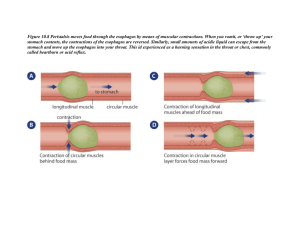
Chapter 9: Digestive System and Nutrition Quiz Next 1. Which of the following best describes the overall function of the digestive system in the human body? a. Maintain homeostasis within the body b. Break down food and absorb nutrition into the blood stream c. Pump stomach contents into the blood stream d. Break down food and absorb nutrition to perform photosynthesis in the body 2. Name one organ of the digestive system: Chapter 9: Digestive System and Nutrition • • • • • • Overview of digestion The mouth, pharynx, and esophagus The stomach and small intestine The accessory organs and regulation of secretions The large intestine and defecation Nutrition and weight control Overview of Digestion The organs of the digestive system are located within a tube called the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Digestive system: break down food into molecules that can be absorbed by the digestive system and carried by the blood to our cells Overview of Digestion Once broken down by the digestive system, these molecules can cross plasma membranes using facilitated and active transport Food also contains water, salts, vitamins, and minerals that help the body function normally. Processes of Digestion • Ingestion • Digestion • Movement • Absorption • Elimination Processes of Digestion • Ingestion: food is taken in through the mouth • Digestion • Movement • Absorption • Elimination Processes of Digestion • Ingestion • Digestion: The breakdown on larger pieces of food into smaller pieces smaller pieces can be acted on by digestive enzymes • Mechanical digestion: Chewing in the mouth and wavelike contractions of smooth muscle in the stomach • Chemical digestion: Digestive enzymes break down food molecules. Occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. • Movement • Absorption • Elimination Processes of Digestion • Ingestion • Digestion: The breakdown on larger pieces of food into smaller pieces smaller pieces can be acted on by digestive enzymes • Mechanical digestion: Chewing in the mouth and wavelike contractions of smooth muscle in the stomach • Chemical digestion: Digestive enzymes break down food molecules. Occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. • Movement • Absorption • Elimination Processes of Digestion • Ingestion • Digestion: The breakdown on larger pieces of food into smaller pieces smaller pieces can be acted on by digestive enzymes • Mechanical digestion: Chewing in the mouth and wavelike contractions of smooth muscle in the stomach • Chemical digestion: Digestive enzymes break down food molecules. Occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. • Movement • Absorption • Elimination Processes of Digestion • Ingestion • Digestion: The breakdown on larger pieces of food into smaller pieces smaller pieces can be acted on by digestive enzymes • Mechanical digestion: Chewing in the mouth and wavelike contractions of smooth muscle in the stomach • Chemical digestion: Digestive enzymes break down food molecules. Occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. • Movement • Absorption • Elimination Processes of Digestion • Ingestion • Digestion • Movement of GI contents along the digestive tract: by contractions of the smooth muscle • Absorption • Elimination Processes of Digestion • Ingestion • Digestion • Movement • Absorption occurs as molecules broken down by chemical digestion (nutrients) cross the wall of the GI tract and enter the cells lining the tract enter the blood for delivery of cells • Elimination Processes of Digestion • • • • • Ingestion Digestion Movement Absorption Elimination: removes molecules that cannot be digested and need to be discharged from the body. Defecation: Removal of indigestible wastes through the anus Processes of Digestion • Ingestion • Digestion • Movement • Absorption • Elimination Wall of the Digestive Tract Think of the GI tract as a garden hose that has a beginning (mouth) and an end (anus). Lumen: central, open, hollow area in an organ Wall of the Digestive Tract Think of the GI tract as a garden hose that has a beginning (mouth) and an end (anus). Mucosa: inner mucous membrane of lumen The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus The mouth, pharynx, and esophagus are in the upper portion of the GI tract. The Mouth The mouth (oral cavity) receives food and begins the process of mechanical and chemical digestion. The Mouth : Teeth Mechanical digestion occurs when our teeth chew food into pieces convenient for swallowing. The Mouth : The Tongue The tongue assists the teeth in mechanical digestion: move food around the mouth and prepares it for swallowing The Pharynx and Esophagus The Pharynx and Esophagus • Both the mouth and the nasal passages lead to the pharynx (throat). • The pharynx opens into both the food passage (esophagus) and the air passage (trachea, or windpipe) The Pharynx and Esophagus: Swallowing • Food enters the esophagus: muscular tube that moves food into the stomach • Other possible passages are blocked by the soft palate and epiglottis The Pharynx and Esophagus: Swallowing The Pharynx and Esophagus: Peristalsis The Pharynx and Esophagus • Esophagus: moves the food from the mouth to the stomach. Pharynx Esophagus Esophageal sphincter Stomach Pharynx Esophagus Esophageal sphincter Stomach The Pharynx and Esophagus • Sphincters: muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. • Heartburn occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter is opened and food moves from the stomach back to the esophagus. Biology Today: Heartburn (GERD) The Stomach • The stomach is an organ that stores food, initiates the digestion of protein, and controls the movement of food into the small intestine. • Nutrients are not absorbed by the stomach. • The stomach does absorb alcohol- it can pass through membranes easily The Stomach • The stomach is an organ that stores food, initiates the digestion of protein, and controls the movement of food into the small intestine. • Nutrients are not absorbed by the stomach. • The stomach does absorb alcohol- it can pass through membranes easily The Stomach • Why does your stomach growl? Peristalsis in your empty stomach! Explain the process of: the digestion of food from the mouth to the stomach. Where does mechanical digestion take place in the body? Where does chemical digestion take place in the body? Chapter 9: Digestive System and Nutrition • • • • • • Overview of digestion The mouth, pharynx, and esophagus The stomach and small intestine The accessory organs and regulation of secretions The large intestine and defecation Nutrition and weight control