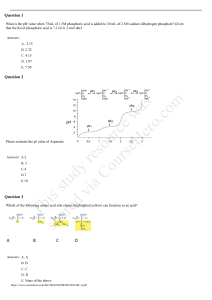
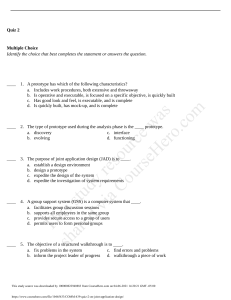
Midterm Review for Desc is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Chapter1 Which type of management system includes the integration of technology and software across an organization? Enterprise resource planning systems Which of the following best characterizes an independent variable? Function value depends upon its value Th Which one of the following indicates the two broad decision categories? Programmed and non-programmed Which of the following categories of modeling techniques provide a course of action to the decision maker? Prescriptive models Which one of the following describes how a decision-maker views or perceives a problem? Framing sh Anchoring effects arise when a seemingly trivial factor serves as a starting point (or anchor) for estimations in a decision-making problem. Decision makers adjust their estimates from this anchor but nevertheless remain too close to the anchor and usually under-adjust. Framing effects refer to how a decision maker views or perceives the alternatives in a decision problem—often involving a win/loss perspective. This study source was downloaded by 100000831008184 from CourseHero.com on 10-12-2021 14:55:22 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/38690366/Midterm-Review-for-Descdocx/ Chapter 11 is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Horizontal pattern—stationary time series-- Denotes a time series whose statistical properties are independent of time. Trend pattern-- Gradual shifts or movements to relatively higher or lower values over a longer period of time. sh Th Seasonal pattern-- Recurring patterns over successive periods of time. Time series plot not only exhibits a seasonal pattern over a one-year period but also for less than one year in duration. This study source was downloaded by 100000831008184 from CourseHero.com on 10-12-2021 14:55:22 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/38690366/Midterm-Review-for-Descdocx/ Four common accuracy measures are the mean absolute deviation (MAD), the mean absolute percent error (MAPE), the mean square error (MSE), and the root mean square error (RMSE). We focus on MSE( mean square error) is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Stationary pattern 1. The moving average technique is probably the easiest extrapolation method for stationary data to use and understand. the moving average technique tends to average out the peaks and valleys occurring in the original data. Smaller MSE means more accurate. Note, however, that the MSE includes and weighs relatively old data with the same importance as the most recent data. Thus, selecting a forecast based on the total MSE of the forecasting functions might not be wise because a forecasting function might have achieved a lower total MSE by fitting older data points very well while being relatively inaccurate on more recent data. Forecasting using moving average technique, assume all the estimation for the future periods are the same. 2. The weighted moving average technique is a simple variation on the moving average technique that allows for weights to be assigned to the data being averaged. 3. Exponential smoothing is another averaging technique for stationary data that allows weights to be assigned to past data. As shown in the previous equation, the forecast Y^ t11 in exponential smoothing is a weighted combination of all previous values in the time series where the most recent observation Yt receives the heaviest weight 1_ 2, the next most recent observation Yt21 receives the next heaviest weight 1_ 11 2 _ 2 2, and so on. Alpha near 1 means that the forecast reacts faster to the change of data. Th Trending pattern Double exponential smoothing (also known as Holt’s method) is often an effective forecasting tool for time series data that exhibits a linear trend. R^2 in regression means that ?% of the variation is accounted for the model sh Component of time series: 1. Trend 2. Seasonal 3. Cyclic Which statement is correct regarding the smoothing coefficient (alpha) in the exponential smoothing model? 1. A small alpha is best when the series varies substantially 2. A large alpha is best when the series has little random variability This study source was downloaded by 100000831008184 from CourseHero.com on 10-12-2021 14:55:22 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/38690366/Midterm-Review-for-Descdocx/ 3. Alpha ranges is value between 0 and 1 What graphic is best for detecting a trend in a time series? Scatter diagram The moving average model consists of one parameter namely the number of period in the moving average. The purpose of data smoothing is to make the presence of a trend clearer by reducing the effects of other fluctuations. (look for a trend) The sum of the digits for three periods is six (1+2+3 =6). Therefore ,the weight for the oldest value is one-sixth (0.17). Lesson 3 - is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Simple Regression (linear regression) - Correlation R measures strength, ranges from -1 to 1, very strong when stronger thatn +/0.75 - Residual analysis is also used to determine if the sample data are appropriate for linear regression, that is, are conditions for regression inference met. - The residuals should show constant variation and a random distribution around 0. - Smallest t-test value and largest p-value means this variable has no significant impact on the function(p value over 5%) - When correlation between IVs is strong, generally .7 or more (+/-), we would opt to remove one of those IVs. - X variable is also called the predictor - The slope is the same sign as the correlation coefficient - COD(coefficient of determination, R^2) = (SST-SSE)/SST=SSR/SST - The method of ordinary least squares is used to fit the regression which is based on the principle of minimizing the sum or the errors squared. The error term is symbolized by the Greek letter α. R^2 ranges from 0 to 1 Basic forecasting ground rules o Use X value within the database range o Common sense o Use only statistically significant variables Lesson 4 sh Th Multiple Regression - The adjusted R-squared is a modified version of R-squared that has been adjusted for the number of predictors in the model. The adjusted Rsquaredincreases only if the new term improves the model more than would be expected by chance. It decreases when a predictor improves the model by less than expected by chance. - A dummy variable can take on one of two possible values. Typically these values are zero or - one (e.g., male = 0 and female = 1). The number of dummy variables required to describe a categorical variable is N -1 where N is the number of categories. A variable that measures four different religions would require three dummy variables (i.e., 4-1 = 3). This study source was downloaded by 100000831008184 from CourseHero.com on 10-12-2021 14:55:22 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/38690366/Midterm-Review-for-Descdocx/ - - The adjusted coefficient of determination is the proportion of total variance in the dependent variable explained by the independent variables adjusted for the sample size and the number of predictor variables. As the sample size increases the difference between Rsquare and the adjusted R-square decreases. Discriminant analysis is a variation of multiple linear regression analysis where the dependent variable is categorical. The simplest model is where Y is binary (e.g., Yes and No). Basic regression model assumption o Linear relationship between X and Y o Residuals are normally distuributed o Error terms are independent - The F statistic is used to judge the overall statistical significance (performance) of the multiple regression model. The F statistic is always takes on a positive value. The testing process is similar to the one used for judging the statistical significance of each f the independent variables. A p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic (e.g., t statistic) at least as extreme as the one that was actually observe assuming that the null hypothesis is true. Typically, the null hypothesis (H0)is rejected if the p-value is less than the stated alpha. - is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m - - Standard Multiple Regression analysis procedure o Full o Backward stepwise o Forward Stepwise - The accuracy of the forecast, as measured by the confidence interval, decreases as the values of the predictor variables used in the regression forecast varies from their mean values (both above and below). eta coefficients (also known as standardized coefficients/slope) are regression model coefficients that have been standardized resulting in a variance of one. This procedure is done so that one can identify the relative impact of changes in each predictor variable on the target variable when each of the predictor variables are measured in different units (e.g., dollars, age, gender). - Lesson 5 Th Maximax-large Maximin-large in min Minmax- min in large EMV-large EOL(expected opportunity loss)-small EVPI: value of the information, max return of the information Why is sensitivity important? Most model coefficients are estimates sh Primary problems in decision-making process - Conflicting objectives Uncertainty regarding the future Lack of data This study source was downloaded by 100000831008184 from CourseHero.com on 10-12-2021 14:55:22 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/38690366/Midterm-Review-for-Descdocx/ The probability of exceeding one standard deviation from the mean in a normal distribution is 0.16 Two basic components of payoff matrix: states of nature and alternatives Implement solutions is not in decision analysis process EMV: Average monetary outcome of a decision if it was repeated a large number of times Maximax: non-probabilistic Lesson 6 sh Th is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Chance nod= event nod Risk averse: marginal utility of money diminishes Bayesian: revision of past probabilities This study source was downloaded by 100000831008184 from CourseHero.com on 10-12-2021 14:55:22 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/38690366/Midterm-Review-for-Descdocx/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)