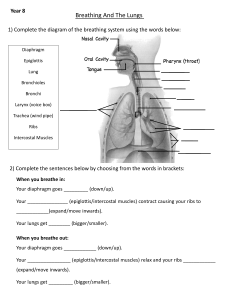
Gharibeh-Introduction to Medicine Mechanics of Respiration The physiology of breathing (ventilation) involves two processes that are vital for providing oxygen to the tissues of the body and removing carbon dioxide from the body. 1-Inspiration Diaphragm is pulled down and flattened (contracts). Ribs move up and outward (muscles of ribs contract). Volume of thoracic cavity increases. Volume of lungs increases. Pressure in lungs decreases. Now the environmental pressure outside the lungs is higher than the pressure inside the lungs. This causes the oxygen rich air to moves into the lungs. 2-Expiration Diaphragm relaxes and returns to resting position. Ribs return to resting position and muscles of ribs relax. Volume of thoracic cavity decreases. Volume of lungs decreases. Pressure in lungs increases. Now it is higher than the environmental pressure outside the body. This causes the air rich in carbon dioxide to rush outside the lungs. Forced breathing is active inspiration and expiration. It occurs during exercises. More muscles are involved. Source: https://teachmephysiology.com/respiratory-system/ventilation/mechanics-of-breathing/