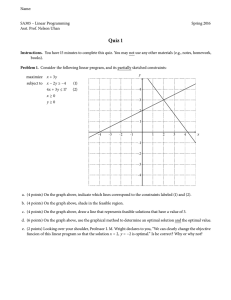
QM Quiz-3 1- The graphical method of solving linear programming can handle only maximizing problems. Select one: a. True b. False 2-The region which satisfies all of the constraints in graphical linear programming is called the Select one: a. region of feasible solutions b. region of optimality c. profit maximization space d. region of optimal solutions 3-A feasible solution in transportation models is one in which all of the supply and demand constraints are satisfied. Select one: a. False b. True 4-A transportation problem with a total supply of 500 and a total demand of 400 will have an optimal solution that leaves 100 units of supply unused. Select one: a. True b. False 5-If an assignment problem consists of 6 workers and 7 projects, Select one: a. each worker will contribute work toward the seventh project b. one worker will be assigned two projects c. one worker will not get a project assignment d. one project will not get a worker assigned 6-In a decision tree, the expected monetary values are computed by working from right to left. Select one: a. False b. True 7-Decision trees Select one: a. are rarely used because one needs specialized software to graph them b. are especially powerful when a sequence of decisions must be made c. give more accurate solutions than decision tables d. give less accurate solutions than decision tables 8-In a decision tree, a square symbol represents a state of nature node. Select one: a. True b. False 9-In terms of decision theory, an occurrence or situation over which the decision maker has no control is called a(n) Select one: a. state of nature b. decision tree c. alternative d. decision under uncertainty 10-Which of the following represents valid constraints in linear programming? Select one: a. All of these are valid linear programming constraints. b. 2X + 7Y ≥ 100 c. 2X ≥ 7X*Y d. 2X * 7Y ≥ 500 11-Which of the following is not needed in order to use the transportation model? Select one: a. the destination points and their demand b. the source points and their capacity c. the fixed costs of source points d. the cost of shipping one unit from each source to each destination 12-In a transportation minimization problem, the negative improvement index associated with a cell indicates that reallocating units to that cell would lower costs. Select one: a. False b. True 13-The corner point solution method requires Select one: a. finding the value of the objective function at the origin b. moving the iso-profit line to the highest level that still touches some part of the feasible region c. finding the coordinates at each corner of the feasible solution space d. moving the iso-profit line to the lowest level that still touches some part of the feasible region 14-The assignment method provides an optimum, one-to-one assignment of jobs to resources. Select one: a. True b. Fals 15-Linear programming is an appropriate problem-solving technique for decisions that have no alternative courses of action. Select one: a. True b. False 16-A transportation problem has 8 origins and 6 destinations. The optimal solution of this problem will fill no more than _______ cells with quantities to be shipped. Select one: a. 48 b. 13 c. 14 d. 2 17-The assignment method is Select one: a. a form of linear programming for optimally assigning tasks or jobs to resources b. a computerized method of determining appropriate tasks for an operation c. a method to highlight overloads in a given work center d. the same thing as the Gantt schedule chart 18-The initial solution to a transportation problem can be generated several ways, so long as Select one: a. all supply and demand conditions are satisfied b. it minimizes cost c. it ignores cost d. degeneracy does not exist 19-Neither the northwest corner rule nor the intuitive method considers shipping cost in making initial allocations. Select one: a. False b. True 20-The transportation model seeks satisfactory, but not necessarily optimal, solutions for shipping goods from several origins to several destinations. Select one: a. False b. True 21-A transportation problem requires exactly as many origins as destinations. Select one: a. True b. False 22-Which of the following combinations of constraints has no feasible region? Select one: a. X + Y > 15 and X – Y < 10 b. X + Y > 100 and X + Y < 50 c. X + Y > 5 and X > 10 d. X > 10 and Y > 20 23-In linear programming, a statement such as "maximize contribution" becomes a(n) Select one: a. decision variable b. objective function c. slack variable d. constraint 24-If demand exceeds supply in a transportation problem, the problem must be balanced by adding a dummy destination with additional supply. Select one: a. False b. True 25-A tabular presentation that shows the outcome for each decision alternative under the various possible states of nature is called a(n) Select one: a. feasible region b. payback period matrix c. decision tree d. payoff table 26-The decision criterion that would be used by an optimistic decision maker solving a problem under conditions of uncertainty would be the Select one: a. minimin criterion b. equally likely criterion c. maximin criterion d. maximax criterion 27-An iso-profit line Select one: a. is parallel to all other iso-profit lines in the same problem b. is a line with the same profit at all points c. can be used to help solve a profit maximizing linear programming problem d. all of these