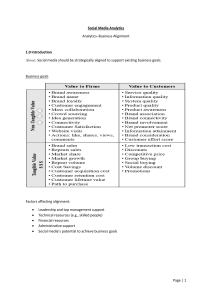
MODULE 1: Introduction to Business Analytics Why Analytics? Analytics helps us see insights and meaningful data that we might not otherwise detect. Business analytics focuses on using insights derived from data to make more informed decisions that will help organizations increase sales, reduce costs, and make other business improvements. Definition of Business Analytics Business analytics is the process of looking at and assessing the wealth of data your company already has at its disposal and using it to make data-driven decisions. It moves beyond just looking at numbers to see what happened. Instead, business analytics also endeavors to give insight into why things happened and suggests what steps to take next. Benefits from Business Analytics In just a few years, the implementation of data analytics has skyrocketed. Big data adoption jumped from 17% in 2015 to 59% in 2018, a whopping 42% increase. Nevertheless, a recent survey also found that many businesses are not tapping into the data they already have at their disposal. Between 60% and 73% percent of all data within an enterprise goes unused for analytics. It’s a startling number when you think about the potential benefits to small businesses. Here are just a few: Keeping you on budget. If you’re like most small companies, your marketing budget is tight. Using business analytics helps you maximize every dollar by helping you get to know your customers better, anticipate their ever-changing needs, get an edge on the competition, and bring innovative ideas and products to the marketplace. Better decision making. Not sure how to use your marketing budget? Or which keywords are most effective? What about predicting your biggest sellers over the holiday season? Business analytics uses data to inform decisions and improve accuracy, efficiency and response time. The ability to measure accomplishments against overall goals. Business analytics gives you a clearer image of goals and objectives. By using data visualization, businesses can track their current and past performance against key performance indicators (KPIs), goals and objectives. Staying in the know. Business owners and marketers can use analytics to track trends, customer behavior and market shifts. This data will allow you to keep on top of things and make changes dynamically when and if supporting data indicates it’s time. Building efficiency. Nowadays, the speed at which businesses can garner data is lightning fast. Thanks to business analytics, you can identify any breakdown in process or performance in almost real-time, saving time, money and resources. What are the different types of business analytics? Think of business analytics as happening in three different stages: 1. Descriptive analytics. Digs into your data and uses KPIs to show you the current state of your business. For example, real-time information about your customers’ demographics, interests or purchasing behavior. Maybe it’s sales numbers or financials. It could be social metrics like how many Facebook likes, tweets, or followers you have. Descriptive analytics doesn’t try to establish cause and effect relationships. It’s essentially cold, hard numbers. 2. Predictive analytics. This type of analytics goes one step further. It tries to predict future actions based upon trending historical data. Here are a few examples: Use past information to figure out what types of products your customers might be interested in based on recent numbers, and whether they are likely to purchase again. If you have a limited budget for your marketing campaign and can’t afford to offer discounts to everyone, based on description analytics, predictive analytics could inform you about the customers who are most likely to buy your product. 3. Prescriptive analytics. This form of business analytics can show you the best course of action for a given situation. While descriptive analytics shows what has already happened, and predictive analytics tries to forecast what might happen next, prescriptive uses that information to give you potential solutions based on similar situations (Year over Year data, seasonality data, product launch data). For example, ticket sales for a holiday show are lagging over last year’s sales. Prescriptive analytics may suggest a need to lower prices or add a matinee performance in response. User-friendly analytics resources for small business Google Analytics. Google is king when it comes to analyzing your online world, whether it’s your website or social presence. Still, a recent study found that less than 30% of small businesses use website analytics, call tracking or coupon codes. About 18% of small businesses admit to not tracking anything at all. That’s where Google Analytics can come in to play. You can sync your Google accounts (including AdSense) to get insight into ROI on marketing, ad campaigns and more. Best of all, you can try the basic version out for free, which may be powerful enough for your small business. If you need more in-depth analytics down the line, you can upgrade later. Easy-to-use software. With today’s intuitive tools, business analytics has never been more natural. Nowadays, there’s plenty of reasonably-priced apps—like Power BI —that lets you easily transform data into visuals, and then analyze and share them with colleagues on any device, giving you unmatched insights. In addition, software like Visio lets you bring ideas life with easy-to-read diagrams created from various sources, including your existing Excel data. Built-in email and spreadsheet tools. Chances are, you have some basic data-gathering capabilities already at your fingertips. Many spreadsheets have easy-to-read charts and graphs on board that’ll help you better understand (and present) your data, via formatting, sparklines and tables, plus capabilities for creating forecasts with just a few clicks. The same goes for email. Find one with a lightweight Customer Relationship Manager (CRM) tool built-in, and you’ll be able to easily manage customer data, including emails, meetings, calls, notes, tasks, deals and deadlines in one place. CRM data can hold a treasure-trove of invaluable information about your company’s customers, and sales and marketing operations. Every type of business can benefit from using business analytics. No matter which tools you choose in the end, gaining better insight into your data will help you stay on budget, on task and in-the-know. Business Analytics Tools What Are Business Analytics Tools? The tools used by business analysts include a variety of application software that captures quantitative and qualitative data from different business systems and incorporates it into a repository. That way, analysts can review and analyze the data to enable smarter decision-making. Most companies deploy a mix of business analytics software, including statistical tools, predictive modeling, and data mining tools. These software applications for business analytics provide organizations with a holistic overview of key insights that improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability. Difference between Business Analytics and Business Intelligence Solutions Although Business Intelligence (BI) tools also compile and analyze data, software for business analytics takes a deeper dive, helping to identify weaknesses, alerting policymakers to unanticipated events, fixing potential problems, and even forecasting future performances. High-caliber tools used by business analysts for requirement gathering provide the knowledge and confidence enterprises need to improve customer satisfaction, increase their competitive edge, and attain business goals. The popularity and demand for premium-quality business analytics tools are at an all-time high because of the rich functionalities these advanced business analytics software deliver in terms of business success and future growth. Gartner Inc., the global research and advisory firm, predicts that 70 percent of the world's large- and medium-sized enterprises will adopt sophisticated business analytics tools in 2021. According to experts, the growing relevance of data analysis will drive improved business decisions and create new job openings in multiple fields. Below are the top ten most widely used business analytics tools and solutions designed for modern enterprises. 1. SAS Business Analytics (SAS BA) The high-grade text analytics capabilities of the SAS-based business analytics software allow users to inspect and transform unorganized text data into relevant information that analysts can explore to discover meaningful insights. SAS BA is fully-loaded with a range of statistical tools, which simplify the process of analyzing large sets of data in real-time. The top-of-the-line business analytics platform also predicts future trends from the information harvested from big data. 2. QlikView QlikView is one of the most preferred tools for business analytics because of its unique features, such as patented technology and in-memory processing, facilitating the delivery of ultra-fast business analytics reports. Included among the best business analyst tools, QlikView allows users to visualize data relationships using specific colors for related and non-related data with automatically maintained data association, compressed to 10 percent of its native size. 3. Board Board features in the list of top-rated business analyst software tools because of its industry-leading business analytics model that permits users to create interactive and intuitive business analytics reports and dashboards. The highly-scalable business analytics platform integrates the best-in-class analytical tools for business, including a powerful statistics suite. The Board business analytics tool can manage massive data volumes, and it can also support accurate scenario analysis and forecasting by manipulating the data supplied to scenarios. 4. Splunk Splunk is one of the most widely used business analytics tools in small and medium scale industries. Initially launched for processing machine log file data, Splunk has added a host of sophisticated features over the years, including a user-friendly web interface and various visualization options. 5. Sisense Sisense - one of the most popular business analyst software tools - incorporates dynamic and robust text analysis functionalities that enable users to transform unstructured text into valuable business intelligence. The Sisense business analytics platform, which features the proprietary Sisense Crowd Accelerated BI, uses open-source language for computational statistics. It allows users to perform extensive analysis and visualization of complex data, which promotes data-driven decisions and improved forecasting of future trends. 6. Microstrategy The Microstrategy business analytics software integrates superior analytics capabilities that allow hassle-free processing of unstructured text data, which specialists can further analyze via the platform's text analytics solutions. One of the most up-to-date business analytics tools, Microstrategy, incorporates insightful analytical and statistical capabilities that enable real-time trend forecasting, with options for third-party data mining. The first-rate business analytics tools, combining a range of business analysis tools and techniques, lets users create and share business analytics reports from anywhere and on any device. 7. KNIME In 2004, a team of expert software engineers from the University of Konstanz in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, developed the innovative KNIME business analytics platform. Renowned as one of the best high-performance business analyst software, KNIME, via its unique data-pipelining approach, facilitates varied components for machine learning and data mining that support persistent analysis, visual programming, and seamless business analytics report. 8. Dundas BI The fully-equipped Dundas BI offers first-class business analytics and business intelligence solutions using the R programming language. With robust business analytics tools, Dundas BI provides automated analytics, trend forecasting, and a high-level dashboard that helps users visualize data and create business analytics reports through easy-to-use drag-and-drop features. 9. TIBCO Spotfire TIBCO Spotfire, recognized as one of the most advanced tools for business analytics, offers powerful and automated analytics solutions that allow data professionals to run business analytics reports and analysis over a defined time span. The latest upgrade of the Spotfire platform has significantly improved TIBCO's scalability, statistical analysis capabilities, and capacity to analyze text-based unstructured data. 10. Tableau Big Data Analytics Experts agree that Tableau Big Data Analytics is one of the best business analyst software, given its dynamic and cutting-edge capabilities for unstructured text analysis. Tableau's business analytics platform, which includes robust and reliable statistical tools, empowers users to perform an in-depth analysis of social media networks, and predict patterns based on current and historical data. Career Options in Business Analytics Since the beginning of the 21st century, a variety of new career options and employment paths emerged, which did not exist before. However, no career choice can match Business Analytics in salaries, learning, and training opportunities in everyday work. With businesses increasingly leveraging business analytics tools, multiple avenues are opening up for qualified business analysts in diverse sectors, including automotive, healthcare, retail, banking, hospitality, and aviation. Depending on your skills and interests, you may specialize in a business analyst role, such as Big Data Engineer, Data Scientist, Database Administrator, Marketing Analytics Manager, or Data Visualization Specialist. The best BI & Reporting tools for Microsoft SQL Server 1. PowerBI PowerBI is the indisputable complements to MSSQL, like Google Data Studio to BigQuery, since both are created by the giant Microsoft. PowerBI is quite well-known in the BI industry, especially for enterprises that adopt the Microsoft ecosystem. It supports an impressive number of data sources, giving companies the power to centralize their data in one place. PowerBI has a user-friendly interface with amazing data visualization capabilities like interactive dashboards, numerous types of charts, powerful filters and much more. What's good about PowerBI? Support hundreds of data sources, from cloud service like Redshift to offline files like Excel. Powerful data visualization capabilities. Besides the basic visualization types, PowerBI allows advanced users to choose from a market place of custom visuals or create their own using wellknown Javascript libraries Frequent updates and innovations. Follow PowerBI's blog and you will see the team is really active in pushing new features and changes. PowerBI has mature data modeling capabilities. What needs to improve? PowerBI has a steep learning curve. Data analysts must learn DAX (Data Analysis Expression) language to fully leverage PowerBI's power, which is complicated and rigid sometimes. The approach is not collaborative and agile because Data Modeling can only be done on a Windows Desktop (Windows-centric, doesn't support Linux/Mac) then publish to the cloud. 2. Holistics A direct competitor of PowerBI is Holistics, a powerful self-service BI tool. Besides providing a powerful visualization layer that is easy to use for non-technical users, it also comes with a modeling layer that lets data analysts model and transforms data in MSSQL and many other SQL data warehouses. Holistics offers a free version to start with and it only charges when your team's need scales up (need to run more queries, use more advanced analytical features). When compared to other freemium products in the same BI landscape like PowerBI, Tableau, or Looker, Holistics' pricing is the most attractive and predictable. You may want to refer to their pricing here. What's good about Holistics? Allow you to query the BigQuery database using customizable SQL queries and get fast results with its cache layer Materialized views of query results are stored back to BigQuery, for immediate access and fast visualizations and reports. Automated scheduling of reports and dashboards with the latest data in BigQuery, sent directly to your email inbox. This feature is fairly basic but not yet implemented in many other tools. Drag-and-drop interface for business users to explore data and generate reports to answer ad-hoc questions. What needs to improve? Compared to the big names like PowerBI or Looker, Holistics.io is a fairly new tool to the market. A lot of advanced features are still being developed at the moment. Holistics has not supported Git-integration and version control, which is preferable to a lot of advanced analysts. Dashboards are not as interactive as PowerBI. Currently, Holistics only supports drill-down by date and drill-through to another dashboard. 3. Domo Domo is a cloud-based analytics and BI platform aimed at senior executives and line-of-business users who need intuitive business-facing dashboards. Domo is often deployed in the line of business with little or no support from IT. Taking a look at Domo's landing page and we'll be easily impressed with their great-brand clients like Cisco, ESPN or Ebay. With beautiful dashboards, a wide range of supported data sources, Domo is easily the go-to tools for a lot of companies. What's good about Domo? Visualization layer is clean and is very business presentable. Domo is great on desktop, tablet and mobile. This gives data presented in Domo extra accessibility and discoverability. Domo has hundreds of connectors including databases, data warehouses, cloud platforms. Also, it supports uploading a wide ranges of file extension like .odt, .xls, .csv, .xml, .json Dashboard loading time is really fast because Domo caches data in their propriety storage Have extensive permission control system that suits large enterprises. What needs to improve? Support issues: The sole operational factor where Domo customers evaluated it as being below average was support. Reference customers continue to cite response time and time to resolution as two of the limitations to its broader deployment. The back end of getting the data into the tool can be a bit complex. It's not as user friendly for nontechnical users. While the visualization tools are excellent, extracting information from the tool has been a little bit of a challenge. 4. Looker Another Google Cloud Platform product, Looker is a powerful BI tool that provides an innovative approach for real-time data exploration and analytics. If you are looking for a tool to centralize your business data, look no further because Looker, with its semantic modeling layer, can help you apply business logic to your data and create a single source of truth for every team to use. What's good about Looker? Looker runs entirely in-browser, so there’s no need for desktop install and it's better for collaboration and data delivery between internal and external users Looker operates entirely on the data in your database. That means that you’re operating directly on your full dataset and getting all the horsepower of your database, whether that be an MPP like Vertica, Redshift, Bigquery; a SQL-on-Hadoop setup like Impala or Spark; or a standard RDBMS like MySQL or Postgres Automated reporting - Looker allows you to schedule emails for daily/weekly/monthly reports or send alerts if there are anomalies in data. Looker has GitHub integration, so you can see every change made to the modeling layer and combine the work of multiple developers seamlessly What needs to improve? Looker has a steep learning curve when it comes to adopting a new language (LookML) & the modelview approach for the end-users. You definitely need to have an internal team that is dedicated to just setting it up and getting the rest of the people on board. Small errors are hard to troubleshoot and result in not using the dashboard much. No SQL CLI makes it disappointing for power users. Relative to other BI tools, the advanced charting functionality is somewhat limited. 5. Tableau When it comes to data visualization Tableau is the champion of my heart. Although the setup process might be quite overwhelming with newbies, once you get used to it, you'll find that there's a long way for other tools in the market to compete with Tableau regarding this aspect. This is simply because Tableau has dominated the market with its highly interactive dashboards, together with its huge library of visuals and supported metadata (check out their built-in map data!) What's good about Tableau? Live and in-memory data – Easily switch between extracted data and live connections, set up automatic extract refreshes and be notified when a data connection fails – all through the Tableau platform. Secure collaboration – Use Tableau Server and Tableau Online to securely share and collaborate on key insights. Friendly drag-and-drop interface – With drag-and-drop abilities, easily integrate data and create visuals to pinpoint patterns with a few clicks. What needs to improve? There are a lot of features on one single interface as Tableau wants to maximize the user experience. But because there is so many things in the user interface, a lot of features go unnoticed and unused. Also since there are so many features and functionalities, it sometimes is difficult to locate a particular functionality Lack of BI capabilities. Tableau lacks functionality required for a full-fledged business intelligence tool, such as large-scale reporting, the building of data tables, and static layouts. Tableau Desktop lacks the basic functionality of cleaning and prepping the data to be imported in Tableau Desktop. This is one of the major features which it lacks, you need additional support from Tableau to get these things added.