be initiated at selected subunits of the γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor. Similarly, the anesthetic effect of N2O may involve actions at GABAA receptors and possibly at Nmethyl-D-aspartate receptors as well. Indications: Moderate to severe pain. Contraindications: -Drug/Alcohol intoxication -AMS -History of COPD -Pneumothorax -Head injury -Abd distention/pain -Recent diving -Suspected GI obstruction Side Effects: +Dizziness +Lightheadedness +AMS +Hallucinations +Nausea/Vomiting Special Considerations: Can potentiate effects of other CNS depressants. Administered as a 50/50 mix with oxygen Pt self-administers ONLY through modified demand valve to reduce the occurrence of adverse effects. Onset & Duration: Immediate onset, effects dissipate within 2-5 min after cessation of administration. Protocols & Dose: D Pain Control (UP11): 50:50 mix if available 61 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 NOREPINEPHRINE BITARTRATE Common names: Class: Action: Levophed® Vasoconstrictor Similar to epinephrine, norepinephrine has direct agonist effects on effector cells that contain alpha- and beta-receptors. As with other catecholamines, the intracellular action of norepinephrine is mediated via cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), the production of which is augmented by beta stimulation and attenuated by alpha stimulation. The primary pharmacodynamic effects of norepinephrine are cardiac stimulation, particularly at lower doses, and vasoconstriction, which tends to predominate with moderate to higher doses of the drug. The hemodynamic consequences of norepinephrine's cardiovascular stimulation include increases in systolic, diastolic, and pulse pressures. Cardiac output is generally unaffected, although it can be decreased, and total peripheral resistance is also elevated. The elevation in resistance and pressure result in reflex vagal activity, which slows the heart rate and increases stroke volume. The elevation in vascular tone or resistance reduces blood flow to the major abdominal organs as well as to skeletal muscle. As with epinephrine, however, coronary blood flow is substantially increased secondary to the indirect effects of alpha stimulation. Indications: Profound, symptomatic hypotension refractory to fluid replacement therapy, particularly in sepsis. Contraindications: -Uncorrected hypovolemia -Hypertension Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Brady/tachycardia +Pulmonary edema +Hypertension +Dyspnea +Palpitations/PVCs +Angina +ST segment changes +Vomiting +Headache +Diaphoresis +Tissue necrosis Special Considerations: Extravasation can cause tissue ischemia, necrosis, and/or gangrene. Volume depletion should always be corrected before initiating vasopressor therapy. Some formulations contain sulfites and should be used with caution in pts with known hypersensitivity to sulfites. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset, duration is limited to 1-2 min after cessation of infusion. Protocols & Dose: Hypotension/Shock (AM5): 4mcg/min IV/IO, Maximum 20mcg/min, Titrate to effect Pediatric Hypotension/Shock (PM3): (2-12 yrs) 0.1-2mcg/kg/min IV Start: 0.05-0.1mcg/kg/min IV, titrate to effect; max 2mcg/kg/min Suspected Sepsis (UP15): 4mcg/minute on infusion pump to goal of MAP > 65mmHg D 62 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ONDANSETRON Common names: Class: Action: Zofran® Antiemetic The process of nausea and vomiting is coordinated by the vomiting center in the central nervous system. Stimulation can be initiated centrally in areas such as the cerebral cortex and otic or vestibular nerves, or peripherally in areas such as the oropharynx, mediastinum, gastrointestinal track, renal pelvis, peritoneum, or genitalia. Centrally, ondansetron blocks the 5-hydroxytryptamine, type 3 (5-HT3) receptor site at the chemoreceptor trigger zone, stopping the vomiting reflex produced by the vomiting center. Peripherally, ondansetron preferentially blocks the serotonin 5-HT3 receptors at the peripheral vagal nerve terminals in the intestines, blocking the signal transmission to the central nervous system and antagonizing the effects of serotonin. Indications: Nausea and vomiting Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Prolonged QT syndrome Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Bronchospasm +Brady/tachycardia +Arrhythmia including v-fib/torsades +AV block +Angioedema +Laryngospasm +Hypotension +Headache +Dyspnea +Drowsiness +ST segment changes Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with liver impairment. Avoid in pts with prolonged QT as drug is known to prolong QT and may lead to arrhythmia. Onset & Duration: IV route onset 5 min, peak 10 min, half-life 3-6 hrs. ODT route onset within minutes, peak 1 hr, half-life 3-6 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Abdominal Pain/Vomiting & Diarrhea (UP3): (Adult) 4-8mg IV/IO/ODT/IM If initial dose 4mg, q15 minutes x1 if needed (Pedi) 4mg ODT; Max 4mg Repeat & Max: D Adult max: 8mg every 8 hours, 24 mg/day max Pediatric max: 0.15mg/kg, 16 mg/day max 63 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 OXYGEN Class: Action: Gas, oxidizing agent The majority of oxygen molecules are carried from the lungs to the body’s tissues by a specialized transport system, which relies on the erythrocyte. Erythrocytes contain a metalloprotein, hemoglobin, which serves to bind oxygen molecules to the erythrocyte. Heme is the portion of hemoglobin that contains iron, and it is heme that binds oxygen. One hemoglobin molecule contains iron-containing heme molecules, and because of this, each hemoglobin molecule is capable of carrying up to four molecules of oxygen. As oxygen diffuses across the respiratory membrane from the alveolus to the capillary, it also diffuses into the red blood cell and is bound by hemoglobin. The following reversible chemical reaction describes the production of the final product, oxyhemoglobin (Hb–O2), which is formed when oxygen binds to hemoglobin. Oxyhemoglobin is a bright red-colored molecule that contributes to the bright red color of oxygenated blood. Indications: Hypoxia; passive application during cardiac arrest and airway procedures; as an adjunct for other therapies. Contraindications: -None in emergency situations Side Effects: +Vasoconstriction Special Considerations: Oxygen should be used sparingly and titrated to 94-99% saturation to avoid adverse effects. Adverse effects may occur with prolonged use in pts with COPD. Use caution in neonates, toxicity can lead to complications such as blindness and chronic disease. Excessive oxygen can cause vasoconstriction that may reduce cellular profusion, and is linked to reperfusion injury secondary to free radicals. Onset & Duration: Absorption is highly dependent on pt’s respiratory and circulatory status. Protocols & Dose: Cardiac/Airway Protocols (AC1)(AC3)(AC8)(AC11)(AR3)(PC1)(PC4)(PC6): Passive O2 @ 15L NC if available Various other protocols: Supplement as appropriate, titrate to saturation ≥ 90%, preferably ≥ 94% D 64 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 OXYMETAZOLINE HCL Common names: Class: Action: Afrin® Sympathomimetic, vasoconstrictor, nasal decongestant Oxymetazoline stimulates alpha adrenergic receptors which cause intense vasoconstriction. When administered intranasally, this action promotes drainage and improves ventilation. Indications: Active nose bleed that is unrelated to significant trauma. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Hypertension -Closed-angle glaucoma Side Effects: +Brady/tachycardia +Coma +Visual impairment +Hyper/hypotension +Respiratory distress +Nausea/vomiting +Nasal irritation Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with existing cardiovascular disease or uncontrolled hypertension. Onset & Duration: Immediate onset. Protocols & Dose: D Epistaxis (UP9): 1 Sprays to Nostril, Followed by Direct Pressure 65 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 OXYTOCIN Common names: Class: Action: Pitocin® Hormone Synthetic oxytocin elicits the same pharmacological response produced by endogenous oxytocin, with cervical dilation, parity, and gestational age as predictors of the dose response to oxytocin administration. Oxytocin increases the sodium permeability of uterine myofibrils, indirectly stimulating contraction of the uterine smooth muscle. The uterus responds to oxytocin more readily in the presence of high estrogen concentrations and with the increased duration of pregnancy. Oxytocin increases the amplitude and frequency of uterine contractions, which transiently impede uterine blood flow and decrease cervical activity, causing dilation and effacement of the cervix. Indications: Severe, uncontrolled, post-partum hemorrhage. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -GI bleeding/bloody stools -Abd pain -Constipation/GI obstruction Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Uterine rupture +Arrhythmia +Cervical laceration +Pulmonary edema +Nausea/vomiting +Hypertension +Blurred vision +Bleeding Special Considerations: Complications from the administration of oxytocin can lead to complete infertility or death, and should be reserved only be when significant bleeding cannot be controlled by other measures, posing an immediate life-threat. It is vital to assure delivery of the baby and placenta are complete prior to administration. Onset & Duration: Immediate onset, effects subsiding ~1 hr after cessation of infusion. Protocols & Dose: D Childbirth/Labor (AO1): 20units IV/IO, Mix 20units in 1000mL LR, 30-60gtts/min 66 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 PROMETHAZINE HCL Common names: Class: Action: Phenergan® Antiemetic, antihistamine, anticholinergic. The predominant action of promethazine is antagonism of H1-receptors. Like other H1-antagonists, promethazine does not prevent the release of histamine, as do cromolyn and nedocromil, but competes with free histamine for binding at H1receptor sites. Histamine receptors in the GI tract, uterus, large blood vessels, and bronchial muscle are blocked. The relief of motion sickness and nausea/vomiting appear to be related to central anticholinergic actions and may implicate activity on the medullary chemoreceptor trigger zone. Other CNS receptor sites can also be affected, since promethazine is believed to indirectly reduce stimuli to the brain stem reticular system. Indications: Nausea/vomiting refractory to other antiemetic treatments, or when other antiemetics are contraindicated. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -History of seizures -Hyperthermia Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Brady/tachycardia +Sedation/hallucinations +Dyspnea +Dystonia +Injection site reaction +Prolonged QT +Elevated blood glucose +Tissue necrosis +Neuroleptic malignant syndrome Special Considerations: May potentiate other CNS depressants and should be used with caution in pts acutely intoxicated. Can cause extreme irritation at the site of administration, consider diluting prior to administering IV/IO to avoid pt discomfort. Onset & Duration: Onset 3-5 min, duration 4-6 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Abdominal Pain/Vomiting & Diarrhea (UP3): (Adult) 12.5mg IV/IO/IM, May repeat x1 if needed (Pedi) 6.25mg IV/IO/IM **Dilute medication with 10mL Saline, SLOW IV PUSH** D 67 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 PROPOFOL Common names: Class: Action: Diprivan® Nonbarbiturate anesthetic Propofol appears to inhibit the NMDA subtype of glutamate receptors by channel gating modulation and has agonistic activity at the GABAA receptor. Propofol enhances the amplitude of currents evoked by subthreshold concentrations of gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA) and directly activates the GABAA receptor in the absence of GABA. The anesthetic and amnesic properties of propofol may be wholly or partly a result of NMDA-mediated excitatory neurotransmission depression. Indications: The use of propofol is limited to interfacility transfer of pts who are already intubated and sedated for transfer by the referring facility. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Sulfite hypersensitivity -Hemodynamic instability Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Apnea +Brady/tachycardia +Arrhythmia including v-fib +Bronchospasm/wheezing +Increased ICP +Laryngospasm +Pulmonary edema +Angioedema +Hypotension +Heart block +ST segment changes Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with renal compromise. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset ~ 30 seconds, duration of effects last 3-5 min after cessation of infusion. Protocols & Dose: D Propofol: *Sedation 25-100 mcg/kg/min *Induction 1-2.5 mg/kg *Maintenance 50-200 mcg/kg/min 68 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 RANITIDINE HCL Common names: Class: Action: Zantac® H2 antagonist Ranitidine competitively inhibits the binding of histamine to receptors on gastric parietal cells (designated as the H2-receptor), thus reducing basal and nocturnal gastric acid secretion. The drug also decreases the amount of gastric acid released in response to stimuli such as food, caffeine, insulin, betazole, or pentagastrin. Ranitidine reduces the total volume of gastric juice, thereby indirectly decreasing pepsin secretion. Indications: Mild to severe allergic reaction. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Angioedema +Bronchospasm +Bradycardia +Dizziness +Headache Special Considerations: Use caution in pts with liver or renal impairment. Onset & Duration: Rapid onset IV, duration of effects 8-12 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis (AM1): 50mg IV/IO/IM Pediatric Allergic Reaction (PM1): 1mg/kg IV/IO/IM, Maximum 50mg D 69 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 ROCURONIUM BROMIDE Class: Action: Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker, paralytic Nondepolarizing agents such as rocuronium produce skeletal muscle paralysis by competing with acetylcholine for cholinergic receptor sites at the myoneural junction. Unlike depolarizing agents, rocuronium has little agonist activity at the motor endplate. Skeletal muscle relaxation proceeds in predictable order, starting with muscles associated with fine movements, e.g., eyes, face, and neck. These are followed by muscles of the limbs, chest, and abdomen and, finally, the diaphragm. Indications: Airway compromise/impending compromise requiring anesthesia to secure intubation; to reduce shivering and maintain hypothermic state during interfacility transfer of pts who are already intubated and undergoing induced hypothermia. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Apnea +Brady/tachycardia +Angioedema +Bronchospasm +Malignant hyperthermia +Prolonged QT +Hypo/hypertension +Nausea/vomiting +Flushing Special Considerations: Only for use in pts > 12 yrs. May exacerbate asthma symptoms. Use caution in pts with family history of malignant hyperthermia. Severe acid/base imbalances from various disease processes may increase the effects of rocuronium. Onset & Duration: Onset 1-8 min, duration of effects dose dependent ranging 12-30 min. Protocols & Dose: Target Temperature Management-Interfacility (AC10): 1mg/kg IV/IO Airway, Drug Assisted (AR3): 1.5mg/kg IV/IO D 70 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 SODIUM BICARBONATE Class: Action: Electrolyte, alkalinizing agent Immediately raises the pH of blood plasma by buffering excess hydrogen ions. This occurs because the Na+ (sodium) and the HCO3- (bicarbonate ion) separate in solution. While separate the negative charge on the bicarbonate is able to accept (and will prefer over sodium) hydrogen ions. The HCO3- then becomes H2CO3 which the body will turn into water and CO2. In tricyclic overdoses the Na+ ion is important also in its use to attempt to overcome the sodium blockade that occurs. Indications: Acute abnormal EKG changes secondary to renal failure, crush syndrome, and tricyclic antidepressant overdose; cardiac arrest of dialysis pt. Contraindications: -None when indicated criteria is met Side Effects: +Metabolic alkalosis +Hypokalemia Special Considerations: Administration may deactivate other medications, timing should be spaced from other medications. Onset & Duration: Immediate onset, duration 1-2 hr. Protocols & Dose: Dialysis/Renal Failure (AM3): 50mEq IV/IO Crush Syndrome Trauma (TB3): (Adult) 50mEq IV/IO (Pedi) 1mEq/kg IV/IO Overdose/Toxic Ingestion (TE7): (Adult) 50mEq IV/IO, q10 min as needed (Pedi) 1mEq/kg IV/IO, q10 min as needed Behavioral (UP6): Police Custody (UP12): *pearl: If pt suspected of EDS suffers cardiac arrest, consider early D 71 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 SUCCINYLCHOLINE CHLORIDE Class: Action: Depolarizing neuromuscular blocker, skeletal muscle relaxant Succinylcholine is a depolarizing skeletal muscle relaxant. It competes with acetylcholine for the cholinergic receptors of the motor endplate, and, like acetylcholine, it combines with these receptors to produce depolarization. Succinylcholine, however, causes a more prolonged depolarization than acetylcholine because it has a high affinity for the cholinergic receptor and a strong resistance to acetylcholinesterase. Depolarization results in fasciculation of the skeletal muscles followed by muscle paralysis. Neuromuscular transmission is inhibited as long as an adequate concentration of succinylcholine remains at the receptor site. The paralysis following succinylcholine administration is selective. Initially, paralysis involves the levator muscles of the face and muscles of the glottis. Paralysis consecutively involves the intercostals, the diaphragm, and all other skeletal muscles. Recovery of muscles generally occurs in the reverse order. Indications: Airway compromise/impending compromise requiring anesthesia to secure intubation. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Known neuromuscular disease -Non-acute burns > 24 hrs -History of malignant hyperthermia syndrome Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Apnea +Brady/tachycardia +Angioedema +Bronchospasm +Malignant hyperthermia +Increased ICP +Hypo/hypertension Special Considerations: Only for use in pts > 12 yrs. Muscle fasciculations caused by succinylcholine may exacerbate bone fractures, another induction agent should be considered if appropriate. Fasciculations may also cause vomiting, compromising airway, suction equipment should be at hand. Severe acid/base imbalances from various disease processes may increase the effects of succinylcholine. Some ethnicities are more prone malignant hyperthermia, use caution in certain populations, like those descended from the Lumbee Tribe. Onset & Duration: Onset < 1 min, duration 2-3 min. Protocols & Dose: D Airway, Drug Assisted (AR3): 2mg/kg IV/IO, May repeat x1 72 | P a g e Revised April 2020 Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 TRANEXAMIC ACID Common names: Class: Action: TXA, Lysteda®, Cyklokapron® Antifibrinolytic, hemostatic agent Tranexamic acid is a hemostatic agent and is a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine. Tranexamic acid binds to the lysine binding site for fibrin on the plasminogen/plasmin molecule. Plasminogen has 4—5 binding sites with low affinity for tranexamic acid and 1 high affinity binding site. The high affinity binding site is involved with the binding of plasminogen to fibrin. Saturation of this high affinity binding site by tranexamic acid displaces plasminogen from the surface of fibrin. This prevents the binding of fibrin to plasmin and preserves and stabilizes the matrix structure of fibrin and diminishes the ability of plasmin to lyse fibrin clots. Indications: Suspected internal hemorrhage with SBP < 90 or HR > 120, or active bleeding. Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Active thromboembolic disease (PE, DVT, etc.) -Suspected intercranial bleeding -Non-acute phase of injury, > 3 hrs old Side Effects: +Anaphylaxis +Seizures +Thrombi +Headache +Dyspnea +Hypotension +Pain +Nausea/vomiting Special Considerations: Pt’s vitals may not reflect shock when pt is taking certain cardiac medications, contact medical control for deviation in these situations. Onset & Duration: Onset and peak < 30 min, half-life 2 hrs. Protocols & Dose: Multiple Trauma (TB6): (Adult) 1g over 10 minutes IV/IO (Pedi) <18yrs: 15mg/kg IV/IO; over 20min, max 1g Epistaxis (UP9): (Adult) Topical TXA D 73 | P a g e Onslow County EMS; Policy 22 D Revised April 2020 74 | P a g e