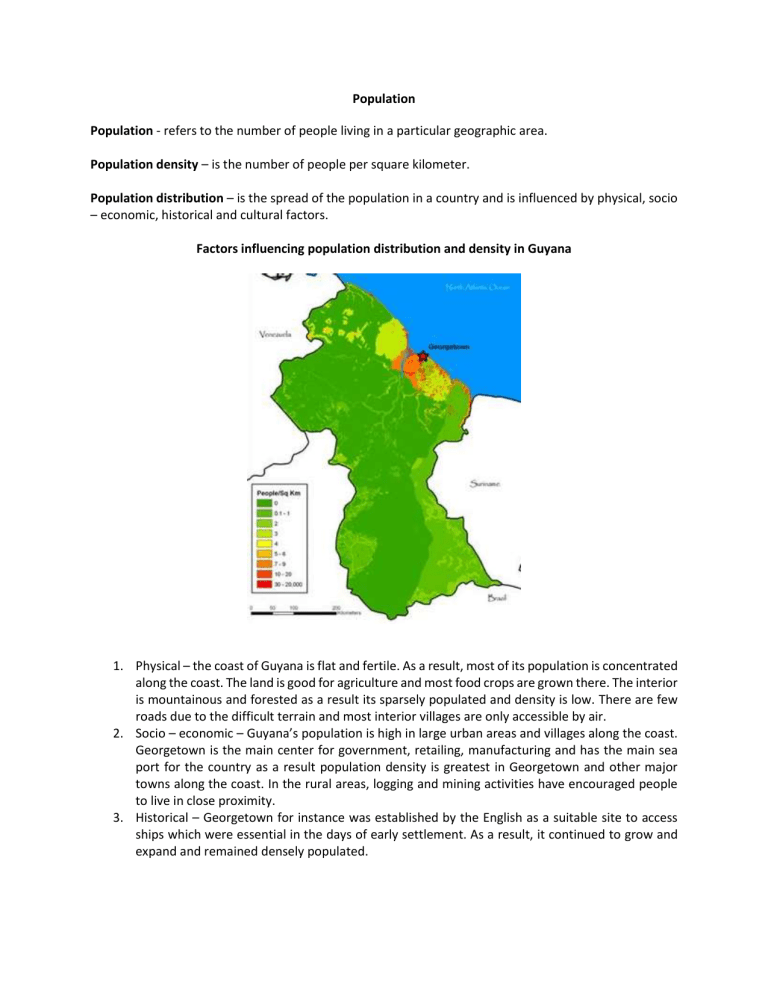
Population Population - refers to the number of people living in a particular geographic area. Population density – is the number of people per square kilometer. Population distribution – is the spread of the population in a country and is influenced by physical, socio – economic, historical and cultural factors. Factors influencing population distribution and density in Guyana 1. Physical – the coast of Guyana is flat and fertile. As a result, most of its population is concentrated along the coast. The land is good for agriculture and most food crops are grown there. The interior is mountainous and forested as a result its sparsely populated and density is low. There are few roads due to the difficult terrain and most interior villages are only accessible by air. 2. Socio – economic – Guyana’s population is high in large urban areas and villages along the coast. Georgetown is the main center for government, retailing, manufacturing and has the main sea port for the country as a result population density is greatest in Georgetown and other major towns along the coast. In the rural areas, logging and mining activities have encouraged people to live in close proximity. 3. Historical – Georgetown for instance was established by the English as a suitable site to access ships which were essential in the days of early settlement. As a result, it continued to grow and expand and remained densely populated. 4. Cultural – many indigenous people in Guyana prefer to live as their forefathers did and continued to live in small villages in the interior. The vast majority lives on the coast in densely packed villages and towns and enjoy festivities and customs. Dot and Choropleth Maps Dot maps – dost are used to represent an amount of people. They give a good visual impression of population density. Choropleth maps – shows the average population density in each administrative area. Population Pyramid A population pyramid, also called an age pyramid or age picture diagram, is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population (typically that of a country or region of the world), which forms the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing. Guyana Population Pyramid Exercise 1 Study the population pyramid of Guyana and answer the questions below. 1. Guyana has an aging population. 2. More than 50% of the population is below the age of 45. 3. There are more males than females over the age of 50. 4. Guyana has a youthful population. 5. What are the advantages of Guyana’s large youthful population? Factors influencing Population Growth in the Caribbean and China The Caribbean China Birth Rate Factors In general, the birth rate has been low due largely to lower fertility rate. In Barbados, the birth rate per 1,000 is 1.1% Death Rate The death rate in the Caribbean has been declining since medical care has improved, but there are more elderly people. 2016 Jamaica, the death rate in 6.6 per 1000. The rate of natural increase in the Caribbean is lower because of falling birth rates. In 2016, China’s birth rate was 12.4 births per 1000. The “one child policy” was successful in reducing birth rate since China has the largest population in the world. Even with the now ‘two child policy’, birth rate is still falling. China has a slightly higher death rate when compared to the Caribbean, 2016 figures was 7.7 deaths per 1000. Natural Increase Migration Most Caribbean nationals migrate to the USA, Canada and Britain. This is due to its close proximity and historical connections. There is a smaller inflow of migrants from China and India coming to work in the Caribbean. Fertility Rate Fertility rate in the Caribbean has decreased due to birth control measures, more working women and fewer families in the agriculture sector. As living conditions and medical care have improved, life expectancy has increased from 69 to 76. All Caribbean governments promote public health to increase life expectancy and reduce infant mortality. Life Expectancy Government Policies Rate of natural increase of China fell gradually from 26.47 per 1000 population in 1970 to 5.66 per 1000 in 2015. Like the Caribbean, this is due to falling birth rates. Due to China’s economic growth, there has been a massive increase in migration, both internal and external. Within China millions of rural workers have migrated to the cities. Outside China, many Chinese have migrated to other parts of the world such as Australia, Malaysia, the USA and Canada. Like the Caribbean, fertility rate in China has decreased. Figures show a decrease from 5.9 in 1970 to 1.7 in 2010. WHO figures have show that Chinese life expectancy rate is also 76 as in the Caribbean. In China, government policies were introduced to reduce growth rate e.g. The One Child and Two child policies, discouraging early marriages, imposing penalties on those with than one child. Migration Human migration is the movement by people from one place to another with the intention of settling, permanently in the new location. In Migration - to move or settle into a different part of one's country or home territory e.g. Persons moving from Mahaica to live in Georgetown. Out Migration – to move in settle in a different country e.g. Immigrating to the United States from Guyana. Types of Migration 1. Regional – people migrating within a particular geographic area e.g. Migration within CARICOM countries. 2. International – people migrating across the world or from continent to continent e.g. Guyanese migrating to the United States. Reasons for In Migration Push Factors 1. Lack of job opportunities – fewer industries in the rural areas 2. Lack of educational opportunities. 3. Lack of social services. Pull factors 1. Availability of jobs - e.g. in Georgetown, there are numerous stores, commercial activities, banks, industries providing jobs. 2. Availability of educational facilities e.g. in Georgetown there are colleges, universities, etc. 3. Availability of social services e.g. hospitals. Reasons for Out Migration Push Factors 1. Political disturbances – in the late 1980s, some Guyanese were forced to migrate to North America because of political disturbances when there were riots and killing. 2. Low wages and lack of jobs – in the 1980s, in Guyana high unemployment existed due to the poor performance of several sectors such as agriculture, and industrial sectors due in part to the unstable political climate. 3. Poor social conditions in territories such as Guyana in the 1970s and 80s caused people to migrate to North America in the hopes of better education and health services. Pull Factors 1. Stable political climate in the United States, Canada and England caused nationals from countries such as Guyana, Trinidad and Jamaica to seek security. In these developed countries democracy exists with freedom and justice. 2. In North America, job opportunities are widely available in certain sectors of the labour market creating opening for better employment and skilled professionals. There are opportunities in the north for unskilled people as well as skilled give examples. Pilot training, law, politics 3. In North America, there are some of the best universities and hospitals. Specialized fields for higher education at the masters and doctorate level. Consequences of In Migration 1. When people for instance migrate from Mahaica in Guyana to Georgetown, especially young people agriculture is affected since there are fewer persons who might be inclined to practice agriculture. 2. It will cause slower or lower population growth since some people of working age move first then they may send for their parents, children and other relatives to join them. 3. Abandoned agriculture lands leads to soil erosion. Consequences of Out Migration 1. Slower population growth – if there is net outward migration, population is reduced. In 2003, Jamaica’s natural population increase was 34,100. There was a net outward migration of 17,700. So, population growth was only 16,400 less than half the natural increase. 2. Brain drain – many of the educated young and healthy people from the Caribbean often migrate to North America and Europe for example, these countries actively recruit teachers and health care workers e.g. nurses and teachers to the UK which cause a shortage of skilled professional. 3. Remittances – most migrants send home money to their families and barrels. Remittances play an important part in the economies of Guyana and Jamaica since they contributes to foreign exchange. 4. Tourism – overseas Caribbean nationals, when they return to their county of birth, are counted as tourists. In Jamaica, they made 6.5% of tourist arrivals in 2003. They spend money on rental cars, restaurants and shopping. Consequences of Out Migration on the host country 1. Caribbean migrants are concentrated in districts such NY or south Florida. Making these areas culturally diverse with Caribbean customs, food, arts, music etc. 2. Many migrants from the Caribbean often migrate because to the US because of that country policy of having 500,000 and so they use their money to establish successful businesses. 3. Caribbean music and carnivals reach all groups in north America. Urbanisation Urbanisation – the increase in the proportion of people living in towns and cities due to rural to urban migration. Urban Growth – is an increase in the size of a city often linked to rural – urban migration. Urban Sprawl – is the expansion of the city into the country side through the growth of suburbs. Exercise Locate Kingston on the map of Jamaica. Causes of Urban Growth in Kingston, Jamaica 1. Suburban developments – development of housing projects in the suburbs of Kingston in areas such as Portmore, Newport and Spanish Town has encouraged people to migrate closer to their places of employment. 2. Natural Increase – a large concentration of population in Kingston has also lead to a large natural increase. This is a result of high birth rates and a low death rate. 3. Migration – people from rural areas of Jamaica continue to migrate to Kingston in the hope of employment and access to social services. Benefits of Urbanisation in Kingston, Jamaica 1. Labour – with migration and natural increase in Kingston, there is a large labour force with a greater choice of skills than in the rural areas. With access to education, people are trained and able to contribute to the development of Jamaica. 2. Commerce – with all the businesses and industrial activities, there is greater spending and availability of customers to buy goods and services. 3. Infrastructure – for government and utility companies it is easier to provide services in the larger populated areas such as Kingston. The area has a modern airport and deep-water harbor. Problems of Urbanisation in Kingston, Jamaica 1. Unemployment and Crime – with the constant influx of migrants to Kingston, the demand for jobs far exceeds availability. As such many young people are not gainfully employed. As a result, gang violence and shootings occur regularly in the city. 2. Congestion – with so many people travelling from the suburbs such as Portmore and Newport, traffic is heavy. Also because of high importation of vehicles, roadways are overcrowded. Some people spend two hours to commute to Kingston. Buses are overcrowded and there is shortage of parking spaces in commercial areas. 3. Poor housing conditions – although good housing areas exists in Kingston, many residents cannot afford to life in these areas. This leads to slums and squatter settlements. In Portmore housing conditions are bad and houses constructed with zinc sheets. There are limited running water, electricity and bathroom facilities. Measures to control or reduce Urbanisation in Kingston, Jamaica 1. Development of housing areas – there has been several private and government housing projects located away from Kingston in areas such as Hatfield and Crofts Hill. Government has built houses and apartments for sale. Additionally, low interest housing loans are available from the government’s National Housing Trust. 2. Rural Development Projects – in rural areas, the government has established farmhouses in areas such as Canaan Mountain. This was done to promote agriculture and settle young farmers. With the creation of agricultural activities, there is hope of curbing rural drift to Kingston. 3. Decentralization of Services – the Jamaican government has built hospitals, schools and improved transport services in several areas away from Kingston. This reduce strain on the facilities available in Kingston.