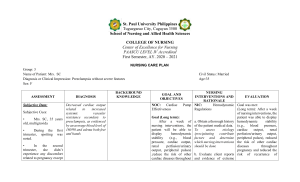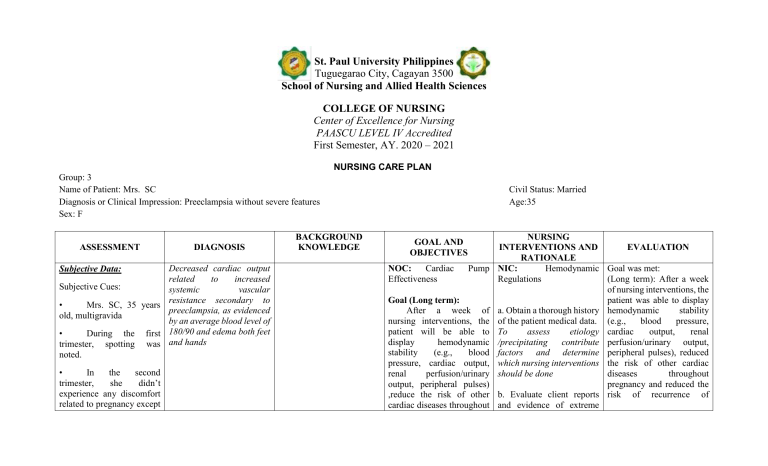
St. Paul University Philippines Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500 School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences COLLEGE OF NURSING Center of Excellence for Nursing PAASCU LEVEL IV Accredited First Semester, AY. 2020 – 2021 NURSING CARE PLAN Group: 3 Name of Patient: Mrs. SC Diagnosis or Clinical Impression: Preeclampsia without severe features Sex: F ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS Decreased cardiac output related to increased Subjective Cues: systemic vascular resistance secondary to • Mrs. SC, 35 years preeclampsia, as evidenced old, multigravida by an average blood level of • During the first 180/90 and edema both feet trimester, spotting was and hands noted. Subjective Data: • In the second trimester, she didn’t experience any discomfort related to pregnancy except BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Civil Status: Married Age:35 NURSING INTERVENTIONS AND EVALUATION RATIONALE NOC: Cardiac Pump NIC: Hemodynamic Goal was met: Effectiveness Regulations (Long term): After a week of nursing interventions, the patient was able to display Goal (Long term): After a week of a. Obtain a thorough history hemodynamic stability nursing interventions, the of the patient medical data. (e.g., blood pressure, patient will be able to To assess etiology cardiac output, renal display hemodynamic /precipitating contribute perfusion/urinary output, stability (e.g., blood factors and determine peripheral pulses), reduced pressure, cardiac output, which nursing interventions the risk of other cardiac renal perfusion/urinary should be done diseases throughout output, peripheral pulses) pregnancy and reduced the ,reduce the risk of other b. Evaluate client reports risk of recurrence of cardiac diseases throughout and evidence of extreme GOAL AND OBJECTIVES that she felt like her diet was uncontrolled. She was fond of eating chocolates, fruit shakes, and ice cream. • On her third trimester, she was surprised upon knowing some deviations from her vital signs. She was troubled about some discomforts in certain areas of her body. • She was then asked by her OB-GYNE to undergo some diagnostic runs. pregnancy and reduce the risk of recurrence of preeclampsia on the next pregnancy. fatigue, intolerance for activity, sudden or progressive weight gain, swelling of extremities, and progressive shortness of breath. Objectives (Short term): After 2-3 days of To assess for signs of poor nursing interventions, the ventricular function and/or patient will: impending cardiac failure. Objective Data: Blood pressure severely elevated. was Third trimester, edema specifically on hands and feet UTZ Result: cord coiling Vital Signs admission: T: 37.4 RR: 17 Abnormal upon Verbalize knowledge of the disease process, individual risk factors, and treatment plan. Identify signs of cardiac decompensation, alter activities, and seek help services for prenatal care. Report adequate fluid and nutritional intake especially foods high in iron. Moreover, participate in activities that reduce the workload of the heart. Shows improved well-being such as preeclampsia on the next pregnancy. (Short term): After 2-3 days of nursing interventions, the patient was able to: Verbalized knowledge of the disease process, individual risk factors, and c. Review and monitor vital treatment plan as evidenced signs, signs of improving by shock, noting decreased cognition and unstable or Identified signs of cardiac subnormal BP, neck vein decompensation, alter edema and reduced urinary activities, and sought help output. services for prenatal care as Early detection of changes evidenced by in these parameters promotes timely intervention to limit degree Reported adequate fluid of cardiac dysfunction and and nutritional intake to note response to especially foods high in activities and interventions. iron. Moreover, participated in activities d. Encourage slower paced that reduce the workload of activities, or shorter periods the heart as evidenced by of activity, with frequent rest periods following exercise prescription; Showed improved wellobserve for being such as baseline symptoms of intolerance. levels for pulse, BP, Take blood pressure and temperature, respiration, P: 80 BP: 180/90 Protein (++++) baseline levels for pulse, BP, temperature, respiration, and relaxed muscle tone. pulse before and after and relaxed muscle tone as activity and note changes. evidenced by Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation is effective in reducing total and cardiovascular mortality and hospital admissions (Heran et al, 2011). e. Weigh the client at the same time daily (after voiding). Daily weight is a good indicator of fluid balance. Use the same scale, if possible, when weighing clients for consistency. Increased weight and severity of symptoms can signal decreased cardiac function with retention of fluids. Clinical practice guidelines state that weighing at the same time daily is useful to assess effects of diuretic therapy (Yancy et al, 2013). f. Advise small, frequent, sodium-restricted, low saturated fat meals. Sodium-restricted diets help decrease fluid volume excess. Low saturated fat diets help decrease atherosclerosis, which can cause coronary artery disease. Clients with cardiac disease tolerate smaller meals better because they require less cardiac output to digest (Hooper et al, 2012). Excess sodium can contribute to elevation of blood pressure, renal impairment, ventricular hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, and fibrosis of coronary arteries (Whelton et al, 2012). g. Administer medications, as prescribed by the doctor, and monitor cardiac responses. To help treat underlying condition. h. Provide strict bed rest in lateral position. Recommend elevation of lower extremities when sitting. Lateral position improves cardiac output by promoting venous return and reduce edema formation. i. Give information about positive signs of improvement such as decreased edema and improved VS. To provide encouragement. j. Discuss potential complications and the possible need for medical follow-up or alternative therapies. Timely recognition and intervention can promote wellness. k. Teach home monitoring of weight, pulse, and/or blood pressure, as appropriate. To detect change and allow for timely intervention. l. Refer to medical social services, cardiac rehabilitation, telemonitoring and case management as necessary for assistance with homecare, access to resources, and counseling about the impact of severe or chronic cardiac diseases. Access to systems that promote care coordination is essential for successful care of the HF client. Good communication and documentation between services, health care providers, and transitions of care is essential to ensure improved outcomes in HF clients (Albert et al, 2015; Smith et al, 2011; Yancy et al, 2013).