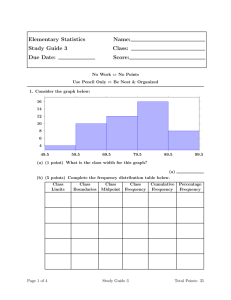
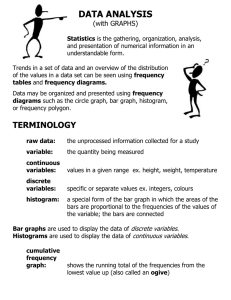
MATH 311 Statistics and probability: Study Unit 3 LECTURER DETAILS Frequency distributions and graphical representation 1. Frequency distributions of continuous data 2. Graphical representation of continuous data 3. Cumulative frequency distributions and polygons 4. Relative frequencies 5. Graphical representations of discrete data Introduction • Data obtained by observation and measurement usually display variation • In order to gain insight in the pattern of variation, we need to order and graphically represent the data • A raw data set does not have immediate meaning Arrays and frequency distributions of data Know the following concepts: Array Frequency Frequency table Example p. 36 • Marks of 30 students (ungrouped data) • Too much to make sense of • Want to divide in classes/ intervals • Rule of thumb: Sturge’s rule: • 𝑘 = 1 + 1,4 ln 𝑛 • 𝑘 is the number of classes (rounded to nearest whole number) • 𝑛 is the number of observations Rule to determine class width: xmax xmin c k Choose “convenient” class width (decimal make it “clumsy” Class width= 10 Number of classes: 7 Example: Histogram The internet usage of 50 students during a certain week is represented as follows: Time spent Number of students Less than 4 hours or [0;4) 2 4 and less than 8 hours or [4;8) 9 8 and less than 12 hours or [8;12) 19 12 and less than 16 hours or [12; 16) 11 16 and less than 20 hours or [16;20) 6 20 and less than 24 hours or [20;24) 3 Histogram Frequency polygon Frequency polygon If only the polygon is shown: Cumulative frequency polygon Time spent (intervals frequency Cumulative frequency 0 0 2 2 9 11 19 30 11 41 6 47 3 50 Example: Cumulative frequency polygon Relative frequency table Example: Relative Frequency polygon Graphical representation of discrete data • Dot plots • Pie charts • Bar charts (different forms) Dot plots Divided bar chart Pie charts • • • • Also known as circle graphs Compare parts to a total Circular regions are subdivided into pie-shaped sectors The area of each sector represents the percent of the total population associated with each category. © North-West University (2012)