![CHM5 Redox[1]](http://s1.studylib.net/store/data/025606487_1-af64800a16024bfb36628ac75d568bd3-768x994.png)
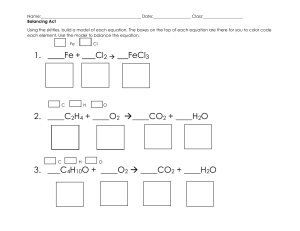
Zinc is a good reducing agent. Zn Zn2+ + 2eThis occurs when it reacts with mineral acids If we add Zn to and acidified transition Metal ion we can often see colour changes. These are due to changes in oxidation numbers Vanadium and Chromium are 2 good examples 51 V 23 Common Ox states +2 +3 +4 +5 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2 52 Cr 24 Common Ox states +2 +3 +6 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 4s1 Vanadium Ammonium Vanadate (V) (white solid) can be added to dilute HCl to give the orange Dioxovanadium (V) ion VO3- + 2H+ VO2+ + H2O If granulated zinc is now added it reduces the vanadium over a period of several minutes and gives several colour changes Blue [VO(H2O)5]2+ Vanadium (IV) Green [VCl2(H2O)4] + Vanadium (III) Violet [V(H2O)6]2+ Vanadium (II) Chromium Chromium in yellow Chromate (VI) is in its highest oxidation state. If we add acid the solution goes orange 2CrO42- + 2H+ Cr2O72- + H2O The Dichromate ion will also be reduced by zinc and HCl Orange Green Cr2O72- Cr (VI) [CrCl2(H2O)4]+ Cr (III) Blue [Cr(H2O)6]2+ Cr (II) Preparation of Ions in solution In redox titrations we saw a reduction of metal in a high oxidation state to a low one MnO4- H+ Mn2+ Cr2O72- H+ 2Cr3+ In alkaline solutions the opposite is possible (oxidation of metals in low oxidation states). If we wish to store solutions such as Fe2+ ions we must store them in acid conditions . In alkaline conditions the ion will precipitate out as the hydroxide. Preparation of metal complexes with high oxidation numbers is done by :i) adding an alkali ii) adding an oxidising agent Preparation of Chromate (VI) in Alkaline Conditions We know addition of NaOH to a Chromium(III) salt will give a green precipitate. Precipitate Cr(H2O)63+ [Cr(H2O)3(OH)3] Excess NaOH cause this green precipitate to dissolve to give a green solution of [Cr(OH)6]3If H2O2 is added to this a yellow solution of Chromate (VI) is produced 2 [Cr(OH)6]3- + 3 H2O2 2CrO42- + 2OH- + 8H2O Needs :- alkaline conditions & oxidising agent H2O2 Oxidation of Complex ions Often the oxygen in air is enough to oxidise species eg. Fe(OH)2 Co(OH)2 Fe(OH)3 Co(OH)3 Metal 2+ ions can be stabilized against this by keeping them in acid conditions. [Co(H2O)6]2+ NH3(aq) Shaken in air [Co(H2O)4(OH)2] Precipitate [Co(H2O)3(OH)3] Blue / green precipitate NH3 Conc [Co(H2O)6 ]2+ [Co(NH3)6]2+ Pale brown precipitate O2 air [Co(NH3)6]3+