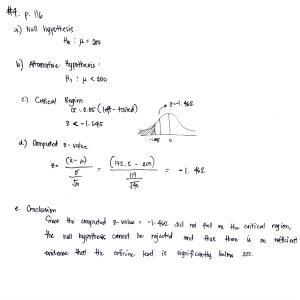
LECTURE DESIGN Given the figure above, we are going to translate the EER diagram (2a) to a Relational Schema (3a). Then taking the tasks of the code (2a) we are going to translate this to Abstract Code w/ SQL (3b). CREATE TABLE STATEMENTS For cannot NULL items that are primary keys. While some items can be NULL, the requirement at times mandate that the information be collected. Accordingly, based on semantic constraints, item are not NULLable. RegularUser has a foreign key and primary key. In Interests, we have a primary key with two attributes that, in combination, uniquely identifies the tuple in the Interests. Attend is a lookup table. Because the user requirements allow for YearGraduate but because YearGraduate is part of the primary key, we need to use the UNIQUE function. UNIQUE only allows for unique entries. As such, even if we have a NULL for one of the attributes, the UNIQUE function will enforce uniqueness. TASKS Above, is a logical read from the database. There are three (3) steps: SELECT, FROM, and WHERE. There are logical writes: DELETE and INSERT and UPDATE.