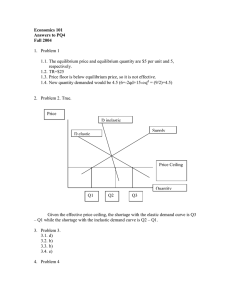
1. A decrease in consumer income decreases the demand for compact discs. As a result of the change to a new equilibrium, there is a(n): a. leftward shift of the supply curve. b. rightward shift of the supply curve. c. upward movement along the supply curve. d. downward movement along the supply curve. ANSWER: d 2. Which of the following would raise both the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity of strawberries? a. A decrease in the demand for strawberries. b. An increase in the demand for strawberries. c. A decrease in the supply of strawberries. d. An increase in the supply of strawberries. ANSWER: b 3. Suppose an increase in symphony tickets prices reduces the total revenue. This is evidence that demand is: a. price elastic. b. price inelastic. c. unitary elastic. d. perfectly elastic. ANSWER: a 4. If a demand curve for a good were completely vertical, it would be considered: a. perfectly elastic. b. perfectly inelastic. c. of unitary elasticity. d. relatively inelastic. ANSWER: b 5. A price ceiling that sets the price of a good below market equilibrium will cause: a. An increase in quantity demanded of the good. b. A decrease in quantity supplied of the good. c. A shortage of the good. d. All of these. ANSWER: d 6. A legally mandated minimum wage is an example of: a. the invisible hand principle. b. a price floor. c. a price ceiling. d. a fringe benefit. ANSWER: b 7. (CHALLENGING) Suppose that the average equilibrium monthly rental price of apartments and rooms in a college town had been steady at $600, but then the college expanded enrollment from 10,000 to 12,000. Suddenly there is a shortage of rental housing at the prevailing price of $600. Which of the following is most likely to be true? a. The shortage occurred because demand increased, and a new market equilibrium will result in higher rental prices and more rental units available on the market. b. The shortage occurred because supply increased, and a new market equilibrium will result in lower rental prices and fewer rental units available on the market. c. The shortage occurred because demand decreased, and a new market equilibrium will result in lower rental prices and fewer rental units available on the market. d. The shortage occurred because demand increased, and a new market equilibrium will result in higher rental prices and fewer rental units available on the market. ANSWER: a 8. In Exhibit 4-2, which of the following might cause a shift from S1 to S2? a. A decrease in input prices. b. A decrease in consumer prices. c. An increase in input prices. d. An increase in consumer income. ANSWER: a 9. Which of the graphs in the figure illustrates an increase in buyers' income, assuming that good X is a normal good? a. Graph A. b. Graph B. c. Graph C. d. None of these. ANSWER: a 10. Which of the graphs in Exhibit 4-4 represents a decrease in the price of a factor of production? a. Graph A. b. Graph B. c. Graph C. d. None of these. ANSWER: c 11. (CHALLENGING) Suppose the president of a college argues that a 25 percent tuition increase will raise revenues for the college. It can be concluded that the president thinks that demand to attend this college is: a. elastic. b. inelastic, but not perfectly inelastic. c. unitary elastic. d. perfectly elastic. ANSWER: b 12.(CHALLENGING) Which of the statements below does not describe a demand curve that is unit elastic? a. The percentage change in the quantity demanded = percentage change in product price. b. An increase in product price will not change total revenue. c. The price elasticity of demand equals one. d. A change in price does not change quantity demanded. e. A decrease in product price will not change total revenue. ANSWER: d 13. If Sam, the Pizza Man, lowers the price of his pizzas from $6 to $5 and finds that sales increase from 400 to 600 pizzas per week, then the demand for Sam's pizzas in this range is: a. price inelastic. b. price elastic. c. unit elastic. d. cross elastic. e. income inelastic. ANSWER: b 14. Elasticity measures how "sensitive" consumers are by measuring their change in ____ as the price of the product changes. a. attitude b. income c. quantity demanded d. supply e. taxes ANSWER: c 15. If the quantity of bread demanded rises 2 percent when the price of bread declines 10 percent, then the price elasticity of demand is: a. 0.2. b. 1. c. 2. d. 10. e. Cannot be determined. ANSWER: a 16. (CHALLENGING) If the equilibrium price of bread is $2 and the government imposes a $1.50 price ceiling on the price of bread, then: a. more bread will be produced. b. there will be a shortage of bread. c. the demand for bread will decrease. d. producers will charge $0.50 for bread. e. $0.50 in tax revenue will be paid for each unit of bread. ANSWER: b 17. (CHALLENGING) Rent controls create distortions in the housing market by: a. increasing rents received by landlords b. raising property values. c. encouraging landlords to overspend for maintenance. d. discouraging new housing construction. e. increasing the supply of housing in the long run. ANSWER: d 18. In Exhibit 4-9 the equilibrium price and quantity in the market are: a. $5.50, 200. b. $1.50, 300. c. $2.00, 100. d. $1.00, 200. ANSWER: d 19. In Exhibit 4-9, which of the following would occur at a price of $2.00? a. Inventories would put upward pressure on price. b. Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied, putting downward pressure on price. c. Inventories would put downward pressure on price. d. The surplus would be so small that there would be only slight downward pressure on price. ANSWER: c 20. Based on the table above, if the price floor is set at $2.00, a. the market is in equilibrium. b. there will be excess quantity demanded. c. there will be excess quantity supplied. d. there is a price ceiling in effect. ANSWER: a