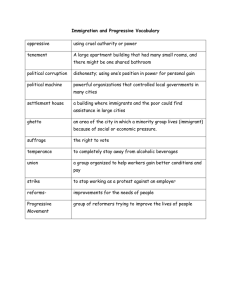
Warm-up 1. What happened in colonial New England town meetings (covenant community)? 2. What do the battles of Lexington and Concord and Fort Sumter have in common? 3. What two things did James Madison write? 4. What did the Compromise of 1877 end? 5. What’s one difference between W.E.B. DuBois and Booker T. Washington? Gilded Age and Progressive Movement Gilded Age (1877-1890): period of rapid industrialization, economic growth, immigration, and urbanization Progressive Movement (1890-1920): Solving the social problems of immigration, urbanization and industrialization. Problems of the Gilded Age • Agricultural expansion was accomplished through wars against the native Americans, leading to new federal Indian policies. • Industrial development brought great fortunes to a few and raised the standard of living for millions of Americans but also brought about the rise of national labor unions and clashes between industry and labor. • Social problems in rural and urban settings gave rise to thirdparty movements and the beginning of the Progressive Movement. Causes of the Progressive Movement 1. Excesses of the Gilded Age • Income disparity: rich people are really rich; poor people are really poor • Robber Barons: businessmen who abused workers to benefit themselves (ex: Rockefeller, Carnegie) • Corruption: abuse of power Causes of the Progressive Movement 2. Working Conditions • Dangerous working conditions • Child labor • Long hours, low wages, no job security, no benefits • Company towns took advantage of families keeping them as wage slaves • Inequality in employment of women Progressive Presidents • Theodore Roosevelt’s “Square Deal”: Emphasized social reform and attacked unfair business practices • William Howard Taft was actually seen as a Progressive failure. • Woodrow Wilson’s “New Freedom”: Emphasized reform for banking, taxes, and business. Goals of the Progressive Movement • Government controlled by people • Guaranteed economic opportunities through government regulation • Elimination of social injustices Progressive Accomplishments Progressive Accomplishments in Local Governments • New government positions to meet needs of increasing urbanization (city commissioner and council manager) • Attempted to fight corruption and respond to the people’s needs. Progressive Accomplishments in State Governments • Referendum: all citizens of a state get to vote on a piece of legislation • Initiative: state citizens get to propose legislation to the state • Recall: state citizens get to remove an elected official before his term is expired (similar to impeachment) What are all 3 of these increasing? Think about what Andrew Jackson did. Progressive Accomplishments in Elections • Primary elections: people of a political party get to decide their candidate in elections • 17th Amendment: U.S. Senators are elected (previously were chosen by state legislatures) • Secret ballot: voters’ choices are anonymous What word that starts with “c” do these limit? Progressive Accomplishments in Child Labor • Muckrakers (literally “poop” rakers) exposed problems in society like child labor by writing news articles and publishing photographs. • Helped push child labor laws in many states, which banned the use of children as workers Impact of Labor Unions Labor unions were formed to demand rights for workers: better pay, fewer hours, safe working conditions, and benefits. Labor Unions • Knights of Labor: America’s first major union • It accepted all workers—skilled and unskilled. • American Federation of Labor (founded by Samuel Gompers): a craft union which only accepted skilled laborers and was more prone to violence. Labor Unions • American Railway Union (founded by Eugene V. Debs): skilled and unskilled workers in railroad • had a successful but violent strike in 1894 (Pullman Strike) • Industrial Ladies’ Garment Workers Union: demanded better conditions in textile industry. • Gained popularity after Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire in 1911 Labor Strikes • Haymarket Square, 1886, Chicago • Homestead Strike, 1892, outside of Pittsburgh • Pullman Strike, 1894, Chicago • These strikes were all violent and led to public fear of labor unions. While many were sympathetic to union causes, they did not like the perceived lawless and anarchist tendencies. An anarchist threw a bomb into a Chicago crowd protesting for an 8-hour workday during the Haymarket Square Riot. 7 policemen and 4 civilians were killed. Gains of Labor Unions • Limited work hours • Regulated work conditions • Preserved rights of unions to organize Antitrust Laws • Trust: a monopoly; one business controls everything • Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890): Prevents any business structure that “restrains trade” (monopolies) • unsuccessful as it was difficult to enforce. • Clayton Anti-Trust Act (1914): Expands Sherman Anti-Trust Act; outlaws pricefixing; exempts unions from Sherman Act Women’s Suffrage • Was a forerunner of modern protest movement • Benefited from strong leadership (Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton) • Encouraged women to enter the labor force during World War I • Resulted in 19th Amendment to the Constitution, which gave women the right to vote Anthony and Stanton: “A Friendship that Changed the World What if you lived in the 1890s and 1900s? Create a short story of your life if you lived during the Progressive Era. Include in your story the following: • As a lower-class worker, how did luxurious lifestyles of the rich of the Gilded Age and your poor working conditions affect you? • How did the presidencies of Teddy Roosevelt and Woodrow Wilson affect you as a worker? • How did you gain more voting rights as a citizen of your state? Think of referendum, recall, etc. • How did labor unions and child labor laws affect you and your workplace? • Say you work for Rockefeller’s Standard Oil Company. How did Anti-Trust Laws affect you? • How did the 19th amendment affect you or women around you?