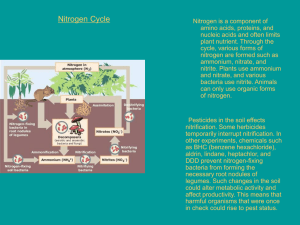
Introduction to Environmental Systems Name_______________________________ 3.3 The Earth’s Spheres • The earth can be divided into four major systems or “spheres” – 1. ______________________ – Earth’s crust, made up of rocks and minerals – 2. ______________________ – all of the water on earth in its liquid and solid phases, including oceans, rivers, ice, groundwater, etc. – 3. __________________ – thin layer of gases separating the earth from space, including water vapor – 4. __________________ – all of the living organisms on Earth and all of the places that those organisms live Lithosphere • The lithosphere is the Earth’s crust and it contains a lot of various rocks, minerals, and elements that we need and use. • A __________________ is a naturally occurring solid made by geologic processes. – Minerals have hard, _____________________ structures with a certain chemical composition Hydrosphere • Water is a unique compound because it has several _________________________________: – Water can be found in all three states of matter • Below freezing, water forms a tightly arranged _____________ structure (ice and snow) – Water molecules can form ____________________________ with other nearby water molecules • Vaporization (evaporation) occurs when those hydrogen bonds break. – When water molecules leave snow and go directly into the air (solid to gas), this is known as _________________________ • The hydrosphere is a major source of ____________________ for organisms. • The actual chemical formula of water is always going to remain the same (_________) despite what phase/state it is in • It is the __________________________________ the molecules that is changing. Atmosphere • The atmosphere is composed mainly of: – _______________________________ – _______________________________ – _______________________________ – _______________________________ – Plants interact with the atmosphere by taking in _______________________________ through their leaves and animals interact with the atmosphere by taking in _________________, usually through the use of a specialized organ such as the lung. Biosphere • The biosphere encompasses all of the _____________________ combined. • It contains not only all of the living organisms like plants and animals, but also the _____________ that those organisms live. • All four of the Earth’s spheres constantly interact with each other and _____________________________. Interactions between Spheres • All four of the Earth’s spheres are in a constant state of interaction with one another. • Gases from the air and _________ (charged atoms) from minerals may dissolve in water. • Because of this, natural water is a _________________ that is constantly subject to change – Various processes may _____________________ some of the dissolved substances in it and/or additional substances may ______________________ in it. • Water molecules enter the air through _________________________ – Water leaves air via __________________________ or ___________________________ – Air moisture constantly fluctuates • _____________ carries dust or mineral particles • Living organisms in the biosphere use materials from the other three spheres to build molecules 3.5 The Cycling of Matter in Ecosystems • The ________________________________________________ states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, so the _______________________ of atoms is the only way to maintain a dynamic system. The Carbon Cycle • The carbon cycle starts with carbon dioxide (CO2)in the air – Becomes organic molecules in organisms – Carbon is respired by plants and animals into the air or is deposited in soil as ________________ (dead organisms) • __________________________ in oceans and on land moves CO2 from air and seawater into plants – ________________________ returns inorganic carbon to seawater • • • Carbon dioxide can also diffuse from the air to water Combustion of fossil fuels releases _________ to the air With _________________________ practices on the rise, we are diverting or removing _______ of the photosynthetic productivity of land plants • Burning fossil fuels has increased atmospheric CO2 by 35% since the Industrial Revolution • Deforestation and soil degradation release significant amounts of CO2 to the atmosphere – Recent ________________________ and changed agricultural practices have improved this The Phosphorus Cycle • Mineral elements like phosphorus originate in rock and soil minerals – A shortage of phosphorus is a ___________________________ – Excessive phosphorus can stimulate ____________________________ • As rock breaks down, phosphate is released • _______________________________: incorporated into organic compounds by plants from soil or water – Cycles through the food chain – Broken down in cell respiration or by decomposers • Enters into chemical reactions with other substances and used in _____________________ • The most serious impact to the cycle comes from our overuse of fertilizers • Phosphorus is mined and made into fertilizers, animal feeds, detergents, etc. • When added to soil, it can ______________________ production • Human applications have tripled the amount reaching the oceans, accelerating the cycle • Excess phosphorus in water causes severe ______________________ – Can cause overgrowth of algae, too many bacteria, and the death of fish – This is known as _____________________________ • Eutrophication (algal bloom) can lead to __________________, which is a lack of oxygen supply The Nitrogen Cycle • Nitrogen is in high demand by aquatic and land plants • _________________ in soils, water, and sediments perform many steps of the cycle • Air is the main reservoir of nitrogen (N2) – _____________________________: most organisms cannot use it in the form of N2 • ________________________________ :forms of nitrogen that can be used by organisms • Plants take up “Nr” as ammonium (NO4+) or nitrate (NO3-) ions – Incorporate them into proteins and nucleic acids – The nitrogen moves through the food chain to ______________________, releasing nitrogen wastes • Soil bacteria (_______________________________) convert ammonium to nitrate to obtain energy – Nitrate is available for plant uptake • Bacteria and cyanobacteria are able to use nonreactive N2 gas through ______________________________ – These bacteria that can convert N 2 gas into other usable forms live in root “__________________” of legume plants • The nitrogen cycle continues with a process known as ________________________. – This is reverse process of nitrification and is responsible for converting nitrogen compounds back to N2 gas • Many crops are legumes and draw N from the air – Peas, beans, soybeans, alfalfa – Increases the rate of nitrogen fixation • Crops are heavily fertilized with nitrogen from industrial fixation which can also lead to ________________ • Industrial fixation of nitrogen results in the release of nitrogen oxides, which can be converted to nitric acid causing ____________________ The Sulfur Cycle • Sulfur is a component of proteins, hormones, vitamins • It is often linked with oxygen (i.e. sulfate – SO4) • Most sulfur is in rocks, __________________, ocean sediments • Sulfur enters the air or soil by: – Weathering of rocks, _____________________________, fossil fuel burning, mining of metals • Plants and microbes take up soil sulfate • In air, sulfur dioxide forms __________________ • Sulfur falls to the water bodies and can be a serious pollutant, heavily impacting ecosystems.