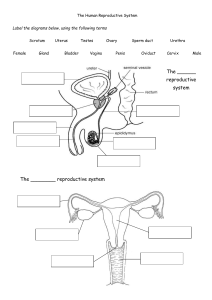
Biology short note for grade 8 Unit 3 Human Biology and Health 3.1. The human reproductive system Introduction What is reproduction? ❖ Is a system consists of reproductive organs for production of offspring. ❖ The reproductive system of humans is by sexual contact between male and female. This reproduction in humans is called sexual reproduction. Types of reproduction 1. Asexual reproduction ❖ Involves only one parent. ❖ There is no gamete (sperm and egg cells) production and no mixing of the cells. i.e no fertilization process. ❖ The offspring are exactly similar with their parents. 2. Sexual reproduction ❖ Involves two parents (usually male and female) ❖ There is gamete production and union of gametes, fertilization. ❖ The offspring are the hybrids of their parents. Primary and secondary sexual characteristics in humans The primary sexual characteristics ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ Human beings are born with a sex that is already determined. Human males are born with penis, testes and scrotum. These structures are called the primary sexual characteristics of male. Human females are born with vagina, ovaries, fallopian tube (oviduct) and uterus. These are the primary sexual characteristics of females. The primary sexual characteristics help to identify between male and female sexes. The Secondary Sexual Characteristics ❖ Is the reproductive age at which the body attains sexual maturity? ❖ It occurs at the age of puberty or adolescence which appears between the ages of 10-15. ❖ During secondary sexual characteristics boys and girls start to experience new characteristics because of sex hormones which bring about these changes. ❖ During puberty or adolescence there is physical, behavioral, social and emotional change. ❖ The sex cells (gametes) and sex hormones in human are produced by glands known as 1 ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ Gonads. The male gonad is called testis and the female gonad is called ovaries. Testis produces sperm cells and sex hormones called testosterone. Ovaries produce egg cells and sex hormones called estrogen and progesterone. 2ry sexual characteristics in Males 2ry sexual characteristics in Females Deepening of voices Enlargement of breast Broadening and widening of chest and shoulder Widening of hips Growing pubic hair( in arm pits & groin) Growing pubic hair( in arm pits & groin) Enlargement of genital organs Enlargement of genital organs. Production of sperm cells and sex hormones Production of egg cells and sex hormones. Nocturnal emission of sperm cells The onset of Menstruation Development of desire to the opposite sex Development of desire to the opposite sex Question; What are the sex hormones of male and female and describe their impact The male and female reproductive organs The male reproductive structure Testes- the male gonad to produce sperm and a hormone called testosterone. ❖ It is made up of a mass of tubules called seminiferous tubules. ❖ The seminiferous tubules are lined up with germinal epithelium that produces sperm cell when they divide. ❖ The follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) which is produced by the pituitary gland stimulates the testis to produce sex hormones. Scrotum – is a sac- like structure or skin-bag hanging down the penis (lower end of the penis). ❖ It has lower temperature than the rest parts of the body. This cools the environment suitable for the maturation of sperm cell and it ventilates the testis. Penis- is an erectile cylindrical organ for sexual intercourse during which it ejaculates semen (sperm and fluid). Epididymis- is a coiled tubule where sperm cell is stored temporarily. Prostate gland- is located below the urinary bladder and secrets a milky alkaline fluid that is used to activate or increase the motility of the sperm cell. 2 ❖ In older men the prostate gland frequently becomes enlarged and contracts the urethra, making urination difficult. Cowper’s gland – are pair of small glands located slightly below the prostate gland on the either side of the urethra. ❖ It has mucous secretions that lubricate the end of penis and urethra. Seminal vesicles- are small pouches behind the bladder which contain stored nutrients during ejaculation to help sperm cell in movement. Urethra – is a tube that passes along the penis through which semen is ejaculated or discharged during sexual intercourse. ❖ It is also responsible for the discharge of the urine. *Ejaculation is the release of semen from the body. Sperm – is a male reproductive cell which is produced by the testis. Semen- is a thick watery fluid that contains sperm cells and seminal fluid. Seminal fluid – is a fluid that is produced by cowper’s gland, seminal vesicles and prostate gland. ❖ It helps to lubricate, transport and nourish the sperm cell. Vas deferens- is a long tube extending from each epididymis to the urethra for transportation of sperm cells mixed with fluid. Check point. I. Answer the following questions. 1. What is reproduction? 2. Compare and contrast between secondary sexual characteristics in males and females? 3. What is Cowper’s gland? 4. What will happen to old men with relation to their prostate gland? 5. Explain the function of scrotum? 6. What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? The Female Reproductive Structures 3 ❖ Female reproductive structure is more complex when compared with the male reproductive organ. ❖ The major structures of the female reproductive structures are:Ovaries- are the female gonads that are made up of follicle cells called graffian follicle. ❖ The graffian follicle releases or produces ova or eggs. ❖ Ovaries are also responsible for production of the female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone). ❖ The sex hormones are responsible for the promotion of female secondary sexual characteristics. ❖ The ovary is stimulated to produce the sex cells by Follicle stimulating hormones (FSH) and Luteinizing hormones (LH) which are secreted by the pituitary gland. Vagina- is a muscular tube where sexual intercourse takes place and it serves as a birth canal. Fallopian Tube (oviduct) - is a narrow tube between the ovary and uterus. ❖ It is a site where fertilization takes place. Uterus (Womb) - is a wider muscular tube where implantation and development of embryo takes place. The fetus develops here for almost nine months. Thus it is the site of pregnancy. Cervix- a narrow ring of muscles that joins the uterus to vagina ❖ It opens during birth and menstruation. ❖ It also helps to prevent the passage of fetus out of the uterus before the actual date of birth. Clitoris- is an erectile and sensitive tissue like penis for sexual stimulation. It is found above the entrance of vagina (upper front part of the vagina). Vulva- the external genital organs of the female reproductive organ Hymen- is a membrane at the external appearance of the vagina. It is considered as the sign of virginity. 4 The menstrual cycle ❖ Menstrual cycle is sequence of events that takes place approximately every four weeks through the fertile age of the women. ❖ It occurs from the age of puberty to around the age of menopause. ❖ Menopause- is the age (approximately 45- 50 years old) when the menstrual cycle stops and marks the end of giving birth. ❖ The menstrual cycle involves two process these are; Ovulation and menstruation. Ovulation- is the process by which a matured ovum is released from the ovary into the oviduct. ❖ It occurs after 14 days of the last menstruation. Menstruation- is removal of unfertilized dead eggs with blood through the vagina. The menstrual cycle occurs in three phases; namely A) Menstrual phase B) Proliferative phase C) Secretory phase A. The menstrual phase ❖ Is characterized by the breaking down of the wall of the uterus and the loss of blood through the vagina. ❖ It lasts from 3 to 5 days. B. The proliferative phase (follicular phase) ❖ Is characterized by the release of egg from the ovary (ovulation). 5 ❖ During this phase the uterine wall starts to become thick and blood vessels develop on it. ❖ It occurs 9-10 days after the last menstruation. C. The secretory phase ❖ During this phase the ovary releases a hormone known as progesterone which further thickens the wall of the uterus and reduces its movement. ❖ The thickening of the uterine wall helps it to accept the fertilized egg. This process is known as implantation. Implantation is the process in which the fertilized egg attaches itself into the uterine wall. If the egg is not fertilized after 10 days of ovulation, the ovary stops the production of estrogen and progesterone. Thus at around the 28th day the wall of the uterus starts to disintegrates and discharged through the vagina in the form of blood. The menstruation occurs every 28 days in average. Thus the days of menstruation can be discussed as:❖ Menstrual (bleeding) period- it lasts from 3 to 5 days. ❖ Critical period- lasts for 10 days. It occurs between 10th – 18th days after the beginning of menstruation. During this time the chance of pregnancy is high. ❖ Safe period- is around 14 days from 28 days of menstrual cycle. Having sexual intercourse during this period minimizes a chance of getting unwanted pregnancy. During menstruation women show some characteristics such as menstrual pain, abdominal pain, emotional sensitivity, nausea etc. These symptoms are called menstrual characteristics. Fertilization ❖ Is the union of a male sex cell or sperm cell and a female cell or egg cell. ❖ Takes place in the fallopian tube if there is sexual intercourse just a few days before or after ovulation. ❖ The fusion of the two nuclei forms a zygote ❖ Then the fertilized ovum or zygote in the fallopian tube find its way to the uterus for implantation. ❖ During pregnancy the corpus leuteum in the ovary produces progesterone for the first few months and placenta produces additional progesterone until birth. 6 ❖ Placenta- is mass of tissue that develops partly from the embryonic tissue and partly from the uterine wall. ❖ The hormone progesterone is produced during pregnancy to avoid overlapping of pregnancy. Check point I. Fill in the blank space with the appropriate words. 1. Normally ovulation occurs on the _____day of the beginning of menstruation. 2. The movement of egg from ovary to the fallopian tube is called_________________. 3. ________________ is the age when menstrual cycle stops and marks the end of giving birth. 4. The tissue that produces additional progesterone during pregnancy is called______________ 5. _________________________is the attachment of the embryo into the uterine wall. 6. The female sex hormones are_______________&_________________. Birth control methods (contraceptive methods) ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ Birth control methods are methods that are used to prevent pregnancy. It is important to avoid unwanted pregnancy. It is also important for family planning. The birth control methods are also called contraception. 7 ❖ The best option for students at your age to avoid unwanted pregnancy is abstinence from sexual intercourse. ❖ There are various contraceptive methods which differ from one another in a way they are used and their effectiveness. ❖ Some of the contraceptive methods used by peoples are: 1. Rhythm or calendar method- based on the understanding of the menstrual cycle and prediction of the ovulation time. ❖ This method works perfectly for those women with a regular menstrual cycle. ❖ Is the least effective method 2. Contraceptive pills- are pills (tablets) that consist of estrogen and progesterone. ❖ Rising of estrogen in the blood is detected by the pituitary gland which slows down the production of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) which is responsible for maturation of egg. If the eggs do not mature there is no pregnancy. ❖ The progesterone prevents ovulation and mucus in the cervix to prevent the entrance of sperm cell. 3) Condom- is a thin rubber or sheath that is used to prevent the sperm from entering the female reproductive organs. 4) Vasectomy- is a male sterilization which involves cutting and tying the vasdeferns. This prevents the movement of sperm along the urethra. 5) Tubectomy- is a female sterilization which involves cutting and tying of the fallopian tube. It prevents the release of egg from ovary to fallopian tube. Check point I. Fill in the blank spaces with appropriate words. 1. The union of sperm cell and egg cell is called__________. 2._________ is a method used to prevent pregnancy. 3. The best contraceptive methods for youngster’s like you is__________. 4. After fertilization, the zygote attaches itself to the wall of the uterus this process is called_____ 8