k g k sch emdoZWliZkBkZWFyYm9ybnNjaG9vbHMub3Jn Electrons and Energy levels reading passage a
advertisement

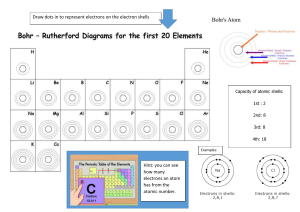
Electrons and Energy Levels I. Electrons are the negatively charged particles of an atom. All of the electrons of an atom create a negative charge that balances the positive charge of the protons in the atomic nucleus. Electrons are extremely small compared to all of the other parts of the atom. 1) What are 3 basic things we need to know about electrons? _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ II. Electrons are located in clouds that surround the nucleus of an atom. These clouds are specific distances away from the nucleus. These clouds are organized into shells or energy levels. 2) What are electrons located in the atom? _____________________________________________________ 3) What are 2 things that describe atomic clouds? ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ III. Because electrons move so quickly, it is impossible to see where they are at a specific moment in time. Electrons zip around in any direction (upwards, downwards, or sidewards), but they stay in their shell. Those shells, energy levels or orbitals, have specific distances from the nucleus. 4) Do electrons revolve around the nucleus OR do they have a different kind of movement? How? ____________________________________________________ _ 5) Why is it impossible to see where they are at a specific moment in time? ___________________________________________________ 6) Examine the image: What is an orbital? ___________________________________________________ 7) What is an energy level? ___________________________________________________ 8) Which energy level is higher n=1 or n=4? IV. After years of experiments, scientists discovered specific areas where electrons are likely to be found. The overall shape of the shells (or energy levels) changes depending on how many electrons an element has. The higher the atomic number, the more shells and electrons an atom will have. 9) What determines the overall shape of the shells in an atom? __________________________________________ 10) Which atom has more shells? ________________________________________ V. According to Bohr's atomic model, electrons revolve in fixed paths around the nucleus . He called these paths “shells” or energy levels. Shells or energy levels are represented by small n. The first shell or energy level is represented by n = 1 or K The second shell or energy level is represented by n = 2 or L The third shell or energy level is represented by n = 3 or M The 4th shell or energy level is represented by n = 4 or N The 5th shell or energy level is represented by n = 5 or O The 6th shell or energy level is represented by n = 6 or P The 7th shell or energy level is represented by n = 7 or Q VI. According to Bohr, an electron can jump, suddenly, between energy levels by absorbing or emitting a photon (light particle) with a precise wavelength. Photons allow the electrons to move between energy states. When an electron is hit by a photon of light, it absorbs the quanta of energy the photon was carrying and moves to a higher energy state. Also, an electron can emit a photon of energy and move down to a lower energy level. 11) How are energy levels represented in Bohr’s model? ___________________________________________________________________ 12) How is the first energy level represented? ___________________________________________________________________ 13) How is the 4th energy level represented? ___________________________________________________________________ 14) According to Bohr’s theory of electrons, what allows electrons to jump from one energy level to another? ___________________________________________________________________ 15) What happens when a photon hits an electron? ___________________________________________________________________ 16) How does an electron move down to a lower energy level? ___________________________________________________________________ 17) What is a photon? ___________________________________________________________________