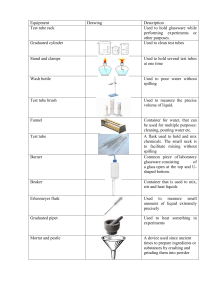
Laboratory Glassware and Equipment Beaker – a piece of glassware in which the opening diameter is approximately the same as the base diameter. i. It is used to hold liquids, and sometimes solids. ii. Graduations on the sides are approximate. iii. These should never be used for measuring volumes, unless you are specifically told you only need an approximate amount. Erlenmeyer Flask – a piece of glassware with the opening diameter significantly smaller than the base diameter. The diameter gradually narrows from the base up to near the top. 1. It is used for holding liquids. 2. It is resistant to splashing when mixing liquids. 3. Graduations on the sides are approximate. Volumetric Flask – a piece of glassware with the opening diameter significantly smaller than the base diameter. The bottom is usually rounded, and there is a line drawn on the next approximately halfway up. 1. It measures an exact amount of a liquid, to two decimal places. (for example, 500.00 mL) 2. It is used for mixing specific concentrations of solutions. Graduated Cylinder – a piece of glassware that is used to determine the volume of a liquid. i. The measurements from a graduated cylinder should be reported to the correct number of decimal places, with the last digit being an estimate. ii. The plastic ring which is around the neck of the cylinder is a safety device to keep it from breaking if it tips over. Burette – used to measure specific amounts of liquids (often determining amounts of acids or bases needed); releasing small amounts of acids or bases into other solutions. Test tube – holds small amounts of liquids for mixing or heating Test tube rack – holding many test tubes filled with chemicals (or for drying after washing) Test tube brush – used to clean the inside of test tubes or graduated cylinder Test tube holder– used for holding test tubes when tubes should not be touched Ring Stand – a heavy metal base with a pole sticking up, used to attach objects to during experiments. The weight attached to the pole MUST be over the base to avoid instability. Metal Ring – a ring with a clamp to attach it to the ring stand, used to support objects during an experiment. Clay Triangle - a triangle of wire, with the center pieces surrounded by tubes. This is used to support a crucible during an experiment. Crucible/Lid – a small porcelain cup and lid used to heat small amounts of material directly over a flame. Bunsen burner – a flamegenerating device, with selfcontained controls for the amount of gas and air proceeding to the reaction. Wire Gauze – supports beakers to be heated by Bunsen burners Watchglass – are for holding small samples or for covering beakers or evaporating dishes Evaporating Dish – used to evaporate excess solvents to create a more concentrated solution Wash bottle – used to wash down specific pieces of equipment with water or keep materials moist. Micropipet– used to measure and dispense very small amounts of liquids. (ex. 0.5 mL) Mortar & pestle– used to grind chemicals to powder Funnel– used to pour liquids into containers with small openings; also used to hold filter paper Triple-Beam Balance – a mechanical balance used to determine the mass of an object, by moving sliders on three bars until the mass on the pan is balanced by the positions of the sliders. 1. When not in use, and the sliders are at the right side of their tracks, the pointer should be exactly on zero. 2. If it needs adjusted, turn the knob under the pan slowly until it reads 0. 3. All readings made by this balance must be reported to 2 decimal places. Analytical Balance – a balance used to determine the mass of an object to a high degree of precision. 1. Readings made by this balance must be reported to 4 decimal places. 2. Because of its high degree of precision, the pan is enclosed in a chamber to eliminate the effect of air currents in the room on the reading. Fume hood - used to ventilate noxious or harmful gases