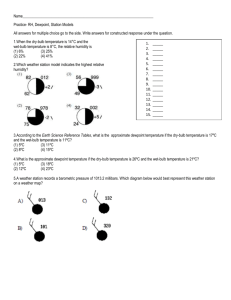
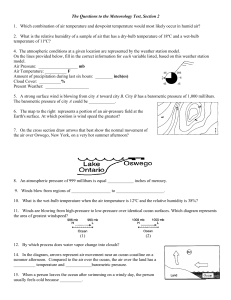
Day 011 - Air Temperature and Dewpoint This is Percy. Percy is a A temperature called When the air temperature When the air temperature parcel of _______. We can’t _______________ is ___________, it gets closer cools enough, Percy always see it, but parcels a special number that tells to the magic temperature. full, and cannot _________ like Percy can carry some when the parcel is full. Here When this happens, Percy any more water. This means ________________. Percy is only _______% full. cannot hold as much it will start to ____________ This is because air temp is __________, and the air whenever air temperature not close to the __________ feels humid. and _______________ are equal. 🔑 MAJOR KEY: _________________________________ _____________________________________________ Day 011 - Air Temperature and Dewpoint This is Percy. Percy is a A temperature called When the air temperature When the air temperature parcel of _______. We can’t _______________ is ___________, it gets closer cools enough, Percy always see it, but parcels a special number that tells to the magic temperature. full, and cannot _________ like Percy can carry some when the parcel is full. Here When this happens, Percy any more water. This means ________________. Percy is only _______% full. cannot hold as much it will start to ____________ This is because air temp is __________, and the air whenever air temperature not close to the __________ feels humid. and _______________ are equal. 🔑 MAJOR KEY: _________________________________ _____________________________________________ answers to questions 65 through 67 on the diagram below, which shows a hygrometer located on sroom. The hygrometer’s temperature readings are used by the students to determine the relaof the air in the classroom. DIAGRAM 1 Psychrometer Diagrams for Practice 30 Which map shows normal paths followed by low-pressure storm centers as they pass acr United States? 24 C O 20 C O Dry-bulb thermometer Wet-bulb thermometer (2) DIAGRAM 4 (3) (1) (4) 31 The diagram below represents the wet-bulb and dry-bulb temperatures on a sling psychrometer. Wet cloth wick Reservoir of water –25 –20 –15 –10 –5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50!C –25 –20 –15 –10 –5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50!C Wet bulb 34 The diagram below shows three stages in the formation of a specific rock. Dry bulb Stage 1 Based on the temperature readings shown in this diagram, determine the relative humidity of the air in the classroom. [1] Stage 2 Remains of partially decayed plants DIAGRAM 2 Stage 3 Burial produces pressure from overlying sediments. Further burial creates more pressure. 12 The diagram below shows dry-bulb and wet-bulb block diagram below show the temperature readings for a parcel of air. rBesides after it hasrelative fallen as precipihumidity, identify another weather variable of the air in the classroom that may be determined by using both temperature readings on the hygrometer. [1] What was the relative humidity of the air when these temperatures were recorded? (1) 5% (3) 20% Describe how water evaporating from the wick attached to the wet-bulb thermometer (2) 17% 63% Which rock is formed as a result of these (4) three stages? 2 lowers the temperature reading of that thermometer. 3 Lake [1] (1) limestone (3) schist DIAGRAM 5 gneiss (4) coalvariables that they measure? 32 Which set of(2) instruments is correctly paired with the weather wind speedbelow – barometer speed – wind vane The diagram shows the temperature readings onwind a weather instrument. An4 Earth science class is preparing a booklet on emergency preparedness.35State one wind direction – wind vane wind direction – barometer safety measure that should be taken to minimize danger from each of the following w ater threats. [ 3] (1) (3) –15 –10 –5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 a Thunderstorm Wet bulb 15 speed 20 25– anemometer 30 35 b Tornado ates the process of transpirawind speed – anemometer –15 –10 –5 0 5 10 wind c Volcanic eruption Dry bulb (3) 3 (4) 4 oint and wind direction shown el below? (2) (4) Based on these readings, the relative humidity of the air is closest to (1) 8% (3) 32% (2) 11% (4) 60% 13 Which atmospheric temperature zone is located between 8 and 32 miles above Earth’s surface and contains an abundance of ozone? (1) troposphere (3) mesosphere (2) stratosphere (4) thermosphere DIAGRAM 3 [20] from the northeast from the southeast from the northwest from the southwest 14 Which natural event temporarily slows or reverses surface ocean currents in the equatorial region of the Pacific Ocean, causing a disruption of normal weather patterns? (1) monsoons (3) El Niño (2) volcanic eruptions (4) deforestation the lower troposphere at the sure belt is sychrometer nd rising ferent rising drsinking the wet and 15 Which form of electromagnetic energy has the longest wavelength? (1) ultraviolet rays (3) gamma rays (2) visible light (4) radio waves inking ewpoint of80a the wet bulb s 10°C and mperature is wind direction – barometer What is the dewpoint of the air? (1) 27°C (3) 3°C (2) 10°C (4) –5°C 002 ding Note ce wind direction – wind vane [3] [OVER] is totally full. It also means thatDIAGRAM any P.S./E. Sci.–June ’13 “spill out” as rain, [6] extra water will snow, or fog, depending on other weather conditions. If you hear a weather forecaster say that the relative humidity is 50 percent, it means that the air contains 50 percent of the water needed for the air to be saturated with, or full of, water vapor. P.S./E. Sci.–August ’10 6 [10] Determining Dewpoint/Relative Humidity There are several ways to measure relative humidity of the air. Unit 1: Weather Instruments and Maps One of the simplest ways to do it is with a device called a psychrometer (SAI kroh meter). A psychrometer is made up of two thermometers. One, called the dry bulb, has nothing on it and is exposed Weather Station Model Diagrams for Practice DIAGRAM 4 DIAGRAM 2 DIAGRAM 5 DIAGRAM 3 Unit 1: Weather Instruments and Maps DIAGRAM 6 81 PART 1 Thinking Frame - See, Think, Wonder QUESTION 1: What do we change on the weather station model to show different amounts of cloud cover? Weather Station Model 1 Weather Station Model 2 Weather Station Model 3 Weather Station Model 4 100% Cloud Cover 50% cloud cover 0% cloud cover ?????? Cloud Cover QUESTION 2: What is the cloud cover on weather station model 4? Weather Station Model 1 Weather Station Model 2 Weather Station Model 3 Weather Station Model 4 Temperature = 25 Dewpoint = 23 Temperature = not given Dewpoint = not given Temperature = 37 Dewpoint = 32 Temperature = ??? Dewpoint = ??? QUESTION 3: What do we change on the weather station model to show the temperature/ dewpoint? QUESTION 4: What are the temperature and dewpoint of weather station model 4? 82 Unit 1: Weather Instruments and Maps PART 2 Thinking Frame - See, Think, Wonder Weather Station Model 1 Weather Station Model 2 Weather Station Model 3 Weather Station Model 4 Wind coming from the southeast Wind coming from the northwest Wind coming from the southwest Wind coming from the ?????? QUESTION 5: What do we change on the weather station model to show different wind direction? QUESTION 6: What is the wind direction of weather station model 4? Weather Station Model 1 Weather Station Model 2 Weather Station Model 3 Weather Station Model 4 Wind speed = 20 knots Wind speed = 5 knots Wind speed = 15 knots Wind speed = ??? QUESTION 7: What do we change on the weather station model to show different wind speeds? QUESTION 8: What is the wind speed of weather station model 4? Unit 1: Weather Instruments and Maps 83