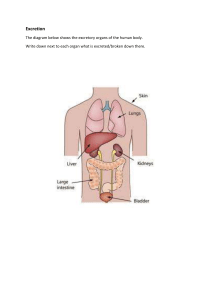
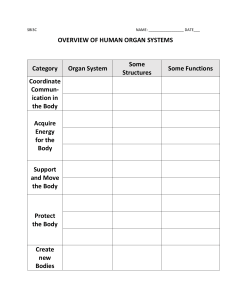
CHAPTER 1 Overview of Anatomy & physiology Levels of Structural Organization Maintaining Life Homoestasis The Language of Anatomy OBJECTIVES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology 1. Define Anatomy & Physiology 2. Explain how anatomy & physiology are related scientific discipline that investigates the structure of the body Greek words: ana-apart; tomy-to cut to dissect to cut apart and separate the parts of the body for the study Anatomy – Levels of Study • Gross Anatomy • Large structures • Easily observable Anatomy – Levels of Study • Microscopic Anatomy • Very small structures • Can only be viewed with a microscope Systematic anatomy - the study of body by systems Regional anatomy the study of organization of body by areas Surface anatomy –study of external features; uses superficial structures to locate deeper structures Scientific discipline that deals with the processes or functions of living things: The study of how the body and its parts work or function ( physio-nature; logy-study) Subdivsion examples: neurophysiology – explains the working of nervous system Cardiac physiology – studies the functions of the heart Major goals of physiology • To understand and predict the body’s responses to stimuli • To understand how the body maintains conditions within a narrow range of values in the presence of a continually changing environment *how they are related? study of the structure and function of the human body ENGAGE… Choose between Anatomy & Physiology Beating of the heart……? Brain structures…..? Cube- shaped epithelial tissues….? Kidney function…..? Bone growth…..? Tiny blood vessels…..? I. Overview of Anatomy and Physiology 1. Define Anatomy & Physiology 2. Explain how anatomy & physiology are related OBJECTIVES II. Levels of Structural Organization 3. Name the six levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are related. 4. Name the 11 organ systems of the body and state briefly their major functions and the major organs of each. Levels of Structural Organization Structural & functional organization The structural and functional characteristics of all organisms are determined by their chemical makeup. Atoms combine to form molecules. basic structural and functional unit of organisms, such as plants and animals. The smallest units of all living things Small structure that make up cells It carry out specific functions within a cell Examples are Nucleus and golgi bodies a group of similar cells that have common function epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous It is composed of two or more tissue types that together perform one or more common functions for the body. Ex: small intestine It is a group of organs classified as a unit because of a common function or set of functions. Ex: digestive system It is any living thing considered as a whole, whether composed of one cell, such as bacterium, or trillions such as human. ENGAGE: Identify the six Levels of structural organization from the following Cardiac muscle …..? Nervous System….? Glucose molecules…? Nucleus of the cell…? Liver….? Bacteria…? II. Levels of Structural Organization 3. Name the six levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are related. OBJECTIVES II. Levels of Structural Organization 4. Name the 11 organ systems of the body and state briefly their major functions and the major organs of each. Integumentary system Skeletal system Muscular system Lymphatic system Respiratory system Digestive system Nervous system Endocrine system Cardiovascular system Urinary system Female reproductive system Male reproductive system Organ System Overview • Integumentary • Forms the external body covering • Protects deeper tissue from injury and drying out • Synthesizes vitamin D • Location of cutaneous nerve receptors(temperature, pressure & pain) • Secretes salts & urea in perspiration • Regulates body temperature • Major organ: skin Organ System Overview • Skeletal • Protects and supports body organs • Provides muscle attachment for movement • Site of blood cell formation ( hematopoises) • Stores minerals • Major Organs: Bones, cartilages, ligaments, joints Organ System Overview • Muscular System • Large freshly muscles attached to bones • Allows locomotion • Maintains posture • Produces heat • Major organ: muscular organ Organ System Overview • Nervous • Fast-acting control system • Responds to internal and external change • Activates muscles and glands • Major Organs: brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Organ System Overview • Endocrine • Secretes regulatory hormones-controls body activities • Growth • Reproduction • Metabolism • Major Organs: pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, thymus, pancreas, pineal, ovaries, testes Organ System Overview • Cardiovascular • Transports materials in body via blood pumped by heart • Oxygen • Carbon dioxide • Nutrients • Wastes • Major organs: Heart & blood vessels Organ System Overview • Lymphatic • Returns fluids from the blood back to blood vessels • Disposes of debris • Involved in immunitydestroys bacteria and tumor cells • Major Organs: lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs-spleen & tonsils Organ System Overview • Respiratory • Keeps blood supplied with oxygen • Removes carbon dioxide • Transported gases to and from the blood through the thin walls of air sacs • Major organs: nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs Organ System Overview • Digestive • Breaks down food • Allows for nutrient absorption into blood • Eliminates indigestible material • Major organs: oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small & large intestines, rectum, accessory organs-liver, salivary glands, pancreas Organ System Overview • Urinary • Eliminates nitrogenous wastes • Maintains acid – base balance • Regulation of materials • Water • Electrolytes • Major Organs : kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra. Organ System Overview • Reproductive • Production of offspring • Testes- (male) produces sperm • Ovaries –(female) produces eggs or ova • Uterus- provides sites for the developing fetus once fertilization has occurred. • Major organs: Male- testes scrotum, penis, accessory glands, duct system • Female: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina EXPLORE : Group Activity:“think, share & tell” Form 11 groups (random counting) A. Name one organ system B. Give the anatomical description/s of the chosen organ system C. Enumerate at least 1 major organs/tissues of the chosen organ system D. Discuss the major function/s E. Think of the best ever code/phrase/unique name for the chosen organ system Example: A. muscular system; B.freshly muscle attached to the bone; C. muscular organ; D. Movement or locomotion; E. ”the walking organ-system” II. Levels of Structural Organization 4. Name the 11 organ systems of the body and state briefly their major functions and the major organs of each.