
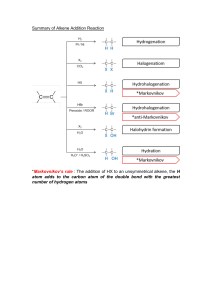
Important notes (Organic Compound) Definition 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Saturated – All the C-C bonds are single Unsaturated – Not all the C-C bonds are single bonds Hydrocarbon – They contain carbon and hydrogen only. Substitution reaction - Atom or group is replaced by another atom or group. Conditions : Ultraviolet light or sunlight Addition reaction – when only one product forms from 2 molecules Homologous series - Family of organic molecules which have the same general formula and similar chemical properties. Characteristics : Trend in physical properties Same/similar chemical properties Same general formula Successive members differ by CH2 Same functional group Structural isomers – Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Cracking – breaks molecules down into smaller ones. General Formula Alkane – CnH2n+2 Alkene – CnH2n Alcohol – CnH2n+1OH / CnH2n+2O Alkyne – triple bond between carbon - CnH2n-2 Esters -CnH2n+1COOH (esters are sweet smelling liquid and form a layer on water like oil) Some chemical equations/reactions conditions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Complete combustion of alkene & alkane– produce carbon dioxide and water Incomplete combustion of alkene & alkane – produce carbon monoxide and water 3. Combustion of alcohol Alcohol + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water Differentiate alkene and alkane – Test : Bromine water Result : Alkene decolourises bromine water, alkane doesn’t Cracking – 450 °C – 800 °C, catalyst (zeolites/aluminosilicates/silica/aluminium oxide/alumina/china/broken pot/chromium oxide), up to 70 atm Esterification –Alcohol + Carboxylic acid Ester (alcohol name followed by carboxylic acid) Conditions : Heat and Catalyst (Concentrated sulfuric acid) Production of alcohol from alkene (Hydration – a type of addition reaction) Reagent = Steam Condition = Catalyst (Phosphoric acid) , 300 °C, 60 atm Equation = Alkene + Steam (H2O) Alcohol Production of alcohol through fermentation Reactants : Glucose/sucrose/starch Process is anaerobic Catalysts : Zymase/Yeast Condition : 37 °C. C6H12O6 2CO2 + C2H5OH How to obtain ethanol from the product : Fractional distillation Comparison of hydration and fermentation Hydration advantages Purer product Faster reaction Continuous process Hydration disadvantages Fossil fuels are non-renewable ‘ Hydration is an equilibrium process meaning lower yield produced Fermentation advantages Renewable feedstock Lower temperature means fossil fuels conserved and lower energy costs Lower pressure 10. Alcohol Carboxylic acid Oxidation reaction Reagent : Acidified potassium manganate (VII) Turns colourless 11. Carboxylic acid and Na2CO3 Bubbles/fizzing 12. Boiling point increases as number of carbon increases. The lighter the hydrocarbon, the more volatile.



![1. [6 points] Provide a Using arrows to show the flow of electrons](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018212695_1-9be6773c23203b7872ba81b45850e99d-300x300.png)