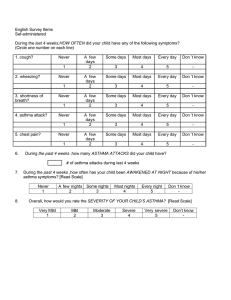
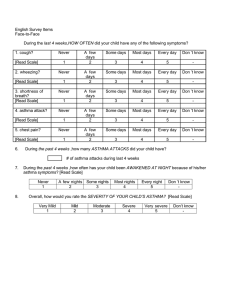
Asthma Management Damaris M. Nyasani Rasmussen College NUR2063: Essentials of Pathophysiology Professor Kristina Bohn February 28, 2021 Asthma is a well-known condition that affects the airways (bronchus and bronchioles) within the lungs. Asthma causes these airways to become inflamed and narrowed at times. Asthma affects people of all ages and infrequently starts during childhood. Some symptoms are having a wheeze, cough, or tightness in the chest. These symptoms range from mild to severe and may happen on a daily basis or just once every while. When the symptoms become severe, it becomes an asthma attack. In such a situation, an action plan is needed in order to prevent further suffering. This may include using medicine and avoiding asthma triggers. Risk Factors As stated earlier, asthma affects people of all ages, but it commonly starts during the patient’s childhood. In some cases, asthma develops in adults, this is more likely to happen to women. This type of asthma is termed as adult-onset asthma. Factors like environment, occupation, family history or genes, your race and ethnicity, or sex may raise the risks for getting asthma. Environments at work or home can make asthma symptoms worse such as exposure to cigarette smoke, industrial dust, or air pollutants. Genes also play an important role in the development of asthma because they affect the development of the immune system. Having a parent who has asthma, increases the risk of getting asthma as a child. African Americans and Puerto Ricans are reported to have a 40% higher chance of getting asthma than any other race. Causes The cause of asthma is currently unknown; therefore, the causes may vary for each person. However, asthma is usually the result of a robust response of the immune to a substance within the lungs. At times, these substances are made of allergens which cause reactions in the body depending on the severity of asthma. The immune reacts to allergens by causing inflammation, (usually in the airways); This inflammation causes tightening within the airways making it difficult for the victim to breathe. Despite having no cure for asthma in the medical industry, there are various treatment plans that help with the condition. Signs and Symptoms The signs and symptoms of asthma are very dependent on the severity and intensity of the condition. When under control, a person may show only a few symptoms. When symptoms worsen, a person can have what is called an asthma attack, or an exacerbation which are episodes that occur when symptoms get much worse and require a change in typical treatment. If not controlled, asthma can cause damage to the airways. The most common signs for Asthma are: Chest tightness, Coughing, Shortness of breath, Wheezing. Diagnosis and Treatment During a doctor’s visit, a variety of tests can be done to diagnose asthma. Examples of these tests are Pulmonary function test, Spirometry with bronchodilator test, and Bronchoprovocation test. These tests are meant to measure the movement of air within your lungs and how the airways are impacted when exposed to certain substances. Treatment is dependent on factors like age, asthma severity, and the body’s response to a given treatment option. Most people are treated long-term with daily controller, along with another inhaler for short-term relief. Short-term relief medicines are meant to quickly open the airways and relax airway muscles while long-term controllers are meant to reduce inflammation and prevent the narrowing of the airways. From the information about J.S. there are symptoms that indicate asthma. These are shortness of breath, presence of a wheeze, allergy towards pollen and dust, and the use of accessory muscles to breathe. From the given symptoms, a treatment of Fluticasone inhaler, oxygen through a nasal cannula and intravenous fluid was provided. However, the treatment could be improved to make the recovery more effective by providing prednisolone. Additionally, giving an antibiotic like macrolide can help take care of the inflammation. Providing salmeterol is also an option since it would be used in the future to help prevent an exacerbation. The numbers displayed were extremely concerning because of how abnormal some of them were. J.S displayed a high respiratory rate which is suggestive of tachypnea. The heart rate was also extremely high(tachycardia). A cause for the tachycardia could be hypoxia explaining the patient’s heart attempt to supply as much oxygen to the body. In addition, the blood pressure was high. All these factors hint towards a respiratory condition. The paCo2 being so low is suggestive of muscle fatigue in the respiratory system. The bicarbonate is high meaning, the renal compensation for respiratory acidosis has started. Thus, the patient has uncompensated respiratory acidosis. Another great indicator is the patient’s body temperature. Patients often have fevers when fighting an infection or when the body is inflamed. In this case, it can be concluded that this exacerbation was caused by an infection in the respiratory tract. And this infection has led to the exacerbation of asthma. Reference Asthma: Types, causes, and diagnosis. (n.d.). Retrieved March 01, 2021, from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323523