Medication Form: Adult/Older Adult Health I
advertisement

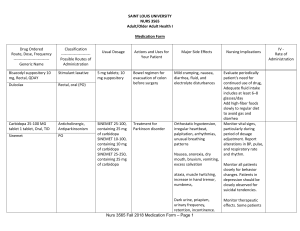
SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY NURS 3565 Adult/Older Adult Health I Medication Form Drug Ordered Route, Dose, Frequency ---------------------------Generic Name Classification ----------------------Possible Routes of Administration Bisacodyl suppository 10 mg, Rectal, QDAY Stimulant laxative Dulcolax Rectal, oral (PO) Carbidopa 25-100 MG tablet 1 tablet, Oral, TID Anticholinergic, Antiparkinsonism Sinemet PO Usual Dosage Actions and Uses for Your Patient Major Side Effects 5 mg tablets; 10 mg suppository Bowel regimen for evacuation of colon before surgery Mild cramping, nausea, diarrhea, fluid, and electrolyte disturbances SINEMET 25-100, containing 25 mg of carbidopa SINEMET 10-100, containing 10 mg of carbidopa SINEMET 25-250, containing 25 mg of carbidopa Treatment for Parkinson disorder Orthostatic hypotension, irregular heartbeat, palpitation, arrhythmias, unusual breathing patterns Nausea, anorexia, dry mouth, bruxism, vomiting, excess salivation ataxia, muscle twitching, increase in hand tremor, numbness, Dark urine, priapism, urinary frequency, retention, incontinence. Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 1 Nursing Implications Evaluate periodically patient's need for continued use of drug, Adequate fluid intake includes at least 6–8 glasses/day Add high-fiber foods slowly to regular diet to avoid gas and diarrhea Monitor vital signs, particularly during period of dosage adjustment. Report alterations in BP, pulse, and respiratory rate and rhythm. Monitor all patients closely for behavior changes. Patients in depression should be closely observed for suicidal tendencies. Monitor therapeutic effects. Some patients IV Rate of Administration Drug Ordered Route, Dose, Frequency ---------------------------Generic Name Classification ----------------------Possible Routes of Administration Usual Dosage Actions and Uses for Your Patient Major Side Effects Nursing Implications IV Rate of Administration manifest increase in bradykinesia Cefepime 2,000 mg in sterile water (PF) 20 mL syringe, Intravenous, q12h Maxipime Antibiotic; cephalosporin IV, IM Mild to Moderate Infections Adult: IV/IM 0.5–1g q12h times 7–10 d prior urine culture grew pseudomonas Moderate to Severe Infections Adult: IV 1–2g q12h times 10 d Escitalopram tablet 10 mg, SSRI Oral, QDAY Lexapro PO Febrile Neutropenia Adult: IV 2 g q8h for 7 d or until resolution of neutropenia 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg tablets; 5 mg/5 mL liquid Antibiotic -associated colitis, diarrhea, nausea, oral moniliasis, vomiting, elevated liver function tests Headache, fever. Depression, Generalized Anxiety Monitor for S&S of hypersensitivity Monitor for S&S of superinfection or pseudomembranous colitis pain, inflammation, rash, pruritus Determine history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillin, or other drugs before therapy is initiated Fatigue, fever, arthralgia, myalgia, HTN, ejaculation disorder, impotence, migraine, tremor, vertigo, Nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain Assess for suicidal tendencies, especially during early therapy. Restrict amt of drug available to patient. Risk may be increased in children, adolescents, and adults ≤24 yr. Assess for serotonin syndrome (mental Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 2 Infuse over 30 min; with Ytype administration set, discontinue other compatible solutions while infusing cefepime Drug Ordered Route, Dose, Frequency ---------------------------Generic Name Classification ----------------------Possible Routes of Administration Fluconazole 400 mg in 200 mL saline IVPB, Intravenous, once Diflucan Antifungal Fludrocortisone tablet 200 mcg, Oral, BID Corticosteroids. Florinef PO IV, PO Crystalloid Fluid 0.9% NaCl injection3 mL, Intracatheter, q8h Usual Dosage Actions and Uses for Your Patient Major Side Effects Nursing Implications changes autonomic instability nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Monitor for allergic response. Monitor BUN, serum creatinine, and liver function. Monitor for S&S of hepatotoxicity. 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg tablets; 10 mg/mL, 40 mg/mL suspension; 2 mg/mL injection to prevent and treat a variety of fungal and yeast infections Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, increase in AST in patients with cryptococcal meningitis and AIDS, rash, headache 0.1 mg tablets/ 100mcg Parkinson’s disease c/b urinary retention and orthostatic hypotension Sodium Chloride Irrigation Sol: 0.45%, 0.9% used to help prevent IV catheters, dehydration, or hypovolemia Vertigo, headache, nystagmus, CHF, hypertension, tachycardia, Hypocalcemia; sodium and fluid retention; hypokalemia and hypokalemic alkalosis, decreased glucose tolerance; hyperglycemia, Hemolysis, hemoptysis hyponatremia hypertension edema, flushing hypokalemia hypernatremia dehydration phlebitis IV, Oral Liquid Formulations Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 3 Monitor weight and I&O, Check BP q4–6h and weight. Monitor for S&S of hypokalemia and hyperkalemic metabolic alkalosis Do not administer unless solution is clear, and seal is intact. Monitor for fever infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or p hlebitis extending from the site of injection, and hypervolemia. IV Rate of Administration Give at a maximum rate of ~200 mg/h. Give after hemodialysis is completed. Drug Ordered Route, Dose, Frequency ---------------------------Generic Name Iopamidol 76 % contrast, Intravenous, Contrast Once Isovue 370 Classification ----------------------Possible Routes of Administration Non-ionic iodinated contrast media IV Usual Dosage Injectable solution (41%; 51%; 61%; 76%); intrathecal solution (41%; 61%) Antibiotic Metronidazole 500 mg in 100 mL IVPB, Intravenous, q8h 250 mg, 500 mg tablets; 375 mg capsules; 750 mg sustained release tablets; 500 mg vials; 0.75% lotion, emulsion; 0.75%, 1% cream; 0.75%, 1% gel Actions and Uses for Your Patient Major Side Effects Nursing Implications Radiography/CT order weight gain, oliguria wheezing, seizure, enlarged thyroid flushing, hives, Blood vessel disease, severe Congestive heart failure Dehydration Kidney disease Monitor for anaphylaxis, symptoms of heart attack, blood clots in the lung, numbness, or weakness as it may be symptoms of stroke. septicemia, and for both pre- and postoperative prophylaxis rash, urticaria, pruritus, flushing, headache, ataxia, confusion, irritability, depression, fleeting joint pains, overgrowth of Candida Monitor especially for seizures and peripheral neuropathy, WBC levels Monitor for S&S of sodium retention, especially in patients on corticosteroid therapy or with a history of CHF. Monitor patients on lithium for elevated lithium levels. Report appearance of candidiasis Flagyl IV, PO, Topical Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 4 IV Rate of Administration Drug Ordered Route, Dose, Frequency ---------------------------Generic Name Classification ----------------------Possible Routes of Administration Usual Dosage Alpha-1 agonists Midodrine tablet 5 mg, Oral, 4X/day Proamatine 2.5 mg, 5 mg tablets Actions and Uses for Your Patient Major Side Effects Nursing Implications urinary retention and orthostatic hypotension Paresthesia, chills, pain, facial flushing. Confusion, anxiety. Hypertension, Dry mouth. Pruritus, piloerection, rash. Dysuria, urinary retention, urinary frequency Monitor regularly supine and standing BP. Stop drug if supine BP increases excessively. PO PPI Pantoprazole injection 40 mg, Intravenous, BID Protonix IV, PO Vancomycin (Vancocin) IV dose per pharmacy, does not apply, AS DIRECTED Antibiotic 40 mg enteric coated tablets; 40 mg vial 125 mg, 250 mg capsules; 1 g, 10 g oral powder; 500 mg, 1 g injection Monitor carefully effect of the drug in diabetics with orthostatic hypotension and those taking fludrocortisone acetate, which may increase intraocular pressure. dysphagia Diarrhea, flatulence, abdominal pain, headache, insomnia, rash. Teach pt. to take last daily dose 4 h before bedtime Monitor for and immediately report S&S of angioedema or a severe skin reaction, swelling of the face, tongue, or lips; difficulty breathing or swallowing. prior urine culture grew pseudomonas, colitis Ototoxicity, superinfections, severe pain, thrombophlebitis at injection site, generalized Monitor I&O: Report changes in I&O ratio and pattern. Oliguria or cloudy or pink urine Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 5 IV Rate of Administration Drug Ordered Route, Dose, Frequency ---------------------------Generic Name Classification ----------------------Possible Routes of Administration Usual Dosage Actions and Uses for Your Patient Major Side Effects tingling following rapid IV infusion. Nursing Implications IV Rate of Administration may be a sign of nephrotoxicity. Monitor I&O: Report changes in I&O ratio and pattern. Oliguria or cloudy or pink urine may be a sign of nephrotoxicity Monitor serial tests of vancomycin blood levels in patients with borderline kidney function, in infants and neonates, and in patients >60 y. Vancocin PO, IV Lactated Ringers infusion, Intravenous, Continuous isotonic, crystalloid fluid Dosage is to be directed by a physician and is dependent upon age, weight, clinical condition of the patient and laboratory determinations. Low Hematocrit Rehydration (water and electrolytes) Fluid Replacement d/t diarrhea hives, itching, swelling of the eyes, face or throat, coughing, sneezing, difficulty breathing, fever, infection at the injection site, and redness/red streaking and swelling form the injection site Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 6 Monitor I&O Risk for hyperkalemia if given with K+ supplement DO NOT administer in cases of alkalosis (once inside body, converts lactate to bicarb 1000ml at 100 rates Drug Ordered Route, Dose, Frequency ---------------------------Generic Name Classification ----------------------Possible Routes of Administration Usual Dosage Actions and Uses for Your Patient Major Side Effects Nursing Implications IV Acetaminophen tablet 650 mg, Oral, q6h PRN Analgesic PO: 325-650mg q4h up to a maximum of 1gram q6h. Suppositories: 650mg q4h not to exceed 4 grams a day for up to 10 days Tylenol Fever reduction. Temporary relief of mild to moderate pain. Negligible with recommended dosage. Acute poisoning: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, lethargy, onset of hepatotoxicity elevation of serum transaminases (ALT, AST) and bilirubin. Chronic ingestion: Neutropenia, pancytopenia, renal damage PO, Rectal Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 7 Monitor for S&S of hepatotoxicity, even with moderate acetaminophen doses, especially in individuals with poor nutrition or who have ingested alcohol over prolonged periods; poisoning, usually from accidental ingestion or suicide attempts; potential abuse from psychological dependence. Do not self-medicate for pain for more than 10 days IV Rate of Administration Hydromorphone injection 0.2 mg, Intravenous, q4h PRN opioid analgesics 1–4 mg q4–6h prn. Cough, Moderate-tosevere pain Confusion, sedation, dizziness, dysphoria, euphoria, floating feeling, hallucinations, headache, respiratory depression, hypotension, bradycardia. constipation, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, urinary retention. flushing, sweating. physical dependence, psychologic dependence, tolerance. Monitor vital signs at regular intervals. Assess effectiveness of pain relief 30 min after medication administration. Monitor drug effects carefully in older adult or debilitated patients and those with impaired renal and hepatic function. Assess effectiveness of cough. Nausea and orthostatic hypotension most often occur in ambulatory patients or when a supine patient assumes the head-up position. Monitor I&O ratio and pattern & bowel pattern. Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 8 Drug Ordered Route, Dose, Frequency ---------------------------Generic Name Classification ----------------------Possible Routes of Administration Dilaudid PO/SQ/IM/IV Ondansetron (disintegrating) tablet 4 mg, Oral, q6h PRN Antiemetics Usual Dosage 4 mg, 8 mg orally disintegrating tablets Actions and Uses for Your Patient Radiotherapyassociated nausea and vomiting Zofran ODT: 4 mg [DSC] [contains aspartame, methylparaben sodium, propylparaben sodium; strawberry flavor] Zofran (ODT) PO, IM, IV Ondansetron injection 4 mg, Intravenous, q6h PRN Antiemetics 2 mg/mL, 32 mg/5 mL injection Major Side Effects Dizziness and lightheadedness, headache, sedation, constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dry mouth, increased liver enzymes. extrapyramidal reactions. Hypotension Hypersensitivity Hiccups Dyspnea, laryngeal edema, stridor Radiotherapyassociated nausea and vomiting Nursing Implications Monitor fluid and electrolyte status. Diarrhea, which may cause fluid and electrolyte imbalance, is a potential adverse effect of the drug. Monitor cardiovascular status, especially in patients with a history of coronary artery disease. Give tablets 30 min prior to chemotherapy and 1–2 h prior to radiation therapy Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia should be corrected prior to ondansetron administration Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 9 IV Rate of Administration Drug Ordered Route, Dose, Frequency ---------------------------Generic Name Zofran Classification ----------------------Possible Routes of Administration IM, PO, IV Usual Dosage Actions and Uses for Your Patient Pt has a history of vertigo, and this prescription helps. Major Side Effects Nursing Implications Dizziness and lightheadedness, headache, sedation, constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dry mouth, increased liver enzymes. extrapyramidal reactions. 1 h preoperatively IM 4 mg injected immediately prior to anesthesia induction or once postoperatively if patient experiences nausea/vomiting shortly after surgery IV 4 mg by slow IV push, may repeat q8h as needed Monitor fluid and electrolyte status. Diarrhea, which may cause fluid and electrolyte imbalance, is a potential adverse effect of the drug. Monitor cardiovascular status, especially in patients with a history of coronary artery disease. Hypotension Hypersensitivity Hiccups Dyspnea, laryngeal edema, stridor Nurs 3565 Fall 2018 Medication Form – Page 10 IV Rate of Administration