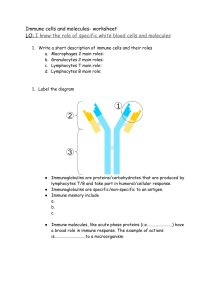
INTRODUCTION Immunology Study of immune system + its responses to microbial infections Infectious disease Cold Chickenpox Chickenpox Whooping cough Bubonic plague TB (Tuberculosis) Malaria Ringworm Athletes’ foot Microbe that causes the disease Rhinovirus Varicella zoster Rubella Bordetella pertussis Yersinia pestis Mycobacterium tuberculosis Plasmodium falciparum P Trichophyton rubrum Trichophyton mentagrophytes Type of microbe Virus Virus Virus Bacterium Bacterium Bacterium Dust mites Mold Insect venoms Animal dander Medications Various foods The immune system Dedicated to surveillance and destruction of: -Foreign material -Disease-causing cellular changes -Infectious biological agents Immunity: resistance mechanisms to disease or host defense mechanism, specifically to infection disease Role of immune system Def. against infections Implications -Deficient immunity → increased susceptibility to infections like AIDS Protozoan Fungus Fungus A microbial pathogen… •Has the instinct to perpetuate requires a host -Replicates in a specific niche in the host’s body -Avoids attacks mounted by the components of the innate and adaptive immune system •May possess some virulence genes for survival, which are expressed while it causes disease in its host •Produces progenies that transfer to new hosts, thus spreading the infection Disease-causing changes in the body Cancer Cells -divide without stopping -less specialized than non-cancer cells -i.e., cancer cells do not mature into distinct cell types -influence the physiology of their microenvironment in order to sustain survival, e.g., blood vessel formation can be induced by cancer cells to surrounding non-cancer cells -often able to evade the immune system Harmful substances from the environment -Allergen- usually harmless substance capable of triggering a response that starts in the immune system and results in an allergic reaction -Response: immune system releases chemicals that typically cause symptoms in the nose, throat, eyes, ears, skin or roof of the mouth. -Common allergens: Def. against tumors Immune sys. can injure cells + induce pathologic inflammation Immune sys. Recognizes + responds to tissue grafts and newly introduced proteins Some current vaccines: Diphtheria Measles Mumps Pertussis Polio (paralytic) *Smallpox- eradicated *Polio- almost eradicated -Vaccination boosts defenses + protects against infections Potential for immunotherapy of cancer Immune responses are the cause of allergic, autoimmune, and other inflammatory diseases Immune resp. = barriers to transplantation + gene therapy Rubella Tetanus Hapatitis B Hemophilus influenza type B Portals of Entry -Skin- poor portal of entry -Mucous membranes- Primary portals of entry and exit -Epithelial tissues (respiratory, gastrointestinal, urogenital systems, eyes) -Covered in mucus -Various defenses Types of Immunity Innate immunity -Immediate protection against microbial invasions -Always present in healthy individuals -blocks entry and rapidly eliminates microbes -Enhance adaptive immune responses -Non-specific targets (e.g., phagocytes) -No immunological memory Adaptive immunity -Develops more slowly -Provides more specialized defense against infections -Specific -Requires expansion + differentiation of lymphocytes -Comprised of Lymphocytes and their antibodies -Highly-specialized -T-cells via antigen recognition -Acts on microbes that infects and divides within host cells -Some T-cells activate phagocytes to destroy microbes via phagocytic lysis, some kill host cell that harbors microbes by cellular digestion -T-Cells= Cell mediated response -B-cells= Humoral response 2 Types of Immunity Cells Humoral factors Anatomical barriers Resident flora Antigen-prsenting cells Basophils Eosinophils Mast cells NK cells Phagocytes Complement proteins Lactoferrin Lysozyme Pepsin Stomach acidity Cilia Mucus Skin Mainly non-pathogenic bacteria 1. Active immunity- when exposed *More long-term Ex: vaccines 2. Passive immunity- receives antibodies *More short-lived ex: Abs to newborn form placenta and breastmilk, pooled Abs for people with Immunodeficient disorders, serum from immunized donors for snake bite Other features of Adaptive Immunity Feature Specificity Diversity Memory Clonal expansion Types of Adaptive Immunity 1. Humoral Immunity -Defense by extracellular mechanism -Mediated by antibodies secreted by B-cells -Antibodies enter circulation + mucosal fluids -Neutralize and eliminate microbes and its toxins outside host cells (blood, plasma extracellular fluid, lumens of mucosal surface (GIT + respiratory tract) 2. Cell-mediated immunity -Defense by intracellular mechanism Specialization Contraction + homeostasis Nonreactivity to self Functional significance Distinct antigens → specific responses Respond to large variety of antigens Enhanced responses to repeated exposures ↑antigen-specific lymphocytes from small number of naïve lymphocytes Optimal for defense against diff. types of microbes Allows immune system to respond to newly encountered antigens Prevents injury to host during responses to foreign antigens. Immunological tolerance Cellular Components of the Adaptive Immune System B cells -Has membrane antibodies or membrane immunoglobins -Antigen-specific receptors -When activated: -Some differentiate into Memory B cells -Others differentiate into Plasma cells *Plasma Cells – secrete antibodies (humoral factors) T cells -Have T cell receptor (TCR) -Antigen specific receptor -TCRs do not recognize the antigen directly, but through “presenting” proteins called the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecules. -Helper T cells – secrete cytokines -Cytotoxic T cells – destroy altered cells, i.e., tumor cells, virally infected cells Natural Killer (NK) cells -large granular lymphocytes with a natural ability to kill tumor cells without a previous activation -mediate immune-surveillance not only via cytotoxic effector-functions, but also, by serving as regulatory lymphocytes able to secrete cytokines and to interact with both innate and adaptive immune cells, such a monocyte/macrophage, dendritic cells (DCs), and T Lymphocytes