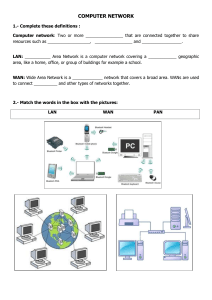
Introduction to INFORMATION NETWORKS Network A computer network consists of two or more computing devices that are connected in order to share the components (resources) and the information. Receiving information from a network is called downloading data. Sending information over a network is called Uploading data. Network Components Any network must have 4 components: ■ Computer Systems ■ Network Media ■ Network interface ■ Network Protocol Types of Networks: • Local Area Networks (LANs). • Wide Area Networks (WANs). A local area network (LAN) is a computer network covering a small geographic area, like a home, office, or group of buildings. Wireless LAN (WLAN) is a LAN without cables. •Wide Area Network(WAN) is a computer network that covers a broad area. •The largest and most well-known example of a WAN is the Internet. •WANs are used to connect LANs and other types of networks together, so that users and computers in one location can communicate with users and computers in other locations A network may be: • Peer to peer • Client/ server Network Peer to peer • Is a network where the computers act as both workstations and servers. • Each machine can have resources that are shared with any other machine. • There is no assigned role for any particular device, and each of the devices can send requests to any other. Advantages Disadvantages • Easy to install • Non-scalable • Not expensive • No centralized administration Client/ server Network • In this network, all data is stored on a main high speed computer (server) • Users can access data from slow speed computers (clients) Advantages Disadvantages • Scalable • Difficult to install • Centralized administration • Expensive The Telephone Network Due to Technology, we can connect computers to telephone system to make world wide WAN Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) ■ PSTN is simply the technical name for the telephone system in use today. Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) ■ ISDN allows transfer of digital data between telephone exchanges. ■ It has much faster transfer rate, like 64 K or 128 kbps Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) ■ It transfer rates up to 40 times faster than PSTN. ■ Through ADSL, we can use internet and phone at the same time. Cable Broadband ■ It uses cable of TV instead of phone line. ■ It provides high speed connection. Wireless Network (WiFi) ■ User can use internet via a wireless router and adapter. ■ Wireless Access Point (WAP) will be via ADSL or cable. Satellite Internet ■ It is used where normal access is not available like ships. ■ Its available in all world but its expensive. Broadband ■ This connection is available on monthly charges ■ It provides high speed connection. Transfer rate ■ data transfer rate is the speed that data can be moved between one device and another. ■ Understand how it is measured: ■ Bits per second (bps). ■ Kilobits per second (kbps). ■ Megabits per second (mbps). ■ Gigabits per second (gbps). ■ Understand the concepts of downloading from, uploading to a network. ISP (Internet service provider) ■ An ISP (Internet service provider) is a company that provides individuals and other companies access to the Internet. ■ Identify important considerations when selecting an internet subscription option like upload speed, download speed and quota, cost. ■ Recognise the status of a wireless network: protect/secure, open. The Internet ■ Internet is a global network of interconnected networks. ■ Internet is open for everyone. Any body can use internet. ■ It was started by US Military. ■ Internet has a huge amount of information about everything of the world. ■ Internet is provided via Internet service Provider (ISP). ■ Internet is used for: – Communication. – Online shopping. – Online Banking. – Online Education. Search Engines ■ A search engine is a website through which users can search internet content. ■ Within the search engine you enter a word or phrase aand it will retrieve documents and information about that word or phrases from the Internet. ■ Google and Yahoo are examples of Search Engine Intranet and Extranet Intranet ■ A private network of an organization is called Intranet. ■ Intranet is accessible only from within the organization. ■ It’s not for all users. It’s open for authorised users only. ■ Intranet provides information, forms and newsletters of the organization. Extranet ■ It is intermediate between intranet or internet. ■ It is partly accessible only to limited external users via internet. ■ Any company can provide specific information to other through extranet. ■ External users can have access by Username and Password. Virtual Private Network (VPN) ■ Gives you online privacy and anonymity by creating a private network from a public internet connection. ■ VPNs mask you Internet protocol (IP) address so your online actions are virtually untraceable. Electronic mail (E-mail) ■ is information stored on a computer that is exchanged between two users over telecommunications. More plainly, e-mail is a message that may contain text, files, images, or other attachments sent through a network to a specified individual or group of individuals. Thank You