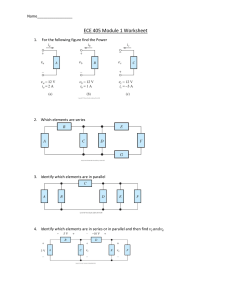
11 TVL – IA (EPAS NC II) Activity Sheet Quarter 4 – Competency 1.1 to 1.6 Assessing Quality of Received Materials or Components REGION VI – WESTERN VISAYAS 1|Page TVL 11 - IA (Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing) Learning Activity Sheet No. 1 First Edition, 2021 Published in the Philippines By the Department of Education Region 6 – Western Visayas Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. This Learning Activity Sheet is developed by DepEd Region 6 – Western Visayas. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this learning resource may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic or mechanical without written permission from the DepEd Regional Office 6 – Western Visayas. Development Team of TVL 11 - IA (Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing) Activity Sheet Writers: Editors: Noel R. De los Santos, Felix T. De los Santos Abraham P. Imas, Lilibeth E. Larupay Remia D. Manejero, Armand Glenn S. Lapor Layout Artists: Lilibeth E. Larupay, Armand Glenn S. Lapor Jo-an R. Pet Schools Division Quality Assurance Team: Abraham P. Imas, Lilibeth E. Larupay Remia D. Manejero, Armand Glenn S. Lapor Division of ILOILO Management Team: Roel F. Bermejo Nordy D. Siason, Jr. Lilibeth T. Estoque Azucena T. Falales Ruben S. Libutaque Lilibeth E. Larupay Abraham P. Imas Remia D. Manejero Regional Management Team Ramir B. Uytico Pedro T. Escobarte Jr. Elena P. Gonzaga Donald T. Genine April C. Velez Rommel C. Fuentes Freddie F. Napay 2|Page Introductory Message Welcome to TVL 11 - IA (Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing)! The Learning Activity Sheet is a product of the collaborative efforts of the Schools Division of Iloilo and DepEd Regional Office VI - Western Visayas through the Curriculum and Learning Management Division (CLMD). This is developed to guide the learning facilitators (teachers, parents and responsible adults) in helping the learners meet the standards set by the K to 12 Basic Education Curriculum. The Learning Activity Sheet is self-directed instructional materials aimed to guide the learners in accomplishing activities at their own pace and time using the contextualized resources in the community. This will also assist the learners in acquiring the lifelong learning skills, knowledge and attitudes for productivity and employment. For learning facilitator: The TVL 11 - IA (Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing) Activity Sheet will help you facilitate the teaching-learning activities specified in each Competency with minimal or no face-to-face encounter between you and learner. This will be made available to the learners with the references/links to ease the independent learning. For the learner: The TVL 11 - IA (Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing) Activity Sheet is developed to help you continue learning even if you are not in school. This learning material provides you with meaningful and engaging activities for independent learning. Being an active learner, carefully read and understand the instructions then perform the activities and answer the assessments. This will be returned to your facilitator on the agreed schedule. 3|Page Quarter 1 – Week 1 Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) No. 1 Name of Learner: _______________________________________________________________ Grade and Section: ________________________________Date: ________________________ TVL 11 - IA (Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing NC II) Activity Sheet Assessing Quality of Received Materials or Components I. II. Learning Competency with Code LO 1. Assess quality of received materials or components. 1.1 Obtain work instructions in accordance with standard operating procedures 1.2 Carry out work in accordance with standard operating procedures 1.3 Check received materials or component parts against workplace standards and specifications 1.4 Isolate faults and faulty materials 1.5 Record and/or report faults and faulty materials to the supervisor concerned in accordance with workplace procedures 1.6 Replace faulty materials and components in accordance with workplace procedures TLE_IAEPAS912AQS-Ia-1 Background Information for Learners Standard Work Instructions and Standard Operation Procedures https://www.rewo.io/standard-work-instructions-and-standard-operation-procedures/ Standard operating procedures and standard work instructions are key to success in manufacturing. They can be improved upon through document reviews, audits, a disciplined problem-solving process and, most importantly, the input from the experts who are performing the tasks. The current documentation should be the starting point for all improvements. Always improve upon existing documentation before creating a new document. Volume does not equate to continuous improvement. Many people think that operating procedures and work instructions are interchangeable terms, but the truth is different. Standardized Work Instructions (SWI) are instructions designed to ensure that your manufacturing processes are consistent, timely and repeatable. Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) are written, step-by-step instructions that describe how to perform a routine activity. An SOP is a procedure specific to an operation that describes the activities necessary to complete tasks in accordance 4|Page with industry regulations, provincial laws or even just your own standards for running your business. Applying of Quality Standards 1. Work instruction is obtained and work is carried out in accordance with the standard operating procedures. 2. Received materials are checked base on the workplace standards and specifications. 3. Faulty materials related to work are identified and isolated. 4. Faults and any identified causes are recorded and/or reported to the concerned person-in-authority in accordance with the workplace procedures. 5. Faulty materials are replaced in accordance with workplace standard operating procedures (SOP) 6. Safety precautions are observed at all times. Factors that must be taken into consideration when choosing the right material for their components and assemblies 1. Selection of Material Material selection is one of the most common tasks for design exertion. The ability to assess the materials impact on the performance of a product is a crucial for reliable performance. Sometimes buyers are also considering the label or name of the company which are producing great quality of materials and are known in the market. 2. Testing of material The testing of material properties is widely understood to be the key to obtaining data for a project, performing failure analysis, or understanding material interactions. Material testing also provides information on the quality of incoming and outgoing products. 3. Cost of Material The cost of material is also considered when buying or selecting materials for a specific project. The amount may vary but never taken for granted the quality and the reliability of the material. Identification and Isolation of Faulty Electronic Components 5|Page PROPER HANDLING OF TEST PROBE IN ISOLATING FAULTY AND GOOD ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS TESTING RESISTOR Good Resistor The meter reading should be closed to the rated value of the resistor depending on the tolerance of the resistor. Defective Resistor • The tester pointer does not deflect at all. The resistor is OPEN. • The resistance reading has a big difference to the resistor rated value. The resistor has change value. TESTING CAPACITOR Good Capacitor- The tester pointer deflects and the move back to its initial position. Open Capacitor- The tester pointer does not deflect at all. Shorted capacitor. • The tester pointer rests on the 0 ohm scale, reverse and forward bias test. . 6|Page Leaky Capacitor- The tester deflects toward the right position but does not return to its initial position or remains stationary TESTING DIODES The tester pointer does not deflect even the prove is reverse The resistance reading deflects and measures the same in both directions. III. Accompanying DepEd Textbook and Educational Sites (With Possible Materials for experiments/activities) Department of Education. Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing. Accessed 7, 2021. http://depedmuntinlupa.ph/pedhs/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/EPAS-8-module-1_week12_LO1.pdf Applying Quality Standards. Accessed June 7, 2021. https://www.slideshare.net/BongBandola/applying-qualitystandard-css-85792577. Page 1 III. Activity Proper 7|Page Activity 1 Directions: True or False. Write true if the statement is correct and false if otherwise. _____1. To ensure that your manufacturing processes are consistent, timely and repeatable, we need a standardized work instruction. _____2. Standard operating procedures are written, step-by-step instruction that describes how to perform a routine activity. _____3. In receiving materials, faulty materials are acceptable in accordance with workplace standard operating procedure. _____4. Received materials are checked based on the workplace standard and specifications. _____5. Material selection is one of the most common tasks for design exertion. Activity 2 Directions: Identify faulty and good electronic components based on the illustration below. 1. __________________________ 2. ___________________________ 3. ___________________________ 4. _____________________________ 8|Page 5. ____________________________ Guide Questions: Read the following questions and write your answer on a separate sheet. 1. Factors that must be taken into consideration when choosing the right material for their components and assemblies. _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 2. Compare standard operating procedures with standard work instructions. _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ 3. Why is it important to know the proper handling of test probe in isolating faulty and good electronic components? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Rubric for Scoring Refer to Assessment Criteria below for Activity 2 IV. Assessment Criteria Score Descriptive Grade 5 4 3 2 1 0 Excellent Very good Good Fair Poor No Answer Reflection 9|Page Supply the statements below: In applying quality standards, I learned that _____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ I will apply this learning in _____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Answer Key Activity 1 1. True 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True Activity 2 1. Shorted Capacitor 2. Open Capacitor 3. Shorted Diodes 4. Good Capacitor 5. Open Diodes V. 10 | P a g e