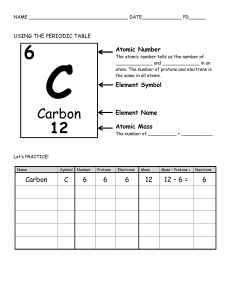
Thursday October 14 2021 AIM • Where does the mass on the periodic table come from? AGENDA • YOYO • Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment Simulation • Isotope/AAM notes & practice YOYO (Do Now) • Take out the regents HW questions. Work in pairs to check and discuss each other’s work. On the do now sheet write “Atomic History HW check” HOMEWORK • Edpuzzle-Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass • Quiz corrections due Monday Answer to History of the Atom Regent Questions pHet Simulation Link - Rutherford https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/rutherford-scattering/lat est/rutherford-scattering_en.html YOYO Look at the two images below. What similarities do you see? What differences do you see? Write down at least 1 similarity and 1 difference that you can observe in these images. Similarities Differences Looking at this picture... Question: What do you notice about the number of ELECTRONS in all three pictures? Looking at this picture... Question: What do you notice about the number of PROTONS in all three pictures? Looking at this picture... Question: What do you notice about the number of NEUTRONS in all three pictures? Looking at this picture... Question: Based on this image, what do you think an isotope is? What stays the same and what changes? Isotopes ● An isotope is a different version of a particular element with a different mass. ● The atomic number (# protons), and the number of electrons DO NOT CHANGE ● The number of neutrons change - that is the only way to change the mass of an atom without changing what atom it is. Changing the Subatomic Particles ● If you change the number of protons...you change the atomic number and the element itself ● If you change the number of electrons...you change the charge and create an ion ○ Lose electrons - become positive ion - cation ○ Gain electrons - become negative ion - anion ● If you change the number of neutrons...you change the mass of the atom only Isotopic Notation ● Isotopes are written with the element symbol and the mass number. Analyzing Isotopes Li-6 ● ● ● ● # Protons:_____ # Electrons: _____ # Neutrons: _____ Isotopic Notation: _______ Li-7 ● ● ● ● # Protons:_____ # Electrons: _____ # Neutrons: _____ Isotopic Notation: _______ Li-8 ● ● ● ● # Protons:_____ # Electrons: _____ # Neutrons: _____ Isotopic Notation: _______ Average Atomic Mass ● Average atomic mass is the average mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element ● It is a weighted average you you must take the percent abundance into account ● This is where the atomic mass on the periodic table comes from 1. Bromine has 2 naturally occurring isotopes. Using the information provided below, calculate the average atomic mass for bromine. 2. Find the average atomic mass for B if 19.9% of B atoms are B-10 with a mass of 10.012 amu and 80.1% are B-11 with a mass of 11.009 amu. 3. Find the average atomic mass for Mg if 78.99% of Mg atoms are Mg-24 with a mass of 23.985 amu, 10.00% are Mg-25 with a mass of 24.985 amu, and 11.01% are Mg-26 with a mass of 25.982 amu. 4. Titanium has five common isotopes: 46Ti (8.0%), 47Ti (7.8%), 48Ti (73.4%), 49Ti (5.5%), 50Ti (5.3%). What is the average atomic mass of titanium?