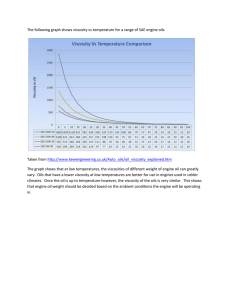
10 TANZA NATIONAL TRADE SCHOOL SPECIAL PROGRAM IN TECHNICAL VOCATIONAL EDUCATION (SPTVE) LEARNING MATERIAL GRADE 8 SECOND QUARTER AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY TANZA NATIONAL TRADE SCHOOL TECHNICAL VOCATIONAL EDUCATION SPTVE AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY Weekly Learning Activity Sheets TABLE OF CONTENTS Pages Duration/ Date Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Content& Performance Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Assessment Criteria . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 2 Technical Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 MELC NO. 1 IDENTIFY TYPES OF LUBRICANTS/COOLANTS AS PER JOB REQUIREMENT Information Sheet no. 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 Week 11 Information Sheet no. 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 Self-check no. 1.1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Information Sheet no. 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Self-check no. 1.1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16== MELC NO. 2 USE AND APPLY LUBRICANTS OR COOLANT IN LINE WITH JOB REQUIREMENTS Operation Sheet no. 2.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 Week 12 Self-check no. 2.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 MELC NO. 3 PERFORM HOUSEKEEPING ACTIVITIES AS PER COMPANY SOP Information Sheet no. 3.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 Week 13 Self-check no. 3.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 INTRODUCTION This learning material contains information and suggested learning activities on using and applying lubricants/coolants. It includes instructions and procedure on how to identify types of lubricants/coolants, use and apply lubricants and coolants and perform housekeeping services. Completion of this module will help you understand the succeeding module on Move and Position Vehicle. This learning material consists of three (3) learning outcomes. Each learning outcome contains learning activities with instruction sheets. Before you follow the instruction, read the information sheets and answer the self-check and activities provided to assess your competence by your teacher. He/she will check if you have acquired the knowledge necessary to perform the skill portion of the particular learning outcome. Upon completing this module, report to your teacher for assessment. If you pass the assessment, you will be given a certificate of completion. SUMMARY OF MOST ESSENTIAL LEARNING COMPETENCIES: Upon completion of the module, you should be able to: ASDS Identify Types of Lubricants/Coolants as Per Job Requirement Use and Apply Lubricants or Coolant in Line with Job Requirements Perform Housekeeping Activities as per Company SOP Page 1 CONTENT STANDARD The learners demonstrate an understanding of using and applying lubricant/coolant PERFORMANCE STANDARD The learners independently apply lubricants/coolant based on service manuals ASDS Page 2 TECHNICAL TERMS 1. VISCOSITY – a measure of the thickness or ability to flow of a lubricant. 2. SAE - Society Automotive Engineers 3. API - American Petroleum Institute 4. W - Winter 5. Lubricant - a material capable of reducing friction when applied between moving parts. 6. Synthetic oil - an artificial oil that is manufactured, and not a natural mineral oil made from petroleum. 7. SOP - Standard Operating Procedure 8. Petroleum - an oily flammable liquid obtained from well drilled in the ground and refined into gasoline, fuel oils, and other products. ASDS Page 3 MELC NO. 1 IDENTIFY TYPES OF LUBRICANTS/COOLANTS AS PER JOB REQUIREMENT INFORMATION SHEET NO. 1.1 Title: IMPORTANCE OF LUBRICANTS/COOLANTS The lubrication system is extremely important to engine service life because it forces oil to high friction points in the engine. Without a lubrication system, friction between parts would destroy an engine very quickly. Many of the engine parts would rapidly overheat and score from this friction. Engine bearings, piston rings, cylinder walls and other components could be ruined. 1. Reduces friction and wear between moving parts. 2. Helps transfer heat and cool engine parts 3. Clean the inside of the engine by removing contaminants (metal, dirt, plastic, rubber, and other particles). 4. Cuts power loss and increases fuel economy. 5. Absorbs shocks between moving parts to quite engine operative and increase engine life. This illustration shows the movement of the oil inside the engine gallery ASDS Page 4 INFORMATION SHEET No. 1.2 IDENTIFY TYPES OF LUBRICANTS/COOLANTS Types of Lubricants ENGINE OIL Engine oil, also called motor oil, is used to produce a lubricating film on the moving parts in an engine. It is commonly refined from crude oil or petroleum which is extracted from deep within the earth. Synthetic oils (manufactured oils) are also available. They can be made from substances other than crude oil. An oil film (thin layer of oil) separates engine parts to prevent metal-on-metal contact. When selecting oil for an engine it is important that the one chosen is suitable for the engine itself and the conditions under which it will be used. Two important factors determining the choice of oils are: a. That the oil meets the quality requirements b. That the oil has the right “thickness” or what we call the right VISCOSITY. ASDS Page 5 This learning element explains what is meant by viscosity and how the oils are graded according to their viscosity. The term viscosity refers to the relative thickness of a liquid. It’s a thin, free-flowing liquid has a low viscosity and a thick, slow-slow-flowing liquid has a high viscosity. The viscosity of a liquid changes when the temperature changes. At high temperature the liquid (oil in this case) becomes thinner (lower viscosity) and at low temperature the liquid becomes thicker (higher viscosity) ASDS Page 6 The correct oil viscosity is essential for the efficient operation of the engine because: When the oil is too thick (high viscosity) it causes resistance and much more power is needed to turn the engine, making it difficult to start when cold. Thick oil does not circulate freely enough during the starting period, causing insufficient lubrication of the bearings and, consequently, increased wear Oil which is too thin, combined with a high engine temperature and a heavy load presents the risk of oil being pressed out from between the working surfaces of the bearings or other engine parts. ASDS Page 7 And this would cause the oil film which is essential to the proper lubrication of the engine to break down. Furthermore between the piston rings and the cylinder. This is most significant characteristic of lubricating with its viscosity. This can be measured in different ways. One way, for instance, is to check the quantity of oil which passes through a tube of standard size during a certain length of time and at a given temperature. POWER TRAIN AND RUNNING GEARS OIL Most gear oil is a mineral oil refined from crude oil. Some gear oil is manufactured or synthetic oil. Chemical additives are mixed with gear oil to improve its load carrying capacity. This makes an extreme of heat on oil viscosity and foaming, rust, corrosion, and oil-seal damage. The gear oil used in many cars and trucks is relatively thick and has a viscosity ranging from SAE 75W to SAE 140. Multi-grade gear oils such as SAE 75W-90, are also used. However, some manufacturers specify synchromesh transmission fluid (STP) for manual transmissions and transaxles. ASDS Page 8 GREASE This is a fluid suck as mineral oil (made from petroleum) thickened with an agent that makes it a semi-solid. The thickening agent that is a metallic soap or non-soap substance such as clay. Soaps commonly used are lithium, calcium, sodium, aluminum and barium. Each of these alone or in combination gives the grease characteristics. Aluminum gives the grease good adhesion. Sodium gives the grease a thick, fibrous appearance. A good grease must have consistency, stability, oxidation, resistance, ability to protect against friction, wear and corrosion, and feed ability. This is ability to flow through dispensing equipment such as wheel bearing, universal joint, ball joint, and chassis fittings. MELC NO. 1 IMPORTANCE OF LUBRICANTS/COOLANTS SELF-CHECK 1.1 DIRECTION: Complete the following: 1. _________ the inside of the engine by removing contaminants. 2. _________ shocks between moving parts to quite engine operative and increase engine life. 3. _________ transfer heat and cool engine parts. 4. _________ power loss and increases fuel economy. 5. _________ friction and wear between moving parts ASDS Page 9 INFORMATION SHEET No. 3 IDENTIFY TYPES OF LUBRICANTS/COOLANTS PRODUCT SPECIFICATION PRODUCT SPECIFICATION SERVICE RATINGS OF OIL Oil is rated by viscosity number and also by its service designation. This is kind of service for which the oil is best suited. There are six service ratings for spark-ignition-engine lubricating oils, SA, SB, SC, SD, and SF. There are four service ratings for compression ignition-engine lubricating oils, CA, CB, CC, and CD. 1. SA Oil This oil is for utility gasoline and diesel engines operating under mild conditions, so protection by additives is not required. This oil may have pour-point and foam depressants 2. SB Oil This oil is for service in gasoline engines operated under such mild conditions that only minimum protection by additives required. 3. SC Oil This oil is for service typical of gasoline engines in the 1964 to 1967 models of passengers’ cars and trucks. It is intended primarily for use in passenger cars. This oil provides control of high and low-temperature engine deposits, wear, rust and corrosion. 4. SD Oil This oil is for service typical of gasoline engine in passenger cars and trucks beginning with 1968 models. This oil provides more protection from high- and low- temperature engine deposits, wear, rust and corrosion than do SC oils. ASDS Page 10 5. SE Oil This oil is for service typical of gasoline engines in passenger cars and some trucks beginning with 1972 (and some 1971) models. This oil provides more protection against oil oxidation, high temperature engine deposits, rust, and corrosion than do oils with the SC and SC ratings. 6. SF Oil SF oil is for service typical of gasoline engines in passenger cars and some trucks beginning in 1981 models. This oil provides more protection than SE oils against sludge, varnish, wear, oilscreen plugging and engine deposits. Notice that this is an open-end series. When the car manufacturers and oil producers see the need for other types of oil, they can bring out SG and SH service-rated oils. SA and SB oils are not recommended for use in automobile engine. These 9 are non-detergent oils. Detergent oils are required in modern automotive engines. Diesel-engine oils must have different properties than oils for gasoline engines. The CA, CB, CC, and CD ratings indicate ample, CA oil is for light-duty service. CD oil is for severe-duty service typical of turbocharged high-output diesel engines operating on fuel oil with high sulfur content. Oil for use in automotive diesel engines should be marked SF/CC or SF/CD. Now, we have a wide range of oil viscosity from very thin oil, SAE 5W up to thick SAE 50 oil. Every SAE grade represents an oil suitable for use within a special range of temperature and for certain type of engine as follows: Oils within the viscosity grades SAE 5W, 10W and 20W are suitable for use in climates with temperatures ranging from very low to moderate. ASDS Page 11 SAE 20 and SAE 30 are suitable for use in moderate to hot climates. SAE 40 and SAE 50 are mostly for use in old engines designed for rather thick oil or in badly worn engines with high oil consumption. However, many engines are operated in climates where the temperature varies considerably from season to season. in addition, it is always preferable for any engine to run on low viscosity oil during the starting period when the engine is cold, on high viscosity oil when the engine is hot and fully loaded. ASDS Page 12 For practical reason it is not possible to use a low viscosity oil for starting and then change to an oil of higher viscosity when running. Oils are available with a very wide viscosity range, for example 10W/50, which can be used in any climate. it is also an advantage for the engine when SAE 10W/50 is used because it enables that cold engine to start on a thin (10W) and when hot, on a sufficiently thick oil (SAE 50). A general technical designation for oils has been accepted as follows: - ASDS single grade oil which only covers one SAE grade (e.g. SAE 30) Page 13 - double grade oil which covers two consecutive SAE grades (e.g. SAE 20W/30). - Multi-grade oil which covers three SAE grades (e.g. SAE 20W/30). - Super multi-grade oil which covers more than three SAE grades (e.g. SAE 15/50). The oils covering more than one SAE grades are often referred to as multi-viscosity, all season or all-weather oils. Bear in mind that SAE grades only tell you the viscosity of the oil and not the quality. ASDS Page 14 Now, how would you select the oil with the right SAE number corresponding to the temperature and running condition? The correct way is, of course, to check what is recommended in the specifications for the engine. - all oil producers have worked out, together with the engine manufacturers, recommendations for the oil viscosity most suitable for given conditions. It is important to know that the SAE grades only give information on the viscosity but not the quality of the oil. For the quality classification see reference book (Automotive Technology by: James E. Duff p.488 ASDS Page 15 MELC NO. 1 IMPORTANCE OF LUBRICANTS/COOLANTS SELF-CHECK 1.2 MULTIPLE CHOICES: Directions: Read and understand each question then write your answer on a separate sheet. 1. Which of the following statements are correct? a. Oil becomes thicker when warm b. Oil becomes thicker when cold c. Oil with high viscosity provides easy starting and good lubrication when cold. d. All of the above mention 2. An oil marked SAE10W/40 means that . a. the oil can be used in cold and hot climates b. the oil is to be used only in cold climates c. the oil is a mixture of SAE 10W and SAE 40 d. both b and c 3. Which SAE grade would you recommend for an engine with high oil consumption? a. SAE 10W b. SAE 20W c. SAE 20 d. SAE 40 4. “SAE grade” means . a. the viscosity c. the relative thickness of the oil b. the quality of the oil d. the API classification of the oil 5. Which of the following statements has a lower viscosity? a. Oil with high viscosity provides easy starting and good lubrication when cold b. SAE 20 c. SAE 40 d. All of the above ASDS Page 16 MELC NO. 2 USE AND APPLY LUBRICANTS OR COOLANT IN LINE WITH JOB REQUIREMENTS OPERATION SHEET NO. 1 CORRECT PROCEDURES IN CHANGING OR APPLYING LUBRICANTS CONDITIONS: Supplies and Materials used oil can engine oil oil filter Tools box wrench filter wrench PPE Manual Ignition key Equipment Vehicle Battery PROCEDURES: The teacher presents a video and discusses the correct procedures in changing oil and in applying lubricants. A. Use lift or floor jack and stands to raise car in level position. Place catch pan under drain plug. ASDS Page 17 B. Unscrew drain plug and allow oil to pour into pan. C. Use filter wrench to remove old filter. Turn counterclockwise. D. Wipe clean oil on new filter o-ring. This will assure proper tightening. ASDS Page 18 E. Install and tighten oil filter by hand. Hands and filter should be clean and dry. Use a rag if needed. F. Tighten the drain plug. Install correct type and quantity of oil. Pour oil filter or breather opening in valve cover. PRECAUTIONS: Be careful of hot oil. It can cause painful burns. SAFETY MEASURES IN HANDLING LUBRICANTS Lubricants that are not properly handled can become contaminated with dirt, water and other fluids, reducing the service lives of the lubricant and the equipment and possibly causing equipment failure Proper oil storage is the first step to preventing contamination. Oil should be store in closed containers that keep airborne particulates and moisture out. According to Jim Morrison, field technician with Petro Canada America Lubricants, Inc., it can be a costly mistake to store oil in open containers or allow drums to be partially open to air. “Air is extremely dirty, therefore, you must never allow oil to get exposed to it,” he says. ASDS Page 19 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS IN APPLYING LUBRICANTS Wear eye protection at all times when in the shop area. Oil and filter change require that the vehicle be safely raised and supported. If using safety stands or ramps to support the vehicle, also block any wheels remaining on the ground. This will prevent the vehicle from moving backwards. Use caution around hot surfaces such as exhaust manifolds, pipes, and mufflers. Hot oil draining from the oil pan or oil filter can cause burns and skin irritation. Always refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s shop manual for specific procedures. ASDS Page 20 MELC NO. 2 USE AND APPLY LUBRICANTS OR COOLANT IN LINE WITH JOB REQUIREMENTS SELF-CHECK NO. 2.1 ESSAY Direction: Discuss the steps to be done in performing oil-change. . ASDS Page 21 MELC NO. 3 PERFORM HOUSEKEEPING ACTIVITIES AS PER COMPANY SOP INFORMATION SHEET NO. 3.1 HOUSEKEEPING PROCEDURES (5-S) A. Concepts of 5S 1. SEIRI ( SORT ) Remove unnecessary items and dispose them properly Make work easy by eliminating obstacles Provide no chance of being disturbed with unnecessary items Prevent accumulation of unnecessary items 2. SEITON (SYSTEMATIZE) Arrange necessary items in good order so that they can be easily picked for use Prevent loss and waste of time. Easy to find and pick up necessary items Ensure first -come-first serve basis. Make work flow smooth and easy. ASDS Page 22 3. SEISO (SWEEP) Clean your workplace completely Easy to check abnormality Prevent machinery and equipment from deterioration. Keep workplace safe and easy to work 4. SEIKETSU (STANDARDIZE) Maintain high standards of housekeeping and workplace organization at all times Maintain cleanliness and orderliness Prevent mismanagement of operation 5. SHITSUKE (SELF-DISCIPLINE) Do things spontaneously without being told or ordered. Standardize good practice ASDS Page 23 B. ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS SEGREGATION & SECONDARY CONTAINMENT 1. Separate acidic chemicals from basic chemicals according to pH. 2. Separate oxidizers from organic chemicals and inorganic reducing agents. (Remember the Fire Triangle) 3. Separate water reactive chemicals from aqueous solutions. 4. Separate chemicals with multiple hazards from all other chemicals. When transporting chemicals form one room to another PLEASE use a chemical safety bucket. GENERAL RULES TO OBSERVE 1. All employees must receive and understand the locally applicable Workplace Hazardous Materials information guide or equivalent (if such a guide exists). In any case the management is responsible for proper instruction. 2. Develop a positive attitude toward laboratory safety: prevention is better than cure 3. Observe normal laboratory safety practices. 4. Good housekeeping is extremely important. Maintain a safe, clean work environment. 5. You may work hard but never in haste. 6. Follow the safety precautions provide by the manufacturer when operating instruments ASDS Page 24 7. Monitor instruments while they are operating 8. Avoid working alone. If you must work alone, have someone contact you periodically 9. Learn what to do in case of emergencies(e.g. fire, chemical spill, see 4 2 6) 10. Learn emergency first aid (see 4, 2, 5, 2). 11. Seek medical attention immediately if affected by chemicals and use first aid until medical aid is available. 12. Report all accidents and near misses to the management. 13. Access to emergency exits, eye-wash fountains and safety showers must not be blocked. Fountains and showers should be checked periodically for proper operation. 14. Wash hands immediately. Use appropriate material for each spillage. 15. Clean up any spillage immediately. Use appropriate materials for each spillage. C. SAFETY SIGN AND SYMBOLS ASDS Page 25 MELC NO. 3 PERFORM HOUSE KEEPING ACTIVITIES AS PER COMPANY SOP SELF-CHECK NO. 3.1 Direction: Identify the following as to what specific S it belongs. _________1. Prevent wrong operation _________2. Standardize good practice _________3. Make work easy by eliminating _________4. Prevent loss and waste of time _________5. Ensure first-come-first-serve basis _________6. Keep work place safe and easy to work _________7. Provide no chance of being disturbed with unnecessary items _________8. Make work flow smooth and easy _________9. Easy to find and pick –up necessary items _________10. Prevent accumulation of necessary items ASDS Page 26 REFERENCES AND FURTHER READING 1. Automotive Mechanics, 10th Edition By: William Crouse and Donald Anglin 2. CBLM-AUTOMOTIVE SERVICING NC I Module Title: Applying Appropriate Sealant/Adhesive By: TEAM LEADER: George Callanta Members : Robert Domingo John Diego Lino Olit Romeo Ibloguin Nelson Senedo English : Belen Tado ASDS Page 27